Zeki Doruk Erden
Evolutionary Developmental Biology Can Serve as the Conceptual Foundation for a New Design Paradigm in Artificial Intelligence
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI), propelled by advancements in machine learning, has made significant strides in solving complex tasks. However, the current neural network-based paradigm, while effective, is heavily constrained by inherent limitations, primarily a lack of structural organization and a progression of learning that displays undesirable properties. As AI research progresses without a unifying framework, it either tries to patch weaknesses heuristically or draws loosely from biological mechanisms without strong theoretical foundations. Meanwhile, the recent paradigm shift in evolutionary understanding -- driven primarily by evolutionary developmental biology (EDB) -- has been largely overlooked in AI literature, despite a striking analogy between the Modern Synthesis and contemporary machine learning, evident in their shared assumptions, approaches, and limitations upon careful analysis. Consequently, the principles of adaptation from EDB that reshaped our understanding of the evolutionary process can also form the foundation of a unifying conceptual framework for the next design philosophy in AI, going beyond mere inspiration and grounded firmly in biology's first principles. This article provides a detailed overview of the analogy between the Modern Synthesis and modern machine learning, and outlines the core principles of a new AI design paradigm based on insights from EDB. To exemplify our analysis, we also present two learning system designs grounded in specific developmental principles -- regulatory connections, somatic variation and selection, and weak linkage -- that resolve multiple major limitations of contemporary machine learning in an organic manner, while also providing deeper insights into the role of these mechanisms in biological evolution.
Continual Reinforcement Learning via Autoencoder-Driven Task and New Environment Recognition
May 13, 2025Abstract:Continual learning for reinforcement learning agents remains a significant challenge, particularly in preserving and leveraging existing information without an external signal to indicate changes in tasks or environments. In this study, we explore the effectiveness of autoencoders in detecting new tasks and matching observed environments to previously encountered ones. Our approach integrates policy optimization with familiarity autoencoders within an end-to-end continual learning system. This system can recognize and learn new tasks or environments while preserving knowledge from earlier experiences and can selectively retrieve relevant knowledge when re-encountering a known environment. Initial results demonstrate successful continual learning without external signals to indicate task changes or reencounters, showing promise for this methodology.
A Proposal for Networks Capable of Continual Learning
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:We analyze the ability of computational units to retain past responses after parameter updates, a key property for system-wide continual learning. Neural networks trained with gradient descent lack this capability, prompting us to propose Modelleyen, an alternative approach with inherent response preservation. We demonstrate through experiments on modeling the dynamics of a simple environment and on MNIST that, despite increased computational complexity and some representational limitations at its current stage, Modelleyen achieves continual learning without relying on sample replay or predefined task boundaries.
Continually Learning Structured Visual Representations via Network Refinement with Rerelation
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Current machine learning paradigm relies on continuous representations like neural networks, which iteratively adjust parameters to approximate outcomes rather than directly learning the structure of problem. This spreads information across the network, causing issues like information loss and incomprehensibility Building on prior work in environment dynamics modeling, we propose a method that learns visual space in a structured, continual manner. Our approach refines networks to capture the core structure of objects while representing significant subvariants in structure efficiently. We demonstrate this with 2D shape detection, showing incremental learning on MNIST without overwriting knowledge and creating compact, comprehensible representations. These results offer a promising step toward a transparent, continually learning alternative to traditional neural networks for visual processing.
Agential AI for Integrated Continual Learning, Deliberative Behavior, and Comprehensible Models
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Contemporary machine learning paradigm excels in statistical data analysis, solving problems that classical AI couldn't. However, it faces key limitations, such as a lack of integration with planning, incomprehensible internal structure, and inability to learn continually. We present the initial design for an AI system, Agential AI (AAI), in principle operating independently or on top of statistical methods, designed to overcome these issues. AAI's core is a learning method that models temporal dynamics with guarantees of completeness, minimality, and continual learning, using component-level variation and selection to learn the structure of the environment. It integrates this with a behavior algorithm that plans on a learned model and encapsulates high-level behavior patterns. Preliminary experiments on a simple environment show AAI's effectiveness and potential.
Directed Structural Adaptation to Overcome Statistical Conflicts and Enable Continual Learning
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Adaptive networks today rely on overparameterized fixed topologies that cannot break through the statistical conflicts they encounter in the data they are exposed to, and are prone to "catastrophic forgetting" as the network attempts to reuse the existing structures to learn new task. We propose a structural adaptation method, DIRAD, that can complexify as needed and in a directed manner without being limited by statistical conflicts within a dataset. We then extend this method and present the PREVAL framework, designed to prevent "catastrophic forgetting" in continual learning by detection of new data and assigning encountered data to suitable models adapted to process them, without needing task labels anywhere in the workflow. We show the reliability of the DIRAD in growing a network with high performance and orders-of-magnitude simpler than fixed topology networks; and demonstrate the proof-of-concept operation of PREVAL, in which continual adaptation to new tasks is observed while being able to detect and discern previously-encountered tasks.
Improved Cooperation by Exploiting a Common Signal
Feb 03, 2021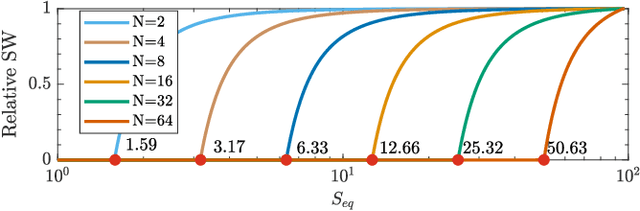
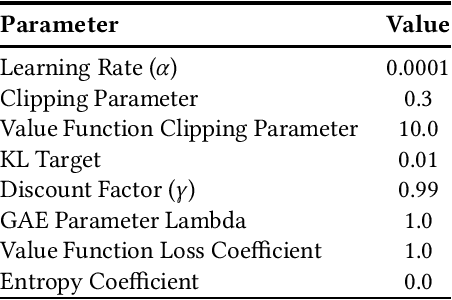
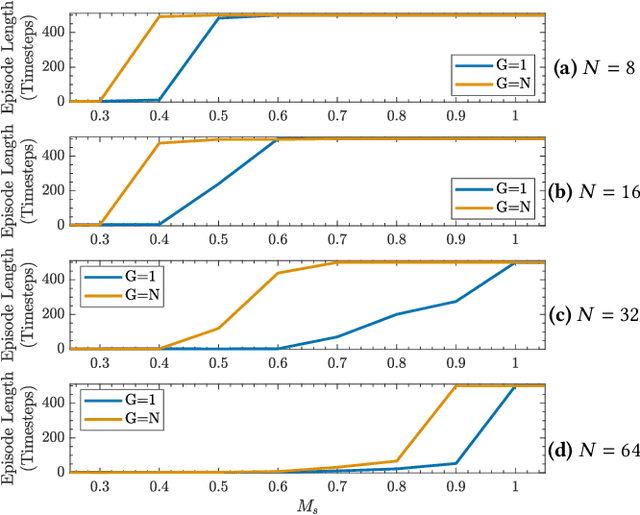
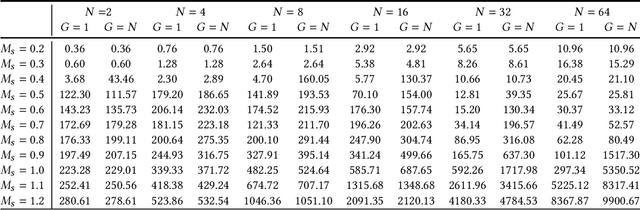
Abstract:Can artificial agents benefit from human conventions? Human societies manage to successfully self-organize and resolve the tragedy of the commons in common-pool resources, in spite of the bleak prediction of non-cooperative game theory. On top of that, real-world problems are inherently large-scale and of low observability. One key concept that facilitates human coordination in such settings is the use of conventions. Inspired by human behavior, we investigate the learning dynamics and emergence of temporal conventions, focusing on common-pool resources. Extra emphasis was given in designing a realistic evaluation setting: (a) environment dynamics are modeled on real-world fisheries, (b) we assume decentralized learning, where agents can observe only their own history, and (c) we run large-scale simulations (up to 64 agents). Uncoupled policies and low observability make cooperation hard to achieve; as the number of agents grow, the probability of taking a correct gradient direction decreases exponentially. By introducing an arbitrary common signal (e.g., date, time, or any periodic set of numbers) as a means to couple the learning process, we show that temporal conventions can emerge and agents reach sustainable harvesting strategies. The introduction of the signal consistently improves the social welfare (by 258% on average, up to 3306%), the range of environmental parameters where sustainability can be achieved (by 46% on average, up to 300%), and the convergence speed in low abundance settings (by 13% on average, up to 53%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge