Zeinab Borhanifard
Pruned Graph Neural Network for Short Story Ordering
Mar 13, 2022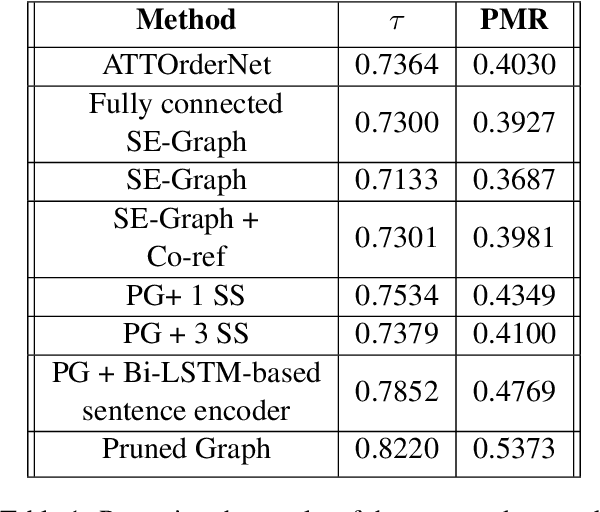
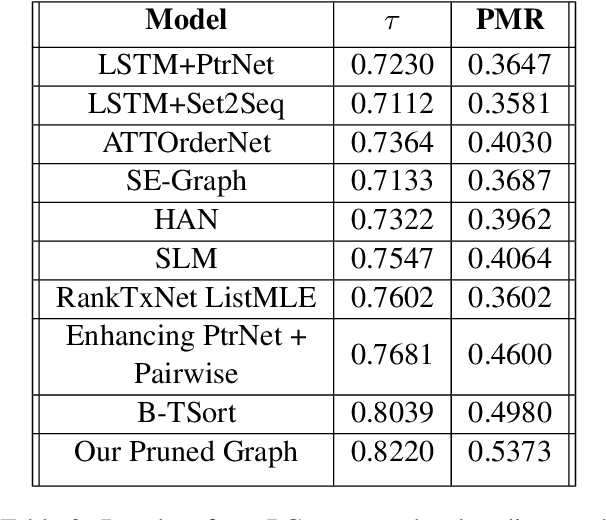
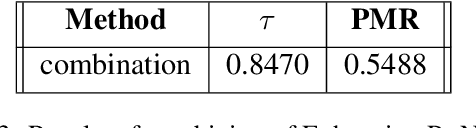
Abstract:Text coherence is a fundamental problem in natural language generation and understanding. Organizing sentences into an order that maximizes coherence is known as sentence ordering. This paper is proposing a new approach based on the graph neural network approach to encode a set of sentences and learn orderings of short stories. We propose a new method for constructing sentence-entity graphs of short stories to create the edges between sentences and reduce noise in our graph by replacing the pronouns with their referring entities. We improve the sentence ordering by introducing an aggregation method based on majority voting of state-of-the-art methods and our proposed one. Our approach employs a BERT-based model to learn semantic representations of the sentences. The results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing baselines on a corpus of short stories with a new state-of-the-art performance in terms of Perfect Match Ratio (PMR) and Kendall's Tau (Tau) metrics. More precisely, our method increases PMR and Tau criteria by more than 5% and 4.3%, respectively. These outcomes highlight the benefit of forming the edges between sentences based on their cosine similarity. We also observe that replacing pronouns with their referring entities effectively encodes sentences in sentence-entity graphs.
Using BERT Encoding and Sentence-Level Language Model for Sentence Ordering
Aug 24, 2021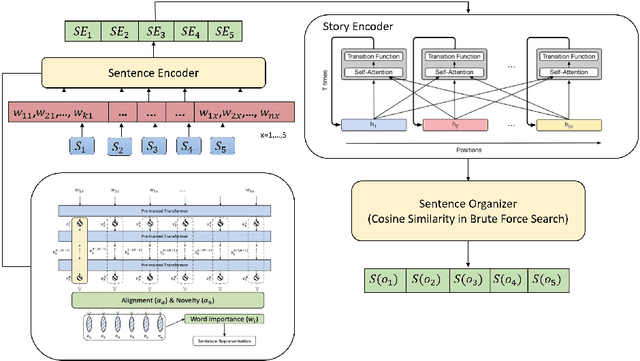
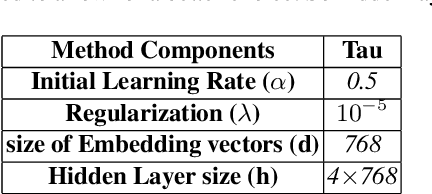
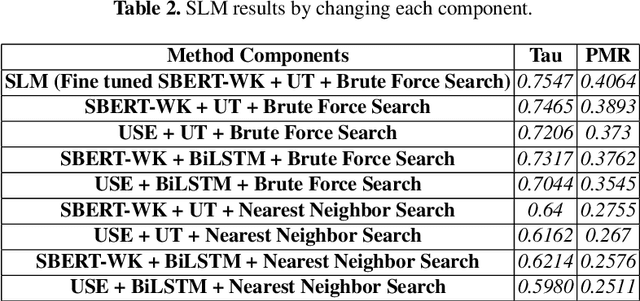
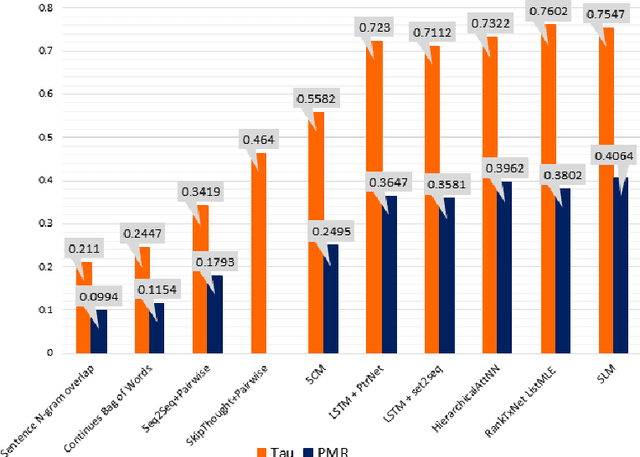
Abstract:Discovering the logical sequence of events is one of the cornerstones in Natural Language Understanding. One approach to learn the sequence of events is to study the order of sentences in a coherent text. Sentence ordering can be applied in various tasks such as retrieval-based Question Answering, document summarization, storytelling, text generation, and dialogue systems. Furthermore, we can learn to model text coherence by learning how to order a set of shuffled sentences. Previous research has relied on RNN, LSTM, and BiLSTM architecture for learning text language models. However, these networks have performed poorly due to the lack of attention mechanisms. We propose an algorithm for sentence ordering in a corpus of short stories. Our proposed method uses a language model based on Universal Transformers (UT) that captures sentences' dependencies by employing an attention mechanism. Our method improves the previous state-of-the-art in terms of Perfect Match Ratio (PMR) score in the ROCStories dataset, a corpus of nearly 100K short human-made stories. The proposed model includes three components: Sentence Encoder, Language Model, and Sentence Arrangement with Brute Force Search. The first component generates sentence embeddings using SBERT-WK pre-trained model fine-tuned on the ROCStories data. Then a Universal Transformer network generates a sentence-level language model. For decoding, the network generates a candidate sentence as the following sentence of the current sentence. We use cosine similarity as a scoring function to assign scores to the candidate embedding and the embeddings of other sentences in the shuffled set. Then a Brute Force Search is employed to maximize the sum of similarities between pairs of consecutive sentences.
NSURL-2019 Task 7: Named Entity Recognition in Farsi
Mar 19, 2020



Abstract:NSURL-2019 Task 7 focuses on Named Entity Recognition (NER) in Farsi. This task was chosen to compare different approaches to find phrases that specify Named Entities in Farsi texts, and to establish a standard testbed for future researches on this task in Farsi. This paper describes the process of making training and test data, a list of participating teams (6 teams), and evaluation results of their systems. The best system obtained 85.4% of F1 score based on phrase-level evaluation on seven classes of NEs including person, organization, location, date, time, money and percent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge