Zaineb Ajra
Using Shallow Neural Networks with Functional Connectivity from EEG signals for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's and Frontotemporal Dementia
Nov 06, 2023
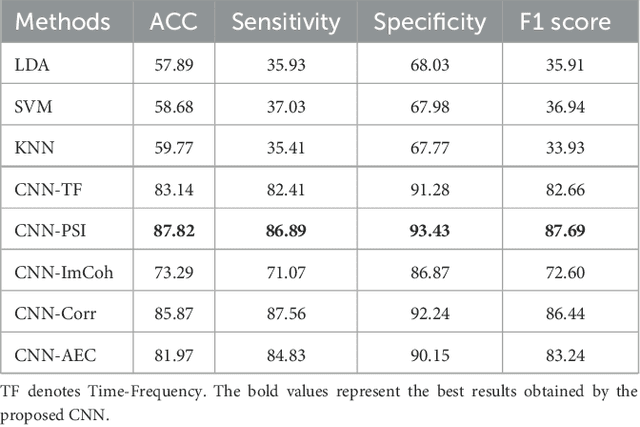

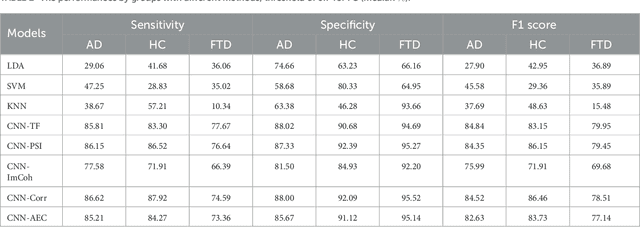
Abstract:{Introduction: } Dementia is a neurological disorder associated with aging that can cause a loss of cognitive functions, impacting daily life. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 50--70\% of cases, while frontotemporal dementia (FTD) affects social skills and personality. Electroencephalography (EEG) provides an effective tool to study the effects of AD on the brain. {Methods: } In this study, we propose to use shallow neural networks applied to two sets of features: spectral-temporal and functional connectivity using four methods. We compare three supervised machine learning techniques to the CNN models to classify EEG signals of AD / FTD and control cases. We also evaluate different measures of functional connectivity from common EEG frequency bands considering multiple thresholds. {Results and Discussion: } Results showed that the shallow CNN-based models achieved the highest accuracy of 94.54\% with AEC in test dataset when considering all connections, outperforming conventional methods and providing potentially an additional early dementia diagnosis tool. \url{https://doi.org/10.3389%2Ffneur.2023.1270405}
Mental arithmetic task classification with convolutional neural network based on spectral-temporal features from EEG
Sep 26, 2022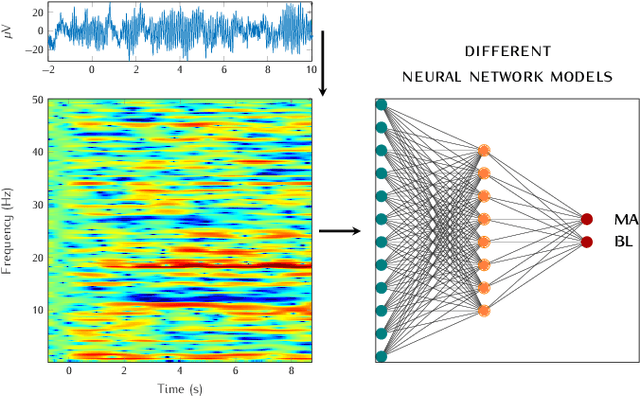
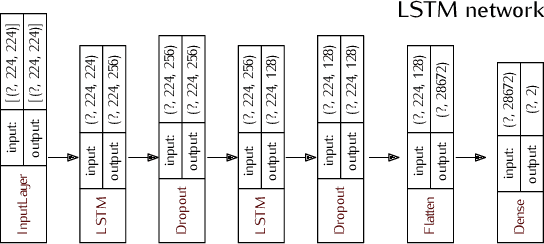
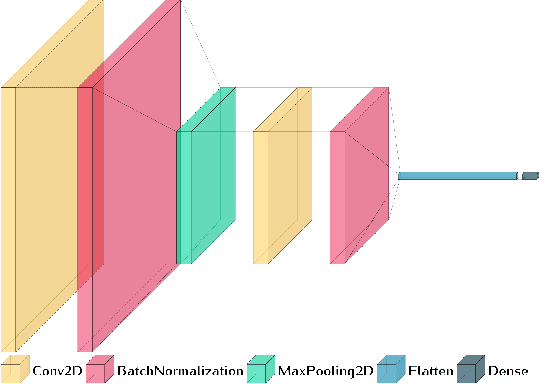
Abstract:In recent years, neuroscientists have been interested to the development of brain-computer interface (BCI) devices. Patients with motor disorders may benefit from BCIs as a means of communication and for the restoration of motor functions. Electroencephalography (EEG) is one of most used for evaluating the neuronal activity. In many computer vision applications, deep neural networks (DNN) show significant advantages. Towards to ultimate usage of DNN, we present here a shallow neural network that uses mainly two convolutional neural network (CNN) layers, with relatively few parameters and fast to learn spectral-temporal features from EEG. We compared this models to three other neural network models with different depths applied to a mental arithmetic task using eye-closed state adapted for patients suffering from motor disorders and a decline in visual functions. Experimental results showed that the shallow CNN model outperformed all the other models and achieved the highest classification accuracy of 90.68%. It's also more robust to deal with cross-subject classification issues: only 3% standard deviation of accuracy instead of 15.6% from conventional method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge