Zahid Iqbal
Adaptive Dual-Mode Distillation with Incentive Schemes for Scalable, Heterogeneous Federated Learning on Non-IID Data
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising decentralized learning (DL) approach that enables the use of distributed data without compromising user privacy. However, FL poses several key challenges. First, it is frequently assumed that every client can train the same machine learning models, however, not all clients are able to meet this assumption because of differences in their business needs and computational resources. Second, statistical heterogeneity (a.k.a. non-IID data) poses a major challenge in FL, which can lead to lower global model performance. Third, while addressing these challenges, there is a need for a cost-effective incentive mechanism to encourage clients to participate in FL training. In response to these challenges, we propose several methodologies: DL-SH, which facilitates efficient, privacy-preserving, and communication-efficient learning in the context of statistical heterogeneity; DL-MH, designed to manage fully heterogeneous models while tackling statistical disparities; and I-DL-MH, an incentive-based extension of DL-MH that promotes client engagement in federated learning training by providing incentives within this complex federated learning framework. Comprehensive experiments were carried out to assess the performance and scalability of the proposed approaches across a range of complex experimental settings. This involved utilizing various model architectures, in diverse data distributions, including IID and several non-IID scenarios, as well as multiple datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approaches significantly enhance accuracy and decrease communication costs while effectively addressing statistical heterogeneity and model heterogeneity in comparison to existing state-of-the-art approaches and baselines, with DL-SH improving global model accuracy by 153%, and I-DL-MH achieving a 225% improvement under non-IID conditions.
Adaptive Distillation for Decentralized Learning from Heterogeneous Clients
Aug 18, 2020
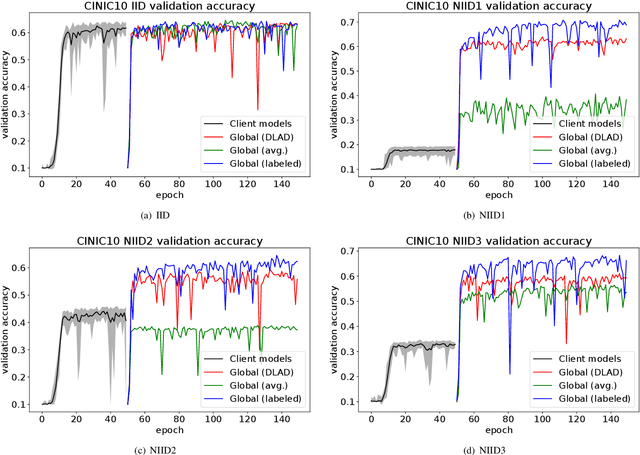
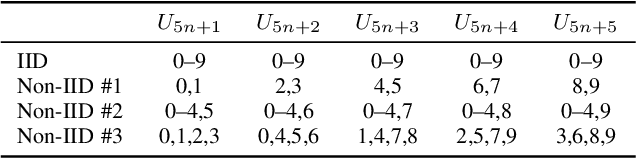
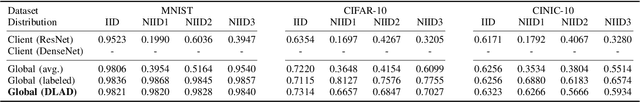
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of decentralized learning to achieve a high-performance global model by asking a group of clients to share local models pre-trained with their own data resources. We are particularly interested in a specific case where both the client model architectures and data distributions are diverse, which makes it nontrivial to adopt conventional approaches such as Federated Learning and network co-distillation. To this end, we propose a new decentralized learning method called Decentralized Learning via Adaptive Distillation (DLAD). Given a collection of client models and a large number of unlabeled distillation samples, the proposed DLAD 1) aggregates the outputs of the client models while adaptively emphasizing those with higher confidence in given distillation samples and 2) trains the global model to imitate the aggregated outputs. Our extensive experimental evaluation on multiple public datasets (MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CINIC-10) demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
An Efficient Indoor Navigation Technique To Find Optimal Route For Blinds Using QR Codes
May 29, 2020
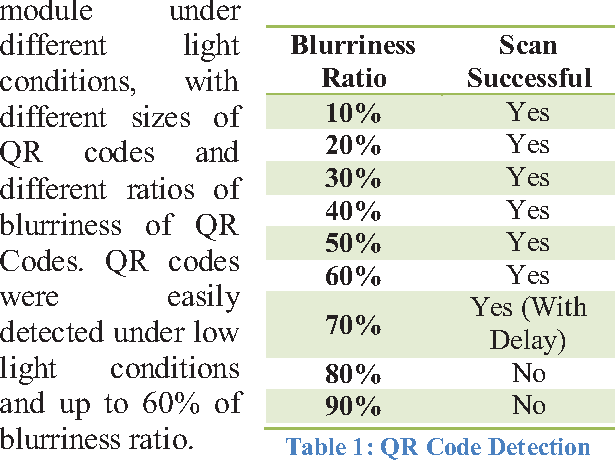
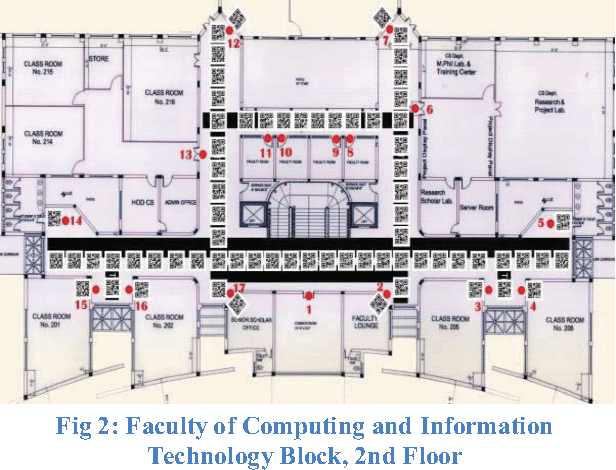
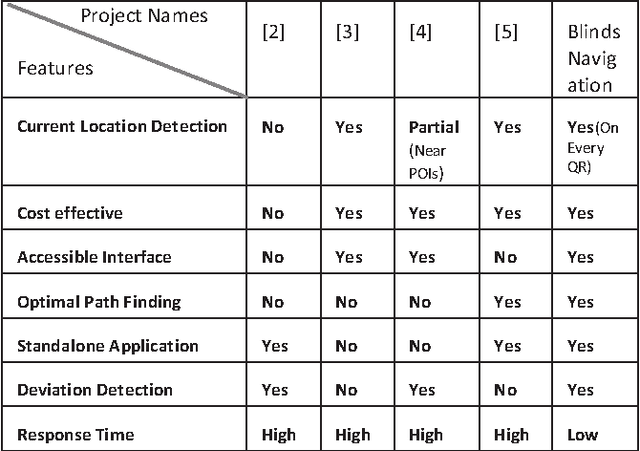
Abstract:Blind navigation is an accessibility application that enables blind to use an android Smartphone in an easy way for indoor navigation with instructions in audio form. We have proposed a prototype which is an indoor navigation application for blinds that uses QR codes. It is developed for android Smart phones and does not require any additional hardware for navigation. It provides automatic navigational assistance on pre-defined paths for blind. QR codes are placed on the floor sections after specific distance that acts as an input for current location detection and navigation. Whenever a QR code is scanned it provides the user with the information of the current location and asks the user to select the destination and then offers optimal and shortest path using path finding algorithms. During navigation whenever the deviation from the proposed path is detected it prompts the user and guides back to the right path by comparing the current path with the generated path. All of the instructions throughout the application are provided in audio form to the user. The interface of the application is well built for blinds which makes the smart phones user-friendly and useable for blind people. The user interacts with the application through a specific set of user-friendly gestures for specific inputs and operations. At the end, we have performed comparison between different state of art approaches and concluded that our approach is more user friendly, cost effective and produced more accurate results.
A Diverse Clustering Particle Swarm Optimizer for Dynamic Environment: To Locate and Track Multiple Optima
May 19, 2020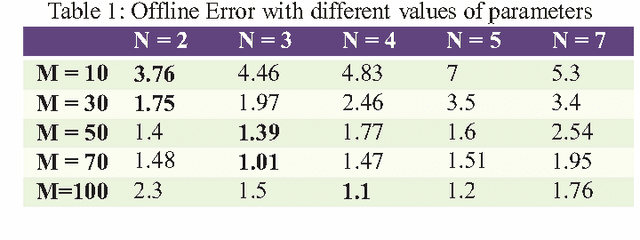
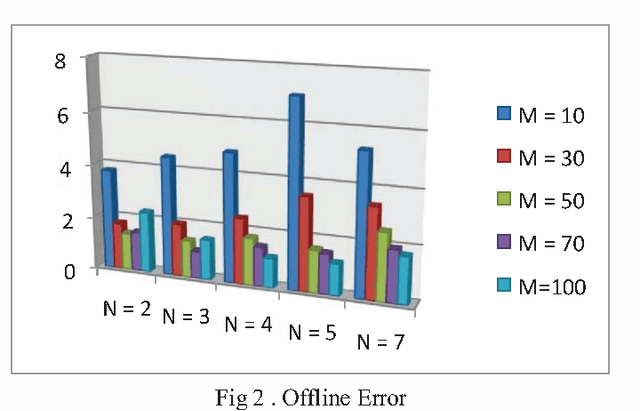
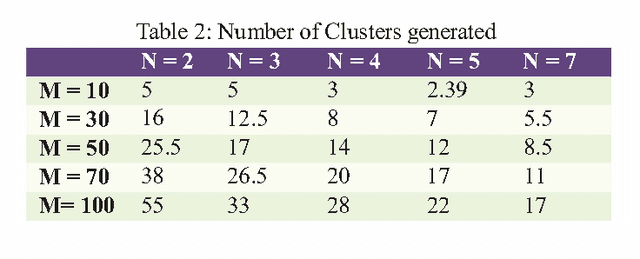
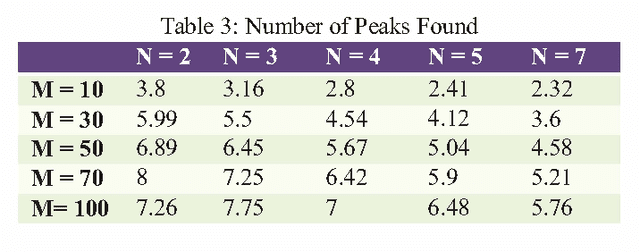
Abstract:In real life, mostly problems are dynamic. Many algorithms have been proposed to handle the static problems, but these algorithms do not handle or poorly handle the dynamic environment problems. Although, many algorithms have been proposed to handle dynamic problems but still, there are some limitations or drawbacks in every algorithm regarding diversity of particles and tracking of already found optima. To overcome these limitations/drawbacks, we have proposed a new efficient algorithm to handle the dynamic environment effectively by tracking and locating multiple optima and by improving the diversity and convergence speed of algorithm. In this algorithm, a new method has been proposed which explore the undiscovered areas of search space to increase the diversity of algorithm. This algorithm also uses a method to effectively handle the overlapped and overcrowded particles. Branke has proposed moving peak benchmark which is commonly used MBP in literature. We also have performed different experiments on Moving Peak Benchmark. After comparing the experimental results with different state of art algorithms, it was seen that our algorithm performed more efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge