Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Yuwei Liao
Fault Detection Using Nonlinear Low-Dimensional Representation of Sensor Data
Oct 02, 2019Figures and Tables: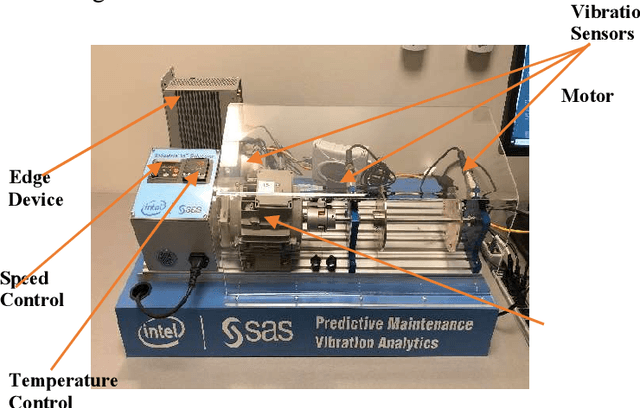
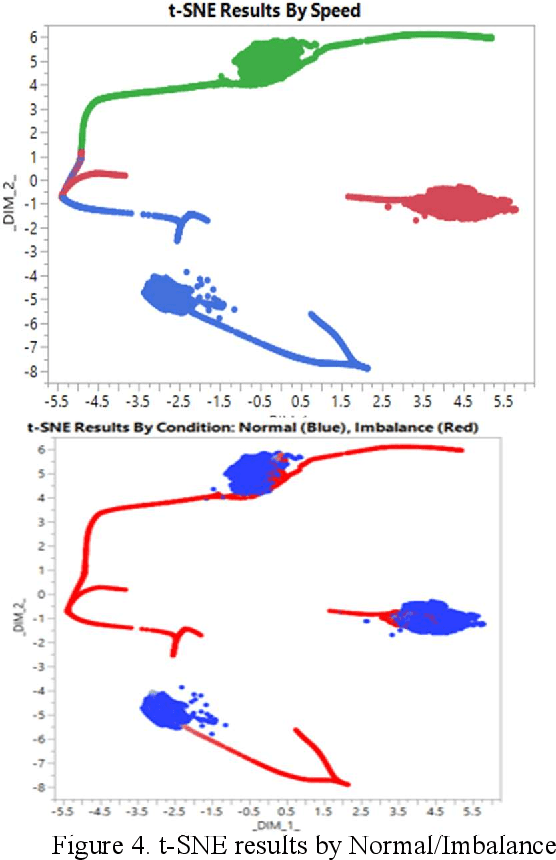
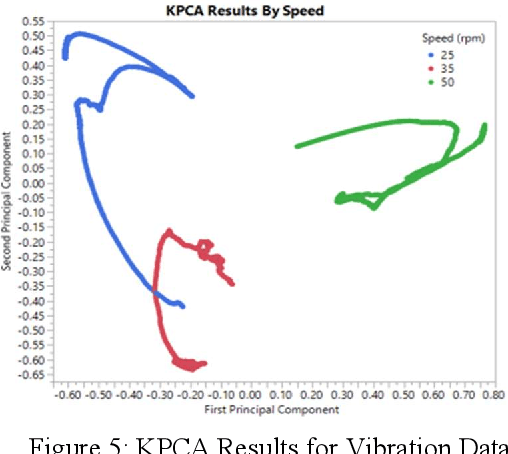




Abstract:Sensor data analysis plays a key role in health assessment of critical equipment. Such data are multivariate and exhibit nonlinear relationships. This paper describes how one can exploit nonlinear dimension reduction techniques, such as the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) and kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) for fault detection. We show that using anomaly detection with low dimensional representations provides better interpretability and is conducive to edge processing in IoT applications.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge