Yuriy Izotov
Neural Network Entropy (NNetEn): EEG Signals and Chaotic Time Series Separation by Entropy Features, Python Package for NNetEn Calculation
Mar 31, 2023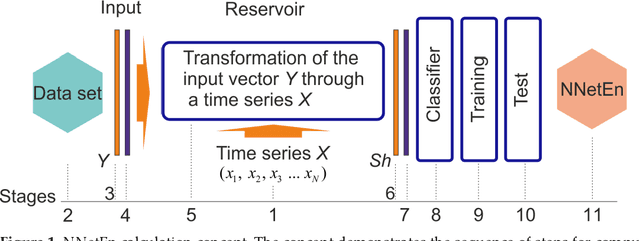
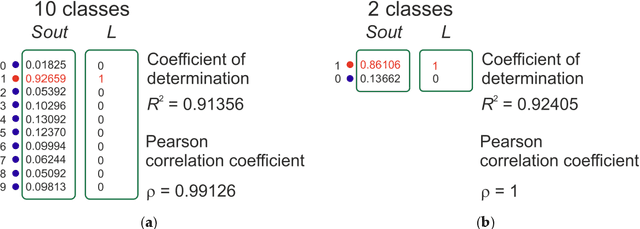

Abstract:Entropy measures are effective features for time series classification problems. Traditional entropy measures, such as Shannon entropy, use probability distribution function. However, for the effective separation of time series, new entropy estimation methods are required to characterize the chaotic dynamic of the system. Our concept of Neural Network Entropy (NNetEn) is based on the classification of special datasets (MNIST-10 and SARS-CoV-2-RBV1) in relation to the entropy of the time series recorded in the reservoir of the LogNNet neural network. NNetEn estimates the chaotic dynamics of time series in an original way. Based on the NNetEn algorithm, we propose two new classification metrics: R2 Efficiency and Pearson Efficiency. The efficiency of NNetEn is verified on separation of two chaotic time series of sine mapping using dispersion analysis (ANOVA). For two close dynamic time series (r = 1.1918 and r = 1.2243), the F-ratio has reached the value of 124 and reflects high efficiency of the introduced method in classification problems. The EEG signal classification for healthy persons and patients with Alzheimer disease illustrates the practical application of the NNetEn features. Our computations demonstrate the synergistic effect of increasing classification accuracy when applying traditional entropy measures and the NNetEn concept conjointly. An implementation of the algorithms in Python is presented.
Machine Learning Sensors for Diagnosis of COVID-19 Disease Using Routine Blood Values for Internet of Things Application
Sep 08, 2022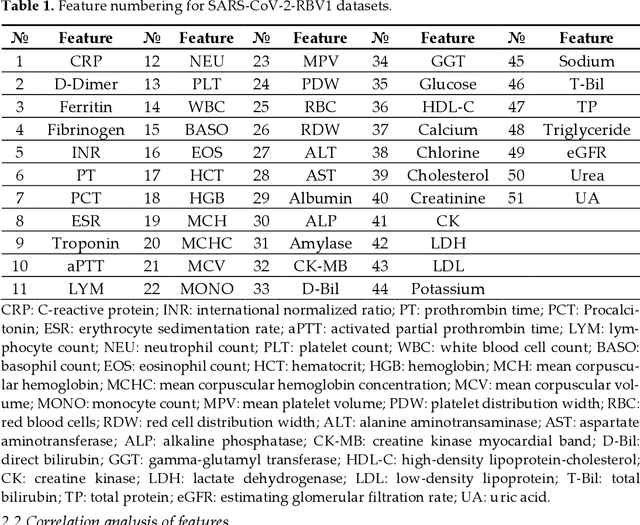
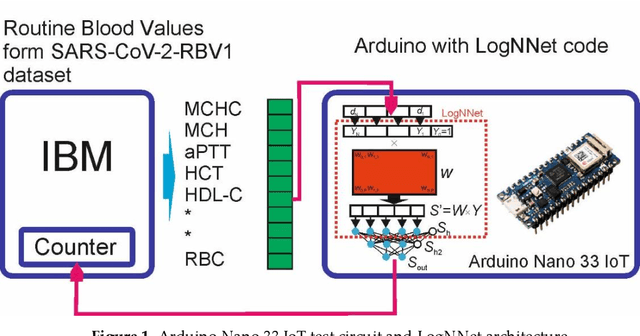
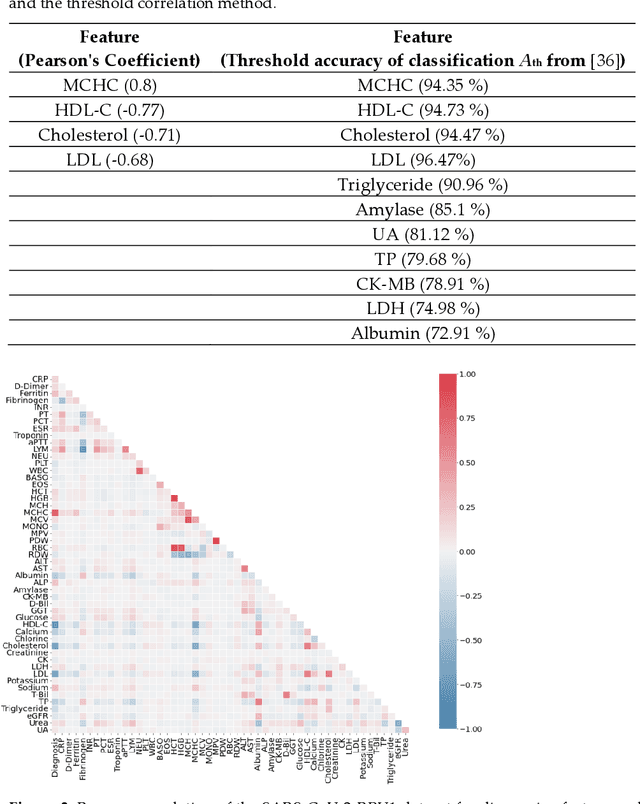
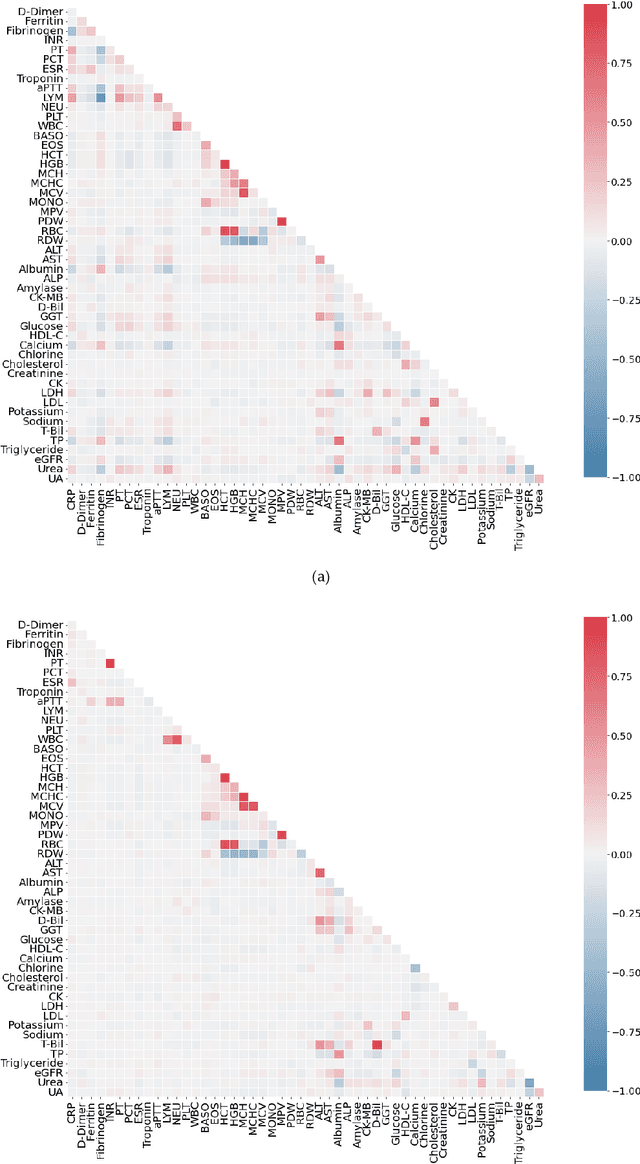
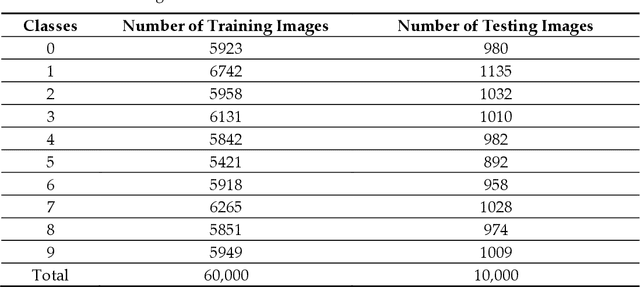
Abstract:Healthcare digitalization needs effective methods of human sensorics, when various parameters of the human body are instantly monitored in everyday life and connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). In particular, Machine Learning (ML) sensors for the prompt diagnosis of COVID-19 is an important case for IoT application in healthcare and Ambient Assistance Living (AAL). Determining the infected status of COVID-19 with various diagnostic tests and imaging results is costly and time-consuming. The aim of this study is to provide a fast, reliable and economical alternative tool for the diagnosis of COVID-19 based on the Routine Blood Values (RBV) values measured at admission. The dataset of the study consists of a total of 5296 patients with the same number of negative and positive COVID-19 test results and 51 routine blood values. In this study, 13 popular classifier machine learning models and LogNNet neural network model were exanimated. The most successful classifier model in terms of time and accuracy in the detection of the disease was the Histogram-based Gradient Boosting (HGB). The HGB classifier identified the 11 most important features (LDL, Cholesterol, HDL-C, MCHC, Triglyceride, Amylase, UA, LDH, CK-MB, ALP and MCH) to detect the disease with 100% accuracy, learning time 6.39 sec. In addition, the importance of single, double and triple combinations of these features in the diagnosis of the disease was discussed. We propose to use these 11 traits and their combinations as important biomarkers for ML sensors in diagnosis of the disease, supporting edge computing on Arduino and cloud IoT service.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge