Yun-Ju Chan
Speech Enhancement-assisted Stargan Voice Conversion in Noisy Environments
Oct 19, 2021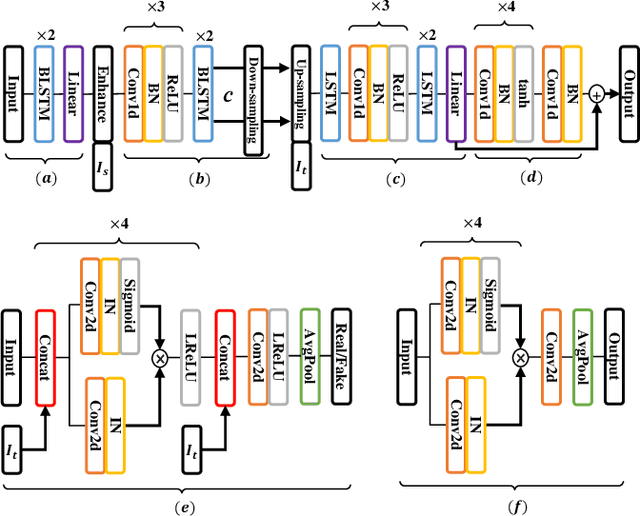
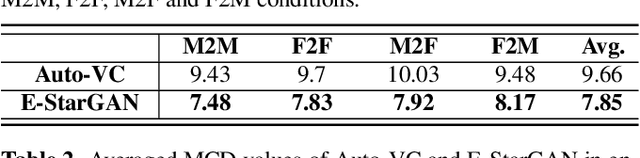
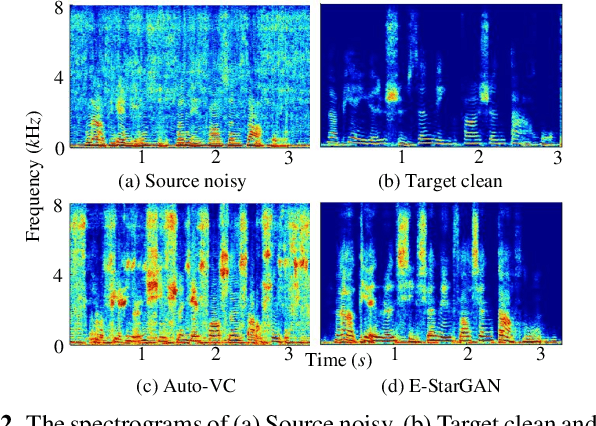
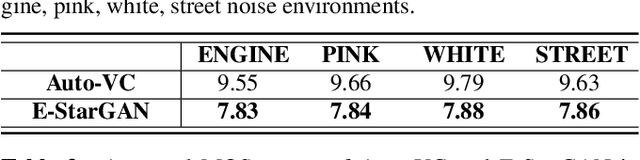
Abstract:Numerous voice conversion (VC) techniques have been proposed for the conversion of voices among different speakers. Although the decent quality of converted speech can be observed when VC is applied in a clean environment, the quality will drop sharply when the system is running under noisy conditions. In order to address this issue, we propose a novel enhancement-based StarGAN (E-StarGAN) VC system, which leverages a speech enhancement (SE) technique for signal pre-processing. SE systems are generally used to reduce noise components in noisy speech and to generate enhanced speech for downstream application tasks. Therefore, we investigated the effectiveness of E-StarGAN, which combines VC and SE, and demonstrated the robustness of the proposed approach in various noisy environments. The results of VC experiments conducted on a Mandarin dataset show that when combined with SE, the proposed E-StarGAN VC model is robust to unseen noises. In addition, the subjective listening test results show that the proposed E-StarGAN model can improve the sound quality of speech signals converted from noise-corrupted source utterances.
Attention-based multi-task learning for speech-enhancement and speaker-identification in multi-speaker dialogue scenario
Jan 07, 2021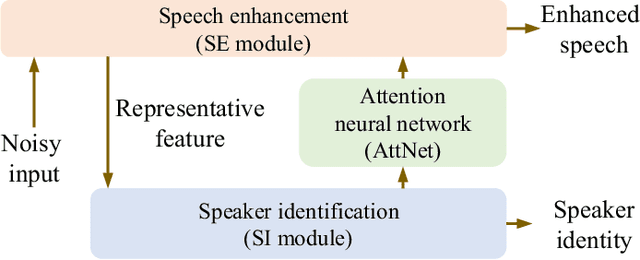
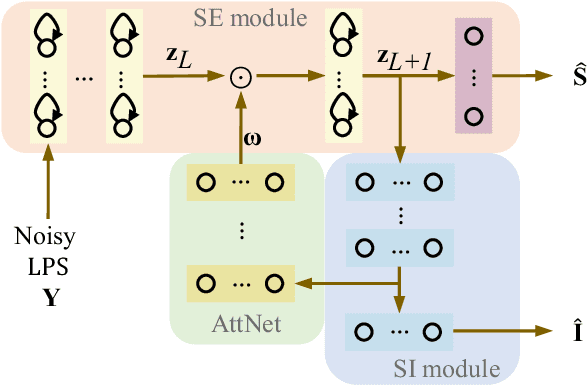
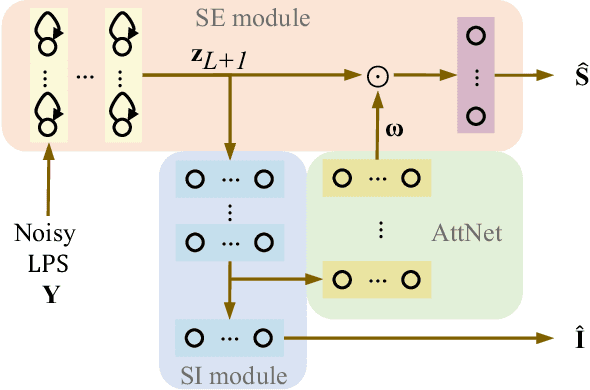
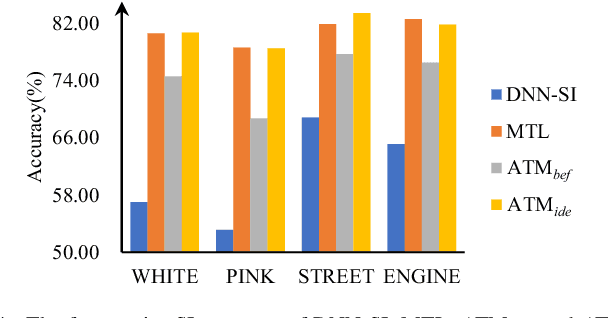
Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) and the attention technique have been proven to effectively extract robust acoustic features for various speech-related applications in noisy environments. In this study, we integrated MTL and the attention-weighting mechanism and propose an attention-based MTL (ATM0 approach to realize a multi-model learning structure and to promote the speech enhancement (SE) and speaker identification (SI) systems simultaneously. There are three subsystems in the proposed ATM: SE, SI, and attention-Net (AttNet). In the proposed system, a long-short-term memory (LSTM) is used to perform SE, while a deep neural network (DNN) model is applied to construct SI and AttNet in ATM. The overall ATM system first extracts the representative features and then enhances the speech spectra in LSTM-SE and classifies speaker identity in DNN-SI. We conducted our experiment on Taiwan Mandarin hearing in noise test database. The evaluation results indicate that the proposed ATM system not only increases the quality and intelligibility of noisy speech input but also improves the accuracy of the SI system when compared to the conventional MTL approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge