Yun Kwok Wing
Data-Efficient Model for Psychological Resilience Prediction based on Neurological Data
Feb 03, 2025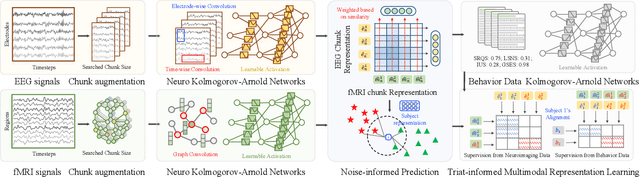
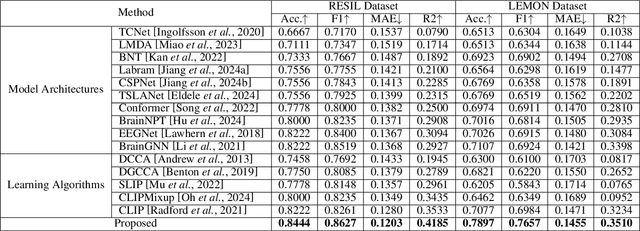
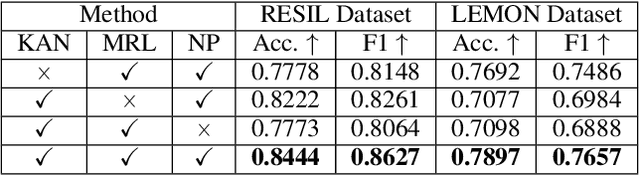
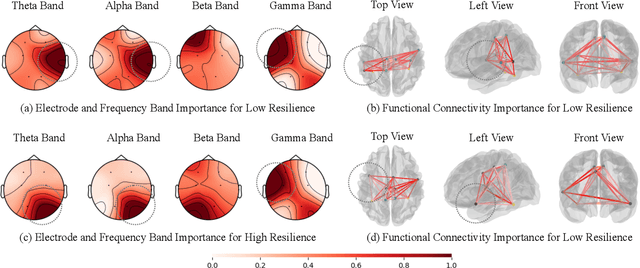
Abstract:Psychological resilience, defined as the ability to rebound from adversity, is crucial for mental health. Compared with traditional resilience assessments through self-reported questionnaires, resilience assessments based on neurological data offer more objective results with biological markers, hence significantly enhancing credibility. This paper proposes a novel data-efficient model to address the scarcity of neurological data. We employ Neuro Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks as the structure of the prediction model. In the training stage, a new trait-informed multimodal representation algorithm with a smart chunk technique is proposed to learn the shared latent space with limited data. In the test stage, a new noise-informed inference algorithm is proposed to address the low signal-to-noise ratio of the neurological data. The proposed model not only shows impressive performance on both public datasets and self-constructed datasets but also provides some valuable psychological hypotheses for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge