Yuanfa Yao
The Affiliated Huizhou Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, China
Poststroke rehabilitative mechanisms in individualized fatigue level-controlled treadmill training -- a Rat Model Study
Feb 20, 2025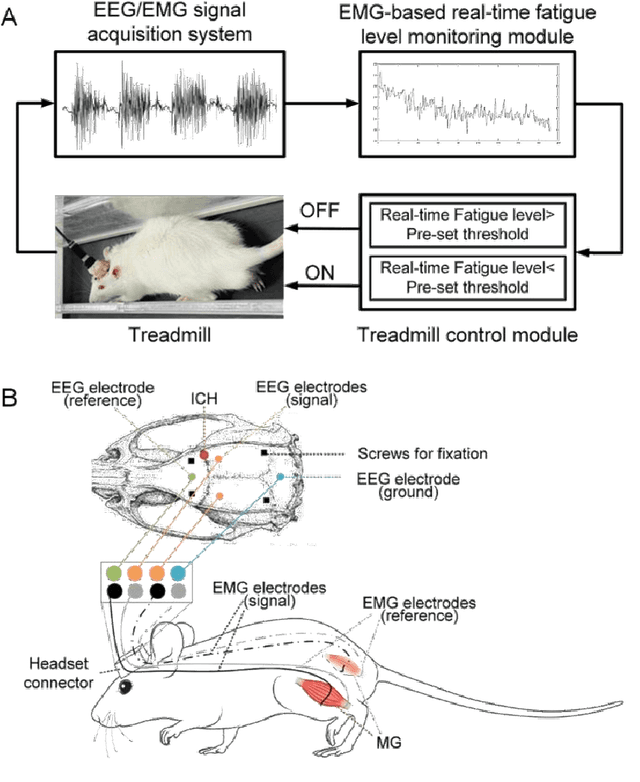
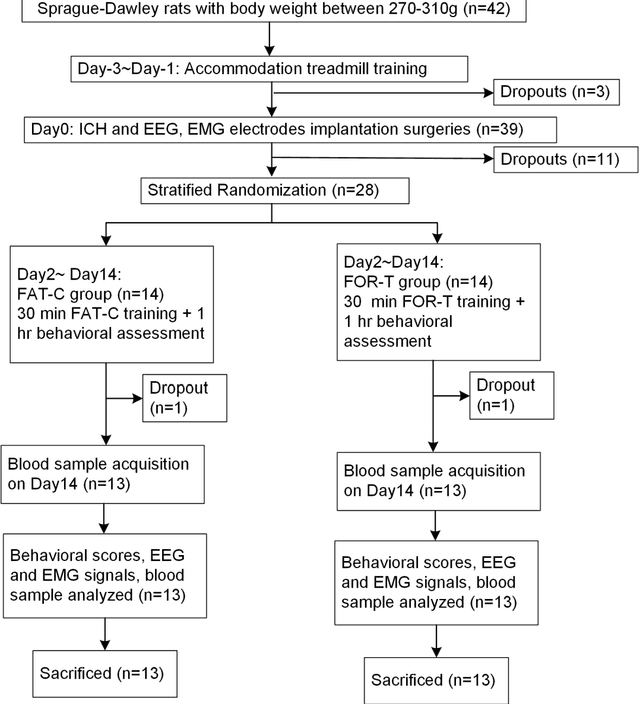
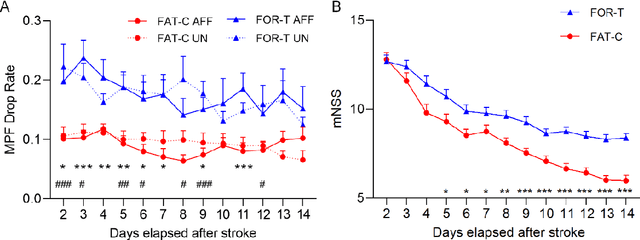
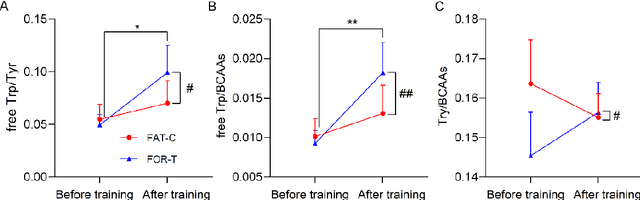
Abstract:Individualized training improved post-stroke motor function rehabilitation efficiency. However, the mechanisms of how individualized training facilitates recovery is not clear. This study explored the cortical and corticomuscular rehabilitative effects in post-stroke motor function recovery during individualized training. Sprague-Dawley rats with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) were randomly distributed into two groups: forced training (FOR-T, n=13) and individualized fatigue-controlled training (FAT-C, n=13) to receive training respectively from day 2 to day 14 post-stroke. The FAT-C group exhibited superior motor function recovery and less central fatigue compared to the FOR-T group. EEG PSD slope analysis demonstrated a better inter-hemispheric balance in FAT-C group compare to the FOR-T group. The dCMC analysis indicated that training-induced fatigue led to a short-term down-regulation of descending corticomuscular coherence (dCMC) and an up-regulation of ascending dCMC. In the long term, excessive fatigue hindered the recovery of descending control in the affected hemisphere. The individualized strategy of peripheral fatigue-controlled training achieved better motor function recovery, which could be attributed to the mitigation of central fatigue, optimization of inter-hemispheric balance and enhancement of descending control in the affected hemisphere.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge