Yuan-Chen Chang
From Deception to Detection: The Dual Roles of Large Language Models in Fake News
Sep 25, 2024

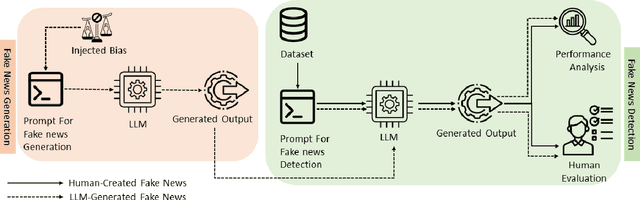

Abstract:Fake news poses a significant threat to the integrity of information ecosystems and public trust. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) holds considerable promise for transforming the battle against fake news. Generally, LLMs represent a double-edged sword in this struggle. One major concern is that LLMs can be readily used to craft and disseminate misleading information on a large scale. This raises the pressing questions: Can LLMs easily generate biased fake news? Do all LLMs have this capability? Conversely, LLMs offer valuable prospects for countering fake news, thanks to their extensive knowledge of the world and robust reasoning capabilities. This leads to other critical inquiries: Can we use LLMs to detect fake news, and do they outperform typical detection models? In this paper, we aim to address these pivotal questions by exploring the performance of various LLMs. Our objective is to explore the capability of various LLMs in effectively combating fake news, marking this as the first investigation to analyze seven such models. Our results reveal that while some models adhere strictly to safety protocols, refusing to generate biased or misleading content, other models can readily produce fake news across a spectrum of biases. Additionally, our results show that larger models generally exhibit superior detection abilities and that LLM-generated fake news are less likely to be detected than human-written ones. Finally, our findings demonstrate that users can benefit from LLM-generated explanations in identifying fake news.
Opinion Mining for Relating Subjective Expressions and Annual Earnings in US Financial Statements
Oct 15, 2012



Abstract:Financial statements contain quantitative information and manager's subjective evaluation of firm's financial status. Using information released in U.S. 10-K filings. Both qualitative and quantitative appraisals are crucial for quality financial decisions. To extract such opinioned statements from the reports, we built tagging models based on the conditional random field (CRF) techniques, considering a variety of combinations of linguistic factors including morphology, orthography, predicate-argument structure, syntax, and simple semantics. Our results show that the CRF models are reasonably effective to find opinion holders in experiments when we adopted the popular MPQA corpus for training and testing. The contribution of our paper is to identify opinion patterns in multiword expressions (MWEs) forms rather than in single word forms. We find that the managers of corporations attempt to use more optimistic words to obfuscate negative financial performance and to accentuate the positive financial performance. Our results also show that decreasing earnings were often accompanied by ambiguous and mild statements in the reporting year and that increasing earnings were stated in assertive and positive way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge