Youngsun Lim
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
Robust Driving QA through Metadata-Grounded Context and Task-Specific Prompts
Oct 21, 2025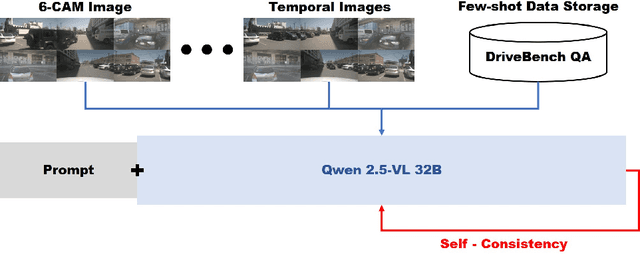
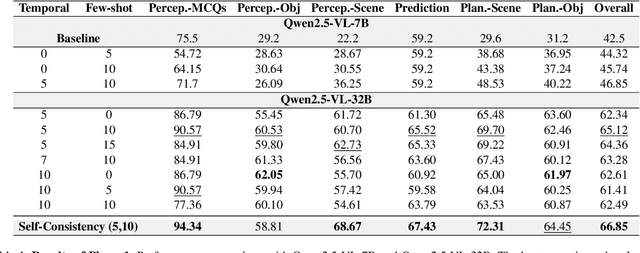
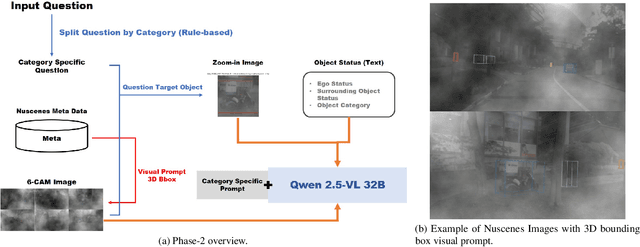
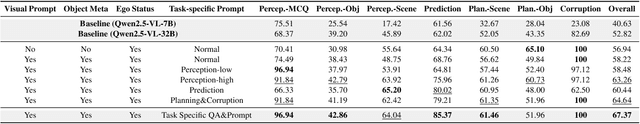
Abstract:We present a two-phase vision-language QA system for autonomous driving that answers high-level perception, prediction, and planning questions. In Phase-1, a large multimodal LLM (Qwen2.5-VL-32B) is conditioned on six-camera inputs, a short temporal window of history, and a chain-of-thought prompt with few-shot exemplars. A self-consistency ensemble (multiple sampled reasoning chains) further improves answer reliability. In Phase-2, we augment the prompt with nuScenes scene metadata (object annotations, ego-vehicle state, etc.) and category-specific question instructions (separate prompts for perception, prediction, planning tasks). In experiments on a driving QA benchmark, our approach significantly outperforms the baseline Qwen2.5 models. For example, using 5 history frames and 10-shot prompting in Phase-1 yields 65.1% overall accuracy (vs.62.61% with zero-shot); applying self-consistency raises this to 66.85%. Phase-2 achieves 67.37% overall. Notably, the system maintains 96% accuracy under severe visual corruption. These results demonstrate that carefully engineered prompts and contextual grounding can greatly enhance high-level driving QA with pretrained vision-language models.
Label-Augmented Dataset Distillation
Sep 24, 2024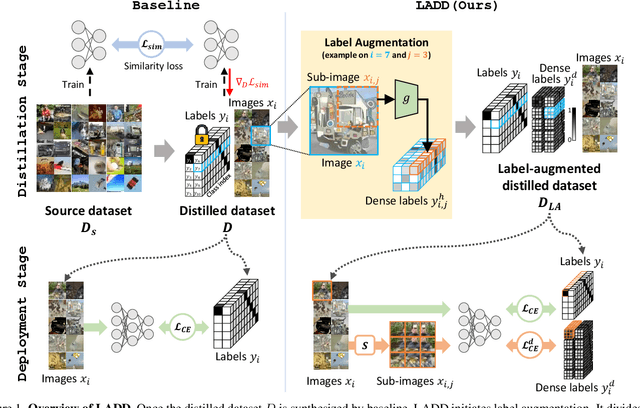
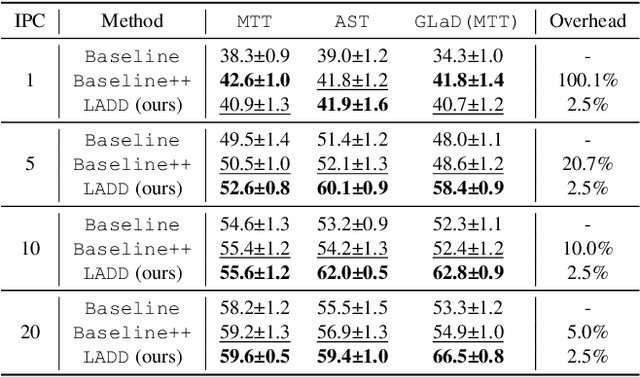
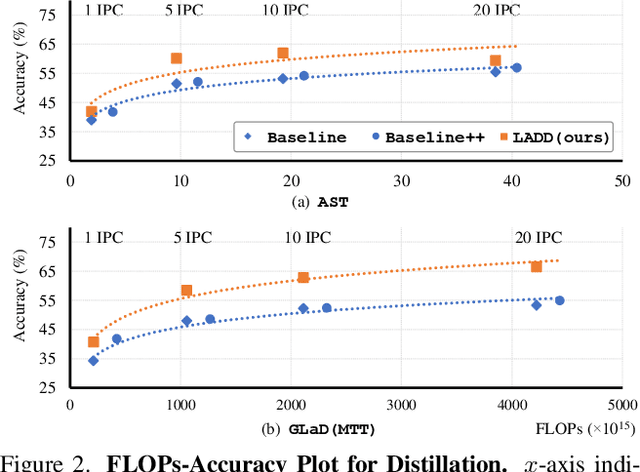
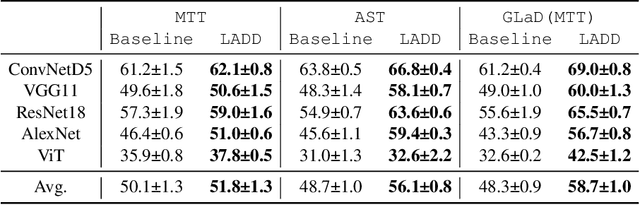
Abstract:Traditional dataset distillation primarily focuses on image representation while often overlooking the important role of labels. In this study, we introduce Label-Augmented Dataset Distillation (LADD), a new dataset distillation framework enhancing dataset distillation with label augmentations. LADD sub-samples each synthetic image, generating additional dense labels to capture rich semantics. These dense labels require only a 2.5% increase in storage (ImageNet subsets) with significant performance benefits, providing strong learning signals. Our label generation strategy can complement existing dataset distillation methods for significantly enhancing their training efficiency and performance. Experimental results demonstrate that LADD outperforms existing methods in terms of computational overhead and accuracy. With three high-performance dataset distillation algorithms, LADD achieves remarkable gains by an average of 14.9% in accuracy. Furthermore, the effectiveness of our method is proven across various datasets, distillation hyperparameters, and algorithms. Finally, our method improves the cross-architecture robustness of the distilled dataset, which is important in the application scenario.
Addressing Image Hallucination in Text-to-Image Generation through Factual Image Retrieval
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image generation has shown remarkable progress with the emergence of diffusion models. However, these models often generate factually inconsistent images, failing to accurately reflect the factual information and common sense conveyed by the input text prompts. We refer to this issue as Image hallucination. Drawing from studies on hallucinations in language models, we classify this problem into three types and propose a methodology that uses factual images retrieved from external sources to generate realistic images. Depending on the nature of the hallucination, we employ off-the-shelf image editing tools, either InstructPix2Pix or IP-Adapter, to leverage factual information from the retrieved image. This approach enables the generation of images that accurately reflect the facts and common sense.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge