Young-Gyu Yoon
Inducing Functions through Reinforcement Learning without Task Specification
Nov 23, 2021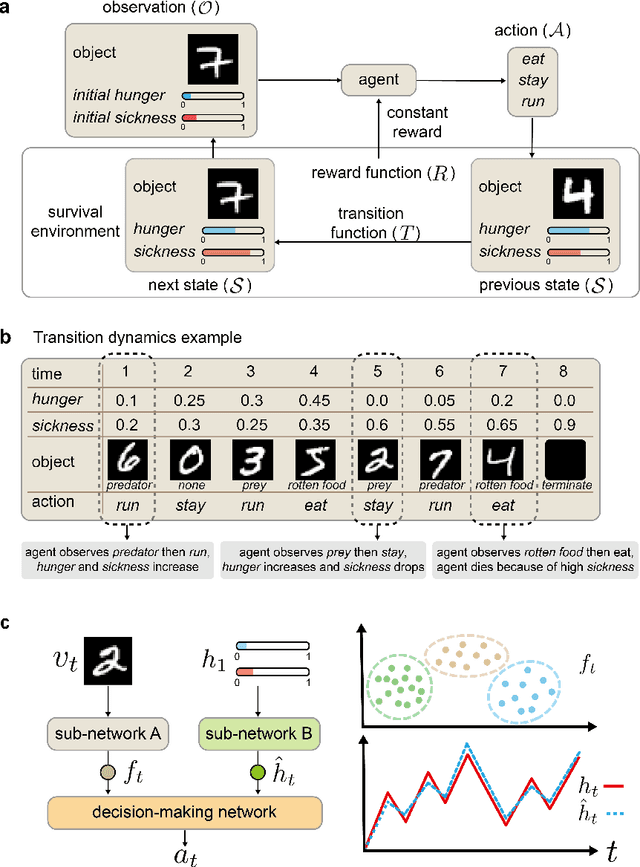
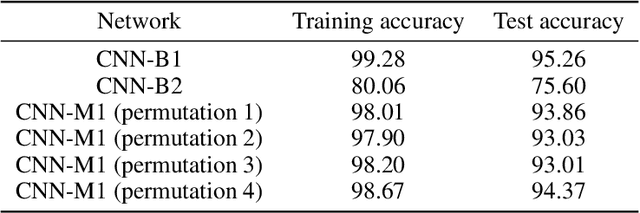
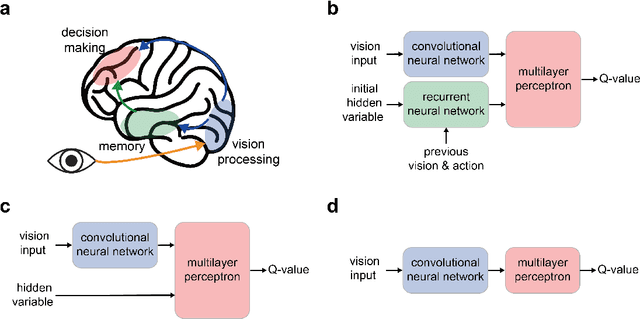
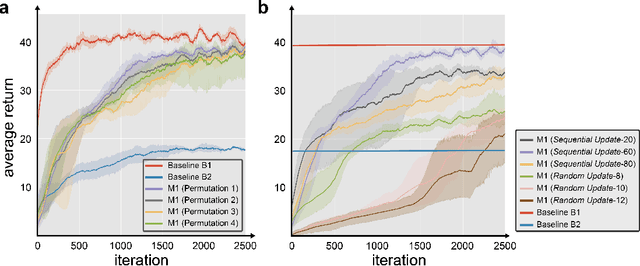
Abstract:We report a bio-inspired framework for training a neural network through reinforcement learning to induce high level functions within the network. Based on the interpretation that animals have gained their cognitive functions such as object recognition - without ever being specifically trained for - as a result of maximizing their fitness to the environment, we place our agent in an environment where developing certain functions may facilitate decision making. The experimental results show that high level functions, such as image classification and hidden variable estimation, can be naturally and simultaneously induced without any pre-training or specifying them.
Efficient Neural Network Approximation of Robust PCA for Automated Analysis of Calcium Imaging Data
Jul 31, 2021



Abstract:Calcium imaging is an essential tool to study the activity of neuronal populations. However, the high level of background fluorescence in images hinders the accurate identification of neurons and the extraction of neuronal activities. While robust principal component analysis (RPCA) is a promising method that can decompose the foreground and background in such images, its computational complexity and memory requirement are prohibitively high to process large-scale calcium imaging data. Here, we propose BEAR, a simple bilinear neural network for the efficient approximation of RPCA which achieves an order of magnitude speed improvement with GPU acceleration compared to the conventional RPCA algorithms. In addition, we show that BEAR can perform foreground-background separation of calcium imaging data as large as tens of gigabytes. We also demonstrate that two BEARs can be cascaded to perform simultaneous RPCA and non-negative matrix factorization for the automated extraction of spatial and temporal footprints from calcium imaging data. The source code used in the paper is available at https://github.com/NICALab/BEAR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge