Yongqing Liu
Modeling and Control for UAV with Off-center Slung Load
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with slung load system is a classic air transportation system. In practical applications, the suspension point of the slung load does not always align with the center of mass (CoM) of the UAV due to mission requirements or mechanical interference. This offset creates coupling in the system's nonlinear dynamics which leads to a complicated motion control problem. In existing research, modeling of the system are performed about the UAV's CoM. In this work we use the point of suspension instead. Based on the new model, a cascade control strategy is developed. In the middle-loop controller, the acceleration of the suspension point is used to regulate the swing angle of the slung load without the need for considering the coupling between the slung load and the UAV. Using the off-center reference frame, an inner-loop controller is designed to track the UAV's attitude without the need of simplification on the coupling effects. We prove local exponential stability of the closed-loop using Lyapunov approach. Finally, simulations and experiments are conducted to validate the proposed control system.
Gradient Mask: Lateral Inhibition Mechanism Improves Performance in Artificial Neural Networks
Aug 14, 2022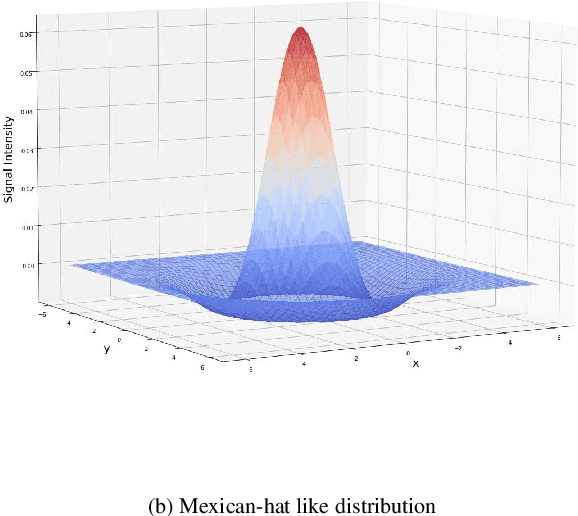
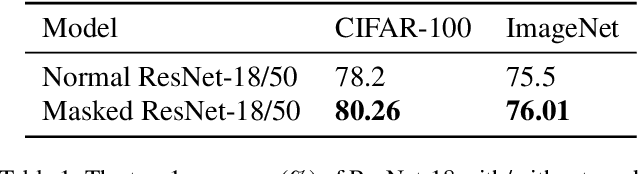
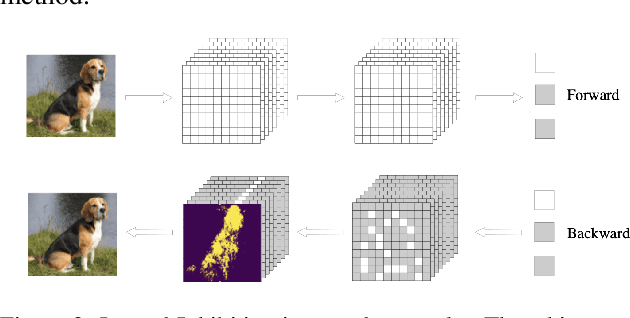
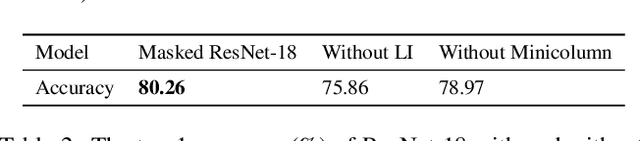
Abstract:Lateral inhibitory connections have been observed in the cortex of the biological brain, and has been extensively studied in terms of its role in cognitive functions. However, in the vanilla version of backpropagation in deep learning, all gradients (which can be understood to comprise of both signal and noise gradients) flow through the network during weight updates. This may lead to overfitting. In this work, inspired by biological lateral inhibition, we propose Gradient Mask, which effectively filters out noise gradients in the process of backpropagation. This allows the learned feature information to be more intensively stored in the network while filtering out noisy or unimportant features. Furthermore, we demonstrate analytically how lateral inhibition in artificial neural networks improves the quality of propagated gradients. A new criterion for gradient quality is proposed which can be used as a measure during training of various convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Finally, we conduct several different experiments to study how Gradient Mask improves the performance of the network both quantitatively and qualitatively. Quantitatively, accuracy in the original CNN architecture, accuracy after pruning, and accuracy after adversarial attacks have shown improvements. Qualitatively, the CNN trained using Gradient Mask has developed saliency maps that focus primarily on the object of interest, which is useful for data augmentation and network interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge