Yocheved Kopel
Dense Fixed-Wing Swarming using Receding-Horizon NMPC
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present an approach for controlling a team of agile fixed-wing aerial vehicles in close proximity to one another. Our approach relies on receding-horizon nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) to plan maneuvers across an expanded flight envelope to enable inter-agent collision avoidance. To facilitate robust collision avoidance and characterize the likelihood of inter-agent collisions, we compute a statistical bound on the probability of the system leaving a tube around the planned nominal trajectory. Finally, we propose a metric for evaluating highly dynamic swarms and use this metric to evaluate our approach. We successfully demonstrated our approach through both simulation and hardware experiments, and to our knowledge, this the first time close-quarters swarming has been achieved with physical aerobatic fixed-wing vehicles.
Planning and Control for a Dynamic Morphing-Wing UAV Using a Vortex Particle Model
Jul 05, 2023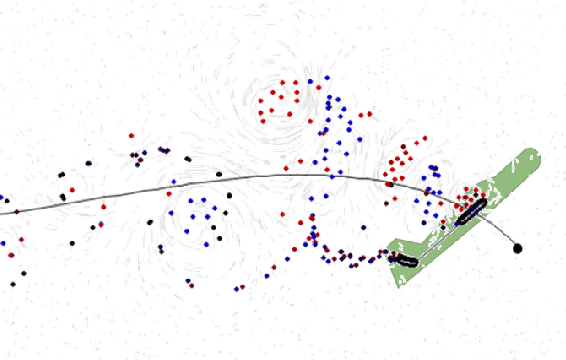
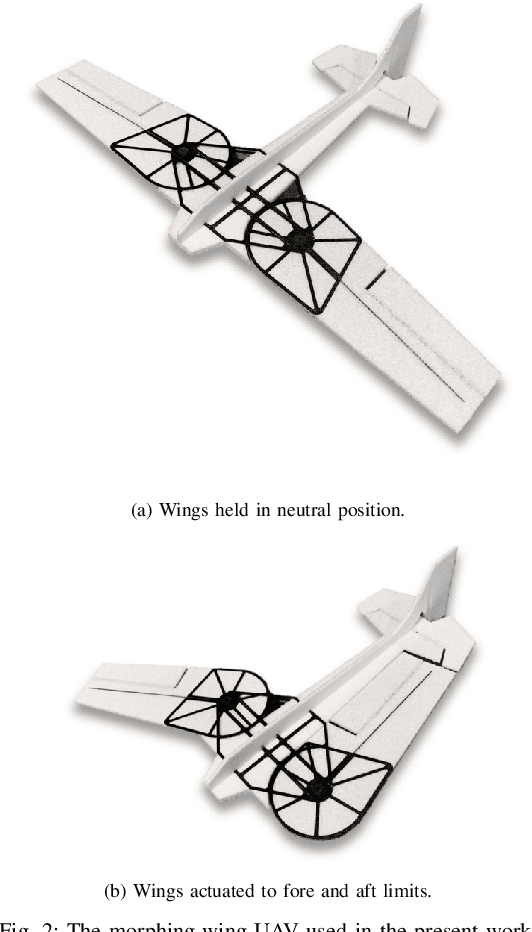
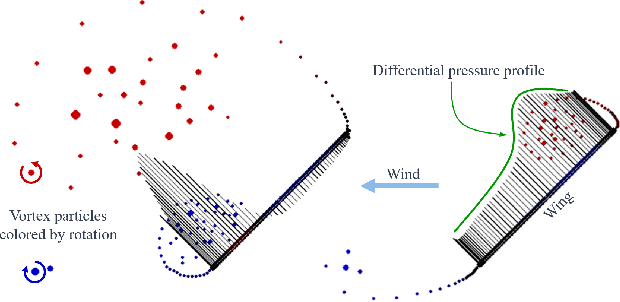
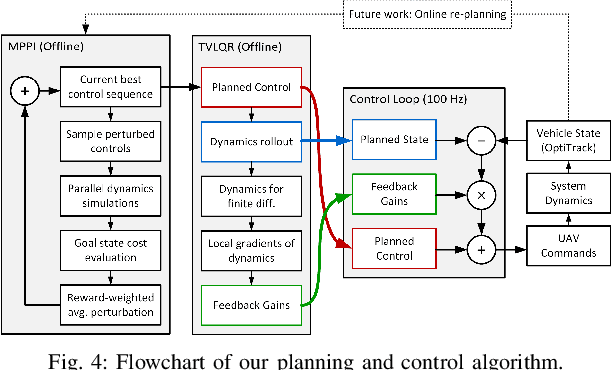
Abstract:Achieving precise, highly-dynamic maneuvers with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) is a major challenge due to the complexity of the associated aerodynamics. In particular, unsteady effects -- as might be experienced in post-stall regimes or during sudden vehicle morphing -- can have an adverse impact on the performance of modern flight control systems. In this paper, we present a vortex particle model and associated model-based controller capable of reasoning about the unsteady aerodynamics during aggressive maneuvers. We evaluate our approach in hardware on a morphing-wing UAV executing post-stall perching maneuvers. Our results show that the use of the unsteady aerodynamics model improves performance during both fixed-wing and dynamic-wing perching, while the use of wing-morphing planned with quasi-steady aerodynamics results in reduced performance. While the focus of this paper is a pre-computed control policy, we believe that, with sufficient computational resources, our approach could enable online planning in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge