Yizheng Sun
MIRA: Medical Time Series Foundation Model for Real-World Health Data
Jun 09, 2025

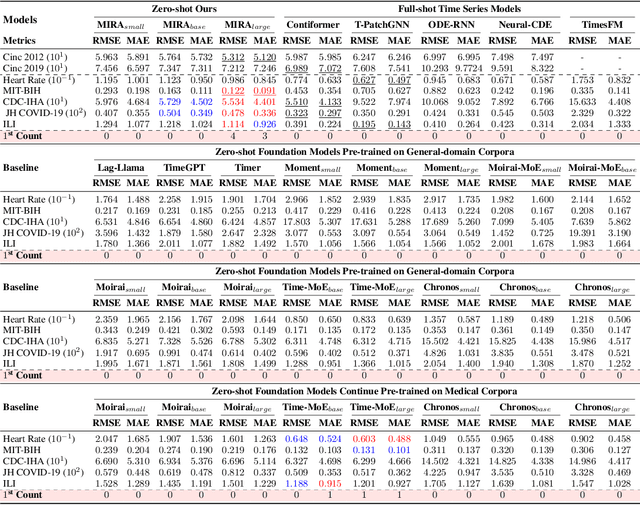
Abstract:A unified foundation model for medical time series -- pretrained on open access and ethics board-approved medical corpora -- offers the potential to reduce annotation burdens, minimize model customization, and enable robust transfer across clinical institutions, modalities, and tasks, particularly in data-scarce or privacy-constrained environments. However, existing generalist time series foundation models struggle to handle medical time series data due to their inherent challenges, including irregular intervals, heterogeneous sampling rates, and frequent missing values. To address these challenges, we introduce MIRA, a unified foundation model specifically designed for medical time series forecasting. MIRA incorporates a Continuous-Time Rotary Positional Encoding that enables fine-grained modeling of variable time intervals, a frequency-specific mixture-of-experts layer that routes computation across latent frequency regimes to further promote temporal specialization, and a Continuous Dynamics Extrapolation Block based on Neural ODE that models the continuous trajectory of latent states, enabling accurate forecasting at arbitrary target timestamps. Pretrained on a large-scale and diverse medical corpus comprising over 454 billion time points collect from publicly available datasets, MIRA achieves reductions in forecasting errors by an average of 10% and 7% in out-of-distribution and in-distribution scenarios, respectively, when compared to other zero-shot and fine-tuned baselines. We also introduce a comprehensive benchmark spanning multiple downstream clinical tasks, establishing a foundation for future research in medical time series modeling.
Silent Hazards of Token Reduction in Vision-Language Models: The Hidden Impact on Consistency
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Vision language models (VLMs) have excelled in visual reasoning but often incur high computational costs. One key reason is the redundancy of visual tokens. Although recent token reduction methods claim to achieve minimal performance loss, our extensive experiments reveal that token reduction can substantially alter a model's output distribution, leading to changes in prediction patterns that standard metrics such as accuracy loss do not fully capture. Such inconsistencies are especially concerning for practical applications where system stability is critical. To investigate this phenomenon, we analyze how token reduction influences the energy distribution of a VLM's internal representations using a lower-rank approximation via Singular Value Decomposition (SVD). Our results show that changes in the Inverse Participation Ratio of the singular value spectrum are strongly correlated with the model's consistency after token reduction. Based on these insights, we propose LoFi--a training-free visual token reduction method that utilizes the leverage score from SVD for token pruning. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that LoFi not only reduces computational costs with minimal performance degradation but also significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of output consistency.
LVPruning: An Effective yet Simple Language-Guided Vision Token Pruning Approach for Multi-modal Large Language Models
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable success by integrating visual and textual modalities. However, they incur significant computational overhead due to the large number of vision tokens processed, limiting their practicality in resource-constrained environments. We introduce Language-Guided Vision Token Pruning (LVPruning) for MLLMs, an effective yet simple method that significantly reduces the computational burden while preserving model performance. LVPruning employs cross-attention modules to compute the importance of vision tokens based on their interaction with language tokens, determining which to prune. Importantly, LVPruning can be integrated without modifying the original MLLM parameters, which makes LVPruning simple to apply or remove. Our experiments show that LVPruning can effectively reduce up to 90% of vision tokens by the middle layer of LLaVA-1.5, resulting in a 62.1% decrease in inference Tera Floating-Point Operations Per Second (TFLOPs), with an average performance loss of just 0.45% across nine multi-modal benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge