Yizhak Yisrael Elboher
Tighter Abstract Queries in Neural Network Verification
Oct 23, 2022Abstract:Neural networks have become critical components of reactive systems in various domains within computer science. Despite their excellent performance, using neural networks entails numerous risks that stem from our lack of ability to understand and reason about their behavior. Due to these risks, various formal methods have been proposed for verifying neural networks; but unfortunately, these typically struggle with scalability barriers. Recent attempts have demonstrated that abstraction-refinement approaches could play a significant role in mitigating these limitations; but these approaches can often produce networks that are so abstract, that they become unsuitable for verification. To deal with this issue, we present CEGARETTE, a novel verification mechanism where both the system and the property are abstracted and refined simultaneously. We observe that this approach allows us to produce abstract networks which are both small and sufficiently accurate, allowing for quick verification times while avoiding a large number of refinement steps. For evaluation purposes, we implemented CEGARETTE as an extension to the recently proposed CEGAR-NN framework. Our results are very promising, and demonstrate a significant improvement in performance over multiple benchmarks.
Neural Network Verification using Residual Reasoning
Aug 05, 2022



Abstract:With the increasing integration of neural networks as components in mission-critical systems, there is an increasing need to ensure that they satisfy various safety and liveness requirements. In recent years, numerous sound and complete verification methods have been proposed towards that end, but these typically suffer from severe scalability limitations. Recent work has proposed enhancing such verification techniques with abstraction-refinement capabilities, which have been shown to boost scalability: instead of verifying a large and complex network, the verifier constructs and then verifies a much smaller network, whose correctness implies the correctness of the original network. A shortcoming of such a scheme is that if verifying the smaller network fails, the verifier needs to perform a refinement step that increases the size of the network being verified, and then start verifying the new network from scratch -- effectively ``wasting'' its earlier work on verifying the smaller network. In this paper, we present an enhancement to abstraction-based verification of neural networks, by using \emph{residual reasoning}: the process of utilizing information acquired when verifying an abstract network, in order to expedite the verification of a refined network. In essence, the method allows the verifier to store information about parts of the search space in which the refined network is guaranteed to behave correctly, and allows it to focus on areas where bugs might be discovered. We implemented our approach as an extension to the Marabou verifier, and obtained promising results.
An Abstraction-Based Framework for Neural Network Verification
Oct 31, 2019
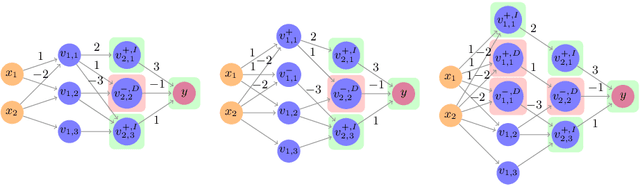
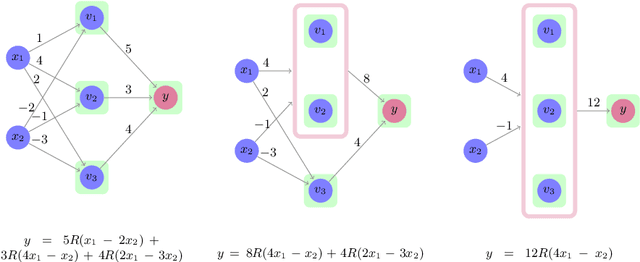
Abstract:Deep neural networks are increasingly being used as controllers for safety-critical systems. Because neural networks are opaque, certifying their correctness is a significant challenge. To address this issue, several approaches have recently been proposed to formally verify them. However, network size is often a bottleneck for such approaches and it can be difficult to apply them to large networks. In this paper, we propose a framework that can enhance neural network verification techniques by using over-approximation to reduce the size of the network - thus making it more amenable to verification. We perform the approximation such that if the property holds for the smaller (abstract) network, it holds for the original as well. The over-approximation may be too coarse, in which case the underlying verification tool might return a spurious counterexample. Under such conditions, we perform counterexample-guided refinement to adjust the approximation, and then repeat the process. Our approach is orthogonal to, and can be integrated with, many existing verification techniques. For evaluation purposes, we integrate it with the recently proposed Marabou framework, and observe a significant improvement in Marabou's performance. Our experiments demonstrate the great potential of our approach for verifying larger neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge