Yijia Zhou
University of Science and Technology of China
A Remote Sim2real Aerial Competition: Fostering Reproducibility and Solutions' Diversity in Robotics Challenges
Aug 31, 2023
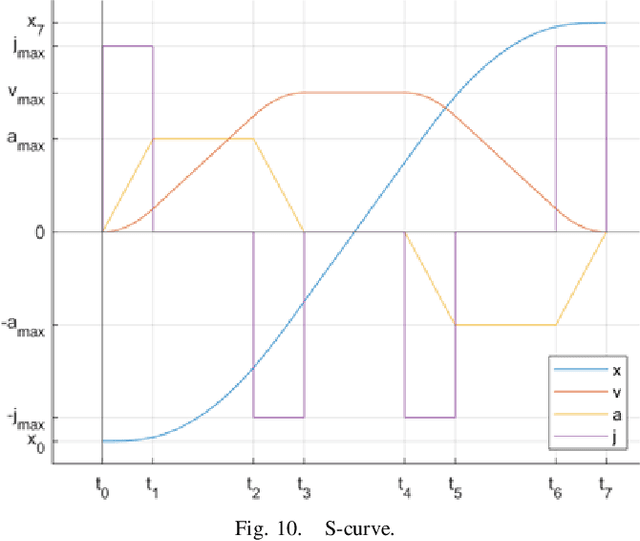
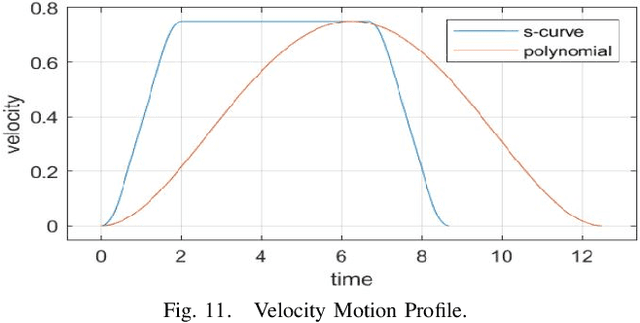

Abstract:Shared benchmark problems have historically been a fundamental driver of progress for scientific communities. In the context of academic conferences, competitions offer the opportunity to researchers with different origins, backgrounds, and levels of seniority to quantitatively compare their ideas. In robotics, a hot and challenging topic is sim2real-porting approaches that work well in simulation to real robot hardware. In our case, creating a hybrid competition with both simulation and real robot components was also dictated by the uncertainties around travel and logistics in the post-COVID-19 world. Hence, this article motivates and describes an aerial sim2real robot competition that ran during the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, from the specification of the competition task, to the details of the software infrastructure supporting simulation and real-life experiments, to the approaches of the top-placed teams and the lessons learned by participants and organizers.
Scalable Clustering: Large Scale Unsupervised Learning of Gaussian Mixture Models with Outliers
Feb 28, 2023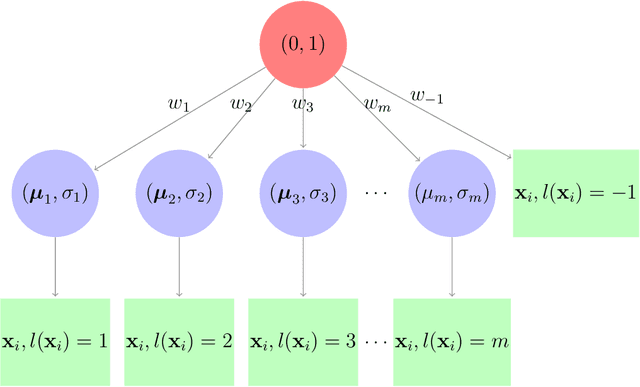
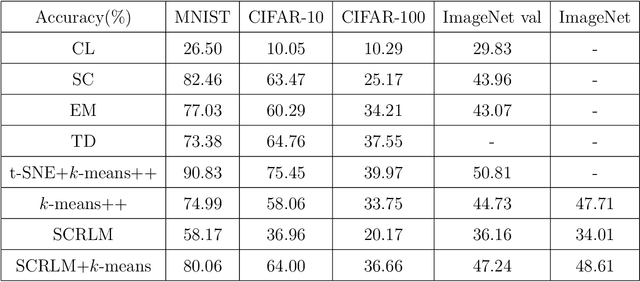
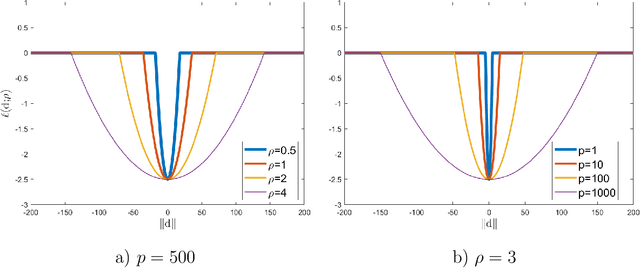
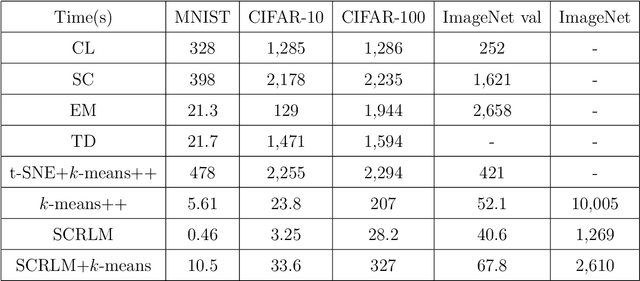
Abstract:Clustering is a widely used technique with a long and rich history in a variety of areas. However, most existing algorithms do not scale well to large datasets, or are missing theoretical guarantees of convergence. This paper introduces a provably robust clustering algorithm based on loss minimization that performs well on Gaussian mixture models with outliers. It provides theoretical guarantees that the algorithm obtains high accuracy with high probability under certain assumptions. Moreover, it can also be used as an initialization strategy for $k$-means clustering. Experiments on real-world large-scale datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm when clustering a large number of clusters, and a $k$-means algorithm initialized by the algorithm outperforms many of the classic clustering methods in both speed and accuracy, while scaling well to large datasets such as ImageNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge