Yihan Dong
Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning with Adversarial Perturbations for Robust Pretrained Language Models
Jul 15, 2021



Abstract:This paper improves the robustness of the pretrained language model BERT against word substitution-based adversarial attacks by leveraging self-supervised contrastive learning with adversarial perturbations. One advantage of our method compared to previous works is that it is capable of improving model robustness without using any labels. Additionally, we also create an adversarial attack for word-level adversarial training on BERT. The attack is efficient, allowing adversarial training for BERT on adversarial examples generated on the fly during training. Experimental results on four datasets show that our method improves the robustness of BERT against four different word substitution-based adversarial attacks. Furthermore, to understand why our method can improve the model robustness against adversarial attacks, we study vector representations of clean examples and their corresponding adversarial examples before and after applying our method. As our method improves model robustness with unlabeled raw data, it opens up the possibility of using large text datasets to train robust language models.
Neural Arithmetic Expression Calculator
Sep 23, 2018

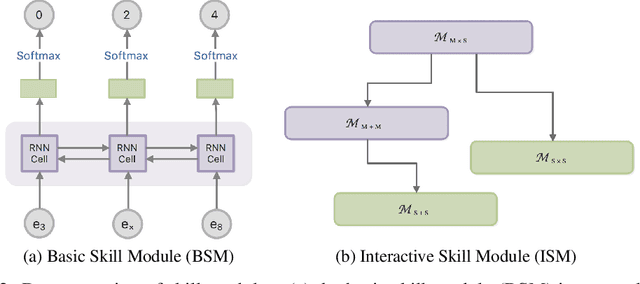
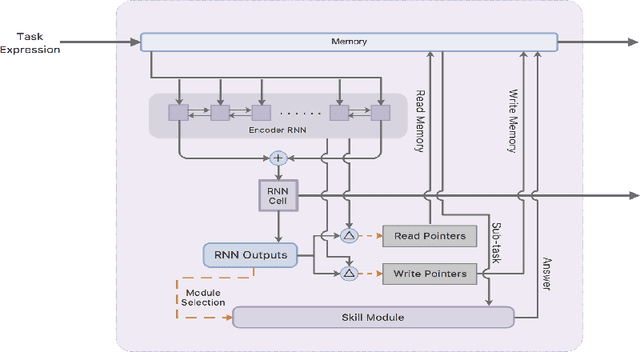
Abstract:This paper presents a pure neural solver for arithmetic expression calculation (AEC) problem. Previous work utilizes the powerful capabilities of deep neural networks and attempts to build an end-to-end model to solve this problem. However, most of these methods can only deal with the additive operations. It is still a challenging problem to solve the complex expression calculation problem, which includes the adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing and bracketing operations. In this work, we regard the arithmetic expression calculation as a hierarchical reinforcement learning problem. An arithmetic operation is decomposed into a series of sub-tasks, and each sub-task is dealt with by a skill module. The skill module could be a basic module performing elementary operations, or interactive module performing complex operations by invoking other skill models. With curriculum learning, our model can deal with a complex arithmetic expression calculation with the deep hierarchical structure of skill models. Experiments show that our model significantly outperforms the previous models for arithmetic expression calculation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge