Yifeng Kou
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Evaluating Deep Clustering Algorithms on Non-Categorical 3D CAD Models
Apr 29, 2024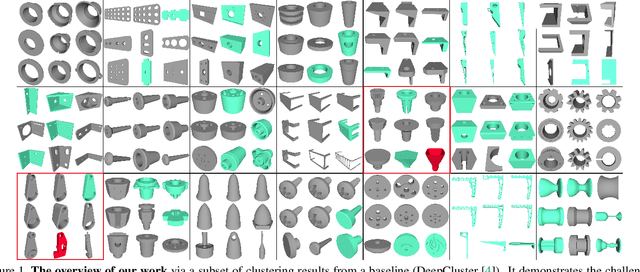
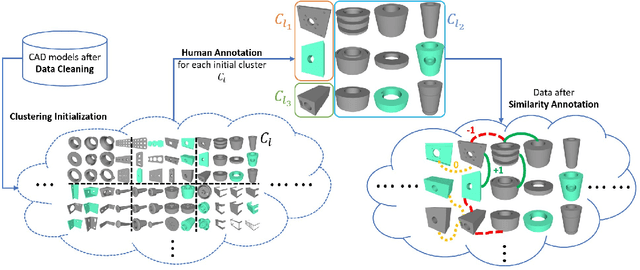
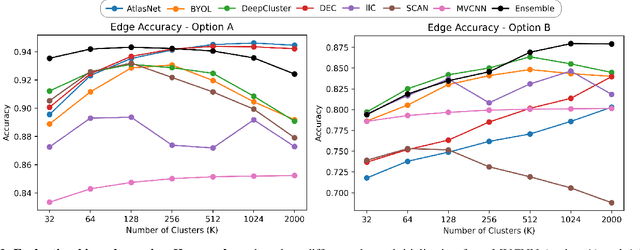

Abstract:We introduce the first work on benchmarking and evaluating deep clustering algorithms on large-scale non-categorical 3D CAD models. We first propose a workflow to allow expert mechanical engineers to efficiently annotate 252,648 carefully sampled pairwise CAD model similarities, from a subset of the ABC dataset with 22,968 shapes. Using seven baseline deep clustering methods, we then investigate the fundamental challenges of evaluating clustering methods for non-categorical data. Based on these challenges, we propose a novel and viable ensemble-based clustering comparison approach. This work is the first to directly target the underexplored area of deep clustering algorithms for 3D shapes, and we believe it will be an important building block to analyze and utilize the massive 3D shape collections that are starting to appear in deep geometric computing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge