Yifan Zang
Goal-Oriented Skill Abstraction for Offline Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Offline multi-task reinforcement learning aims to learn a unified policy capable of solving multiple tasks using only pre-collected task-mixed datasets, without requiring any online interaction with the environment. However, it faces significant challenges in effectively sharing knowledge across tasks. Inspired by the efficient knowledge abstraction observed in human learning, we propose Goal-Oriented Skill Abstraction (GO-Skill), a novel approach designed to extract and utilize reusable skills to enhance knowledge transfer and task performance. Our approach uncovers reusable skills through a goal-oriented skill extraction process and leverages vector quantization to construct a discrete skill library. To mitigate class imbalances between broadly applicable and task-specific skills, we introduce a skill enhancement phase to refine the extracted skills. Furthermore, we integrate these skills using hierarchical policy learning, enabling the construction of a high-level policy that dynamically orchestrates discrete skills to accomplish specific tasks. Extensive experiments on diverse robotic manipulation tasks within the MetaWorld benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of GO-Skill.
* ICML2025
Not All Tasks Are Equally Difficult: Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning with Dynamic Depth Routing
Dec 22, 2023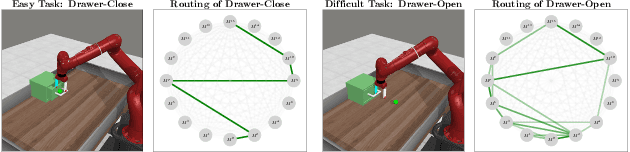
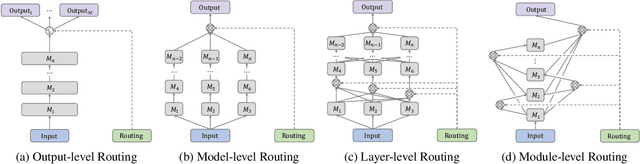

Abstract:Multi-task reinforcement learning endeavors to accomplish a set of different tasks with a single policy. To enhance data efficiency by sharing parameters across multiple tasks, a common practice segments the network into distinct modules and trains a routing network to recombine these modules into task-specific policies. However, existing routing approaches employ a fixed number of modules for all tasks, neglecting that tasks with varying difficulties commonly require varying amounts of knowledge. This work presents a Dynamic Depth Routing (D2R) framework, which learns strategic skipping of certain intermediate modules, thereby flexibly choosing different numbers of modules for each task. Under this framework, we further introduce a ResRouting method to address the issue of disparate routing paths between behavior and target policies during off-policy training. In addition, we design an automatic route-balancing mechanism to encourage continued routing exploration for unmastered tasks without disturbing the routing of mastered ones. We conduct extensive experiments on various robotics manipulation tasks in the Meta-World benchmark, where D2R achieves state-of-the-art performance with significantly improved learning efficiency.
* AAAI2024, with supplementary material
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge