Yicheng Qian
Weakly Supervised Video Representation Learning with Unaligned Text for Sequential Videos
Mar 28, 2023



Abstract:Sequential video understanding, as an emerging video understanding task, has driven lots of researchers' attention because of its goal-oriented nature. This paper studies weakly supervised sequential video understanding where the accurate time-stamp level text-video alignment is not provided. We solve this task by borrowing ideas from CLIP. Specifically, we use a transformer to aggregate frame-level features for video representation and use a pre-trained text encoder to encode the texts corresponding to each action and the whole video, respectively. To model the correspondence between text and video, we propose a multiple granularity loss, where the video-paragraph contrastive loss enforces matching between the whole video and the complete script, and a fine-grained frame-sentence contrastive loss enforces the matching between each action and its description. As the frame-sentence correspondence is not available, we propose to use the fact that video actions happen sequentially in the temporal domain to generate pseudo frame-sentence correspondence and supervise the network training with the pseudo labels. Extensive experiments on video sequence verification and text-to-video matching show that our method outperforms baselines by a large margin, which validates the effectiveness of our proposed approach. Code is available at https://github.com/svip-lab/WeakSVR
SVIP: Sequence VerIfication for Procedures in Videos
Dec 14, 2021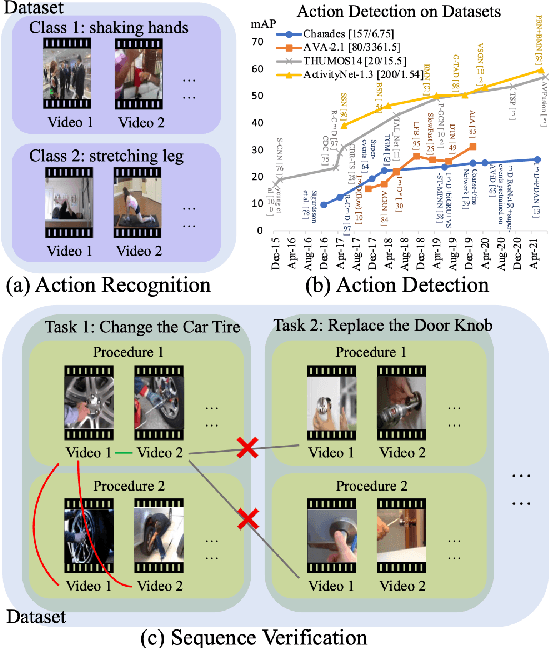

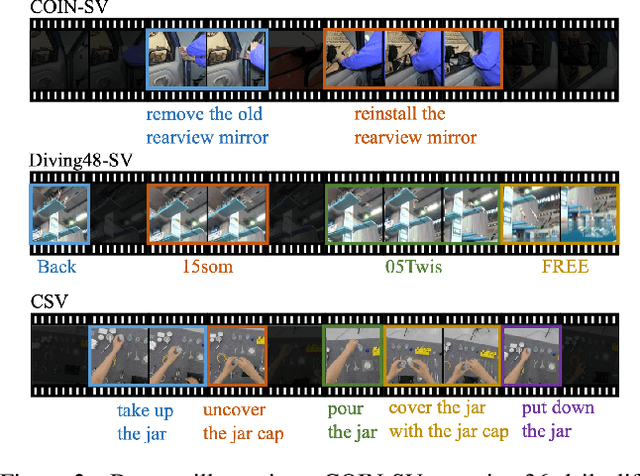
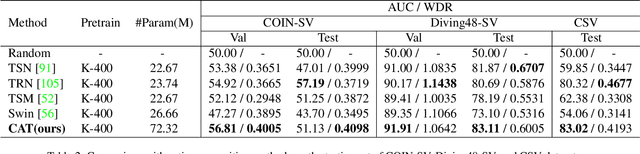
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel sequence verification task that aims to distinguish positive video pairs performing the same action sequence from negative ones with step-level transformations but still conducting the same task. Such a challenging task resides in an open-set setting without prior action detection or segmentation that requires event-level or even frame-level annotations. To that end, we carefully reorganize two publicly available action-related datasets with step-procedure-task structure. To fully investigate the effectiveness of any method, we collect a scripted video dataset enumerating all kinds of step-level transformations in chemical experiments. Besides, a novel evaluation metric Weighted Distance Ratio is introduced to ensure equivalence for different step-level transformations during evaluation. In the end, a simple but effective baseline based on the transformer with a novel sequence alignment loss is introduced to better characterize long-term dependency between steps, which outperforms other action recognition methods. Codes and data will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge