Yassine Habchi
Deep Transfer Learning for Kidney Cancer Diagnosis
Aug 08, 2024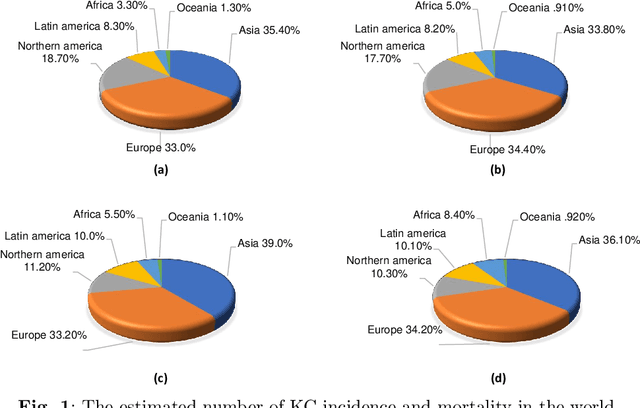
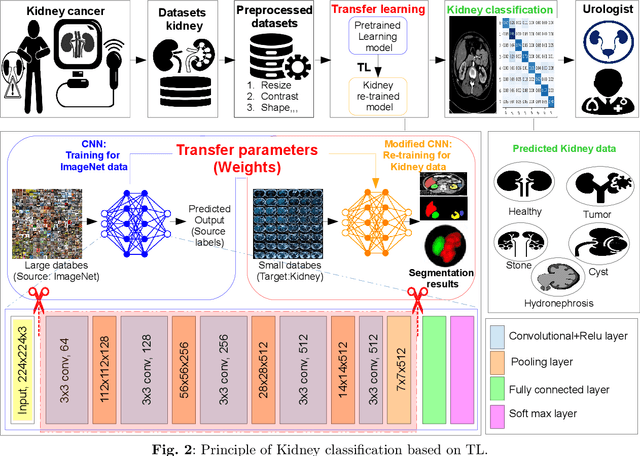
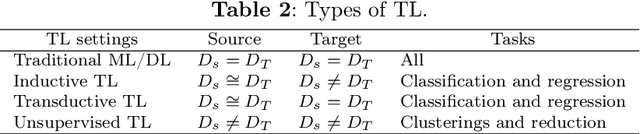
Abstract:Many incurable diseases prevalent across global societies stem from various influences, including lifestyle choices, economic conditions, social factors, and genetics. Research predominantly focuses on these diseases due to their widespread nature, aiming to decrease mortality, enhance treatment options, and improve healthcare standards. Among these, kidney disease stands out as a particularly severe condition affecting men and women worldwide. Nonetheless, there is a pressing need for continued research into innovative, early diagnostic methods to develop more effective treatments for such diseases. Recently, automatic diagnosis of Kidney Cancer has become an important challenge especially when using deep learning (DL) due to the importance of training medical datasets, which in most cases are difficult and expensive to obtain. Furthermore, in most cases, algorithms require data from the same domain and a powerful computer with efficient storage capacity. To overcome this issue, a new type of learning known as transfer learning (TL) has been proposed that can produce impressive results based on other different pre-trained data. This paper presents, to the best of the authors' knowledge, the first comprehensive survey of DL-based TL frameworks for kidney cancer diagnosis. This is a strong contribution to help researchers understand the current challenges and perspectives of this topic. Hence, the main limitations and advantages of each framework are identified and detailed critical analyses are provided. Looking ahead, the article identifies promising directions for future research. Moving on, the discussion is concluded by reflecting on the pivotal role of TL in the development of precision medicine and its effects on clinical practice and research in oncology.
Machine Learning and Vision Transformers for Thyroid Carcinoma Diagnosis: A review
Mar 17, 2024

Abstract:The growing interest in developing smart diagnostic systems to help medical experts process extensive data for treating incurable diseases has been notable. In particular, the challenge of identifying thyroid cancer (TC) has seen progress with the use of machine learning (ML) and big data analysis, incorporating transformers to evaluate TC prognosis and determine the risk of malignancy in individuals. This review article presents a summary of various studies on AIbased approaches, especially those employing transformers, for diagnosing TC. It introduces a new categorization system for these methods based on artifcial intelligence (AI) algorithms, the goals of the framework, and the computing environments used. Additionally, it scrutinizes and contrasts the available TC datasets by their features. The paper highlights the importance of AI instruments in aiding the diagnosis and treatment of TC through supervised, unsupervised, or mixed approaches, with a special focus on the ongoing importance of transformers in medical diagnostics and disease management. It further discusses the progress made and the continuing obstacles in this area. Lastly, it explores future directions and focuses within this research feld.
AI in Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis: Techniques, Trends, and Future Directions
Aug 25, 2023
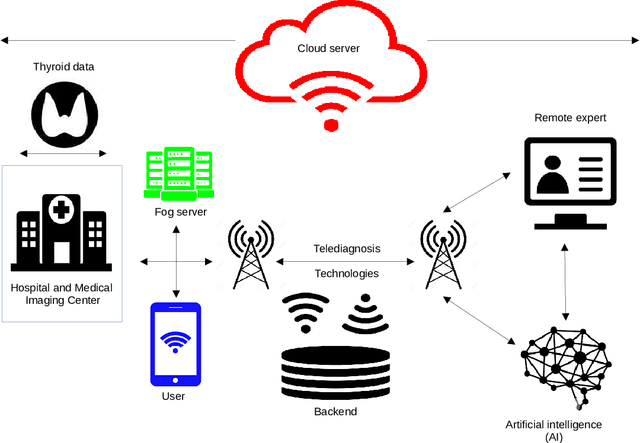
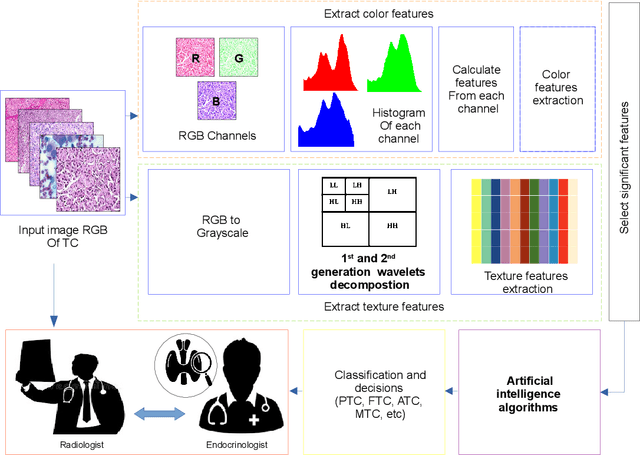
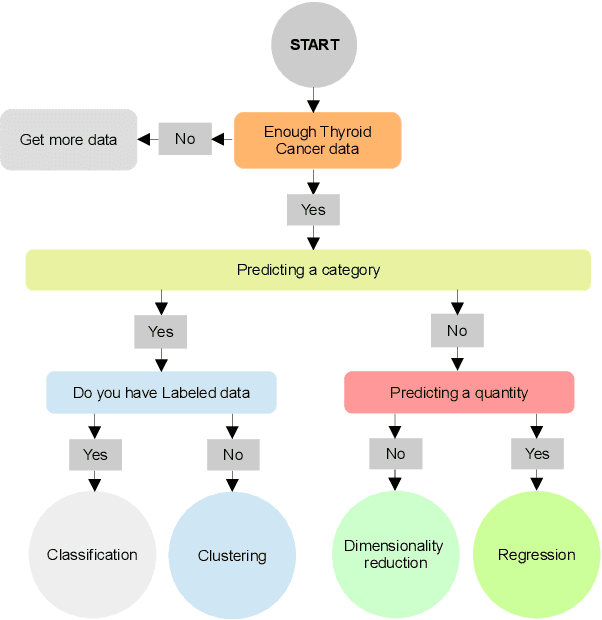
Abstract:There has been a growing interest in creating intelligent diagnostic systems to assist medical professionals in analyzing and processing big data for the treatment of incurable diseases. One of the key challenges in this field is detecting thyroid cancer, where advancements have been made using machine learning (ML) and big data analytics to evaluate thyroid cancer prognosis and determine a patient's risk of malignancy. This review paper summarizes a large collection of articles related to artificial intelligence (AI)-based techniques used in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Accordingly, a new classification was introduced to classify these techniques based on the AI algorithms used, the purpose of the framework, and the computing platforms used. Additionally, this study compares existing thyroid cancer datasets based on their features. The focus of this study is on how AI-based tools can support the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer, through supervised, unsupervised, or hybrid techniques. It also highlights the progress made and the unresolved challenges in this field. Finally, the future trends and areas of focus in this field are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge