Yanyu Ye
Multi Task Consistency Guided Source-Free Test-Time Domain Adaptation Medical Image Segmentation
Oct 18, 2023


Abstract:Source-free test-time adaptation for medical image segmentation aims to enhance the adaptability of segmentation models to diverse and previously unseen test sets of the target domain, which contributes to the generalizability and robustness of medical image segmentation models without access to the source domain. Ensuring consistency between target edges and paired inputs is crucial for test-time adaptation. To improve the performance of test-time domain adaptation, we propose a multi task consistency guided source-free test-time domain adaptation medical image segmentation method which ensures the consistency of the local boundary predictions and the global prototype representation. Specifically, we introduce a local boundary consistency constraint method that explores the relationship between tissue region segmentation and tissue boundary localization tasks. Additionally, we propose a global feature consistency constraint toto enhance the intra-class compactness. We conduct extensive experiments on the segmentation of benchmark fundus images. Compared to prediction directly by the source domain model, the segmentation Dice score is improved by 6.27\% and 0.96\% in RIM-ONE-r3 and Drishti GS datasets, respectively. Additionally, the results of experiments demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms existing competitive domain adaptation segmentation algorithms.
Local-Global Pseudo-label Correction for Source-free Domain Adaptive Medical Image Segmentation
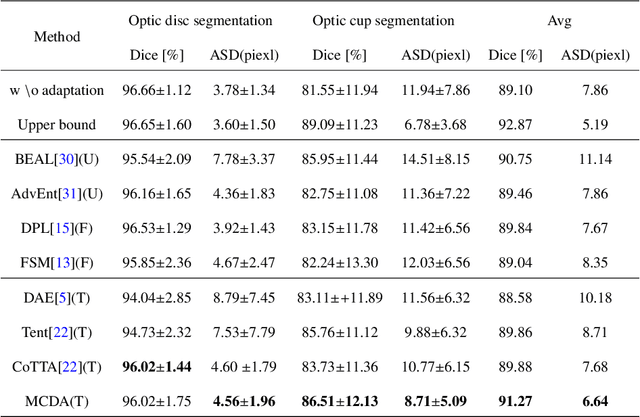
Aug 28, 2023Abstract:Domain shift is a commonly encountered issue in medical imaging solutions, primarily caused by variations in imaging devices and data sources. To mitigate this problem, unsupervised domain adaptation techniques have been employed. However, concerns regarding patient privacy and potential degradation of image quality have led to an increased focus on source-free domain adaptation. In this study, we address the issue of false labels in self-training based source-free domain adaptive medical image segmentation methods. To correct erroneous pseudo-labels, we propose a novel approach called the local-global pseudo-label correction (LGDA) method for source-free domain adaptive medical image segmentation. Our method consists of two components: An offline local context-based pseudo-label correction method that utilizes local context similarity in image space. And an online global pseudo-label correction method based on class prototypes, which corrects erroneously predicted pseudo-labels by considering the relative distance between pixel-wise feature vectors and prototype vectors. We evaluate the performance of our method on three benchmark fundus image datasets for optic disc and cup segmentation. Our method achieves superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art approaches, even without using of any source data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge