Yannis Haralambous
Arabic Language Text Classification Using Dependency Syntax-Based Feature Selection
Oct 17, 2014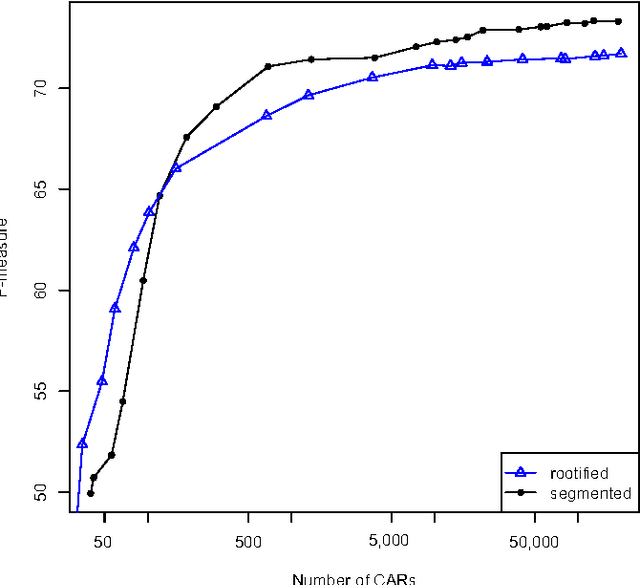
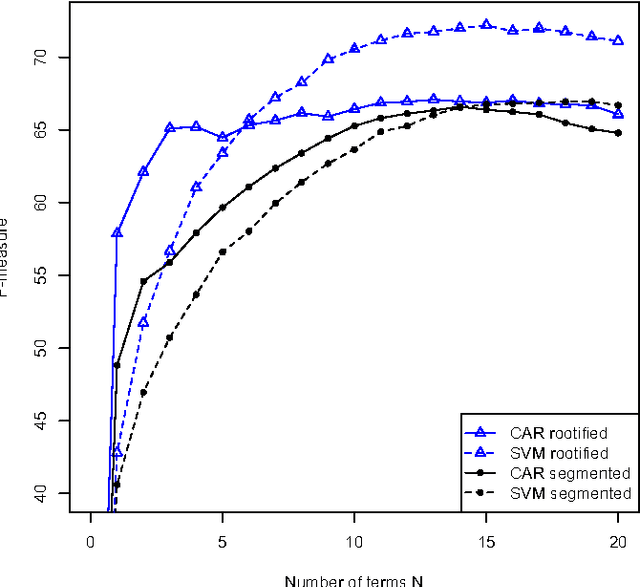
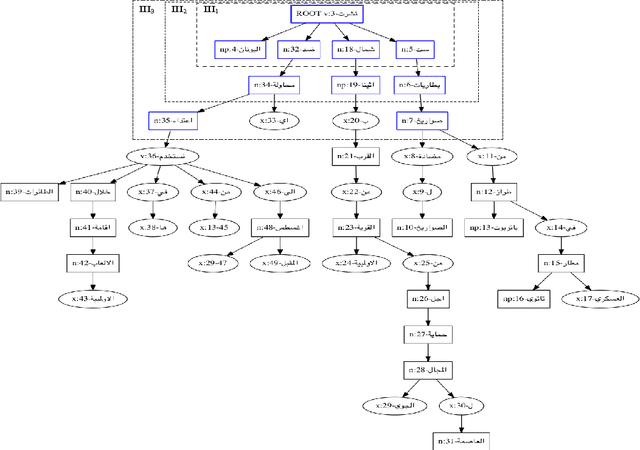
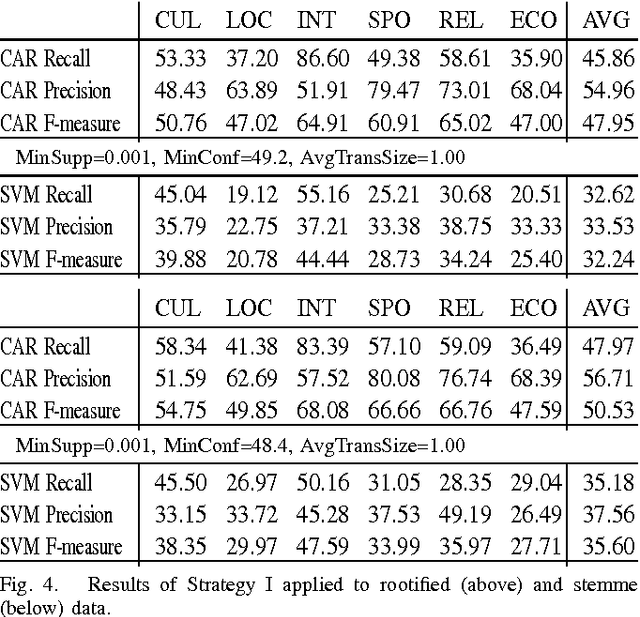
Abstract:We study the performance of Arabic text classification combining various techniques: (a) tfidf vs. dependency syntax, for feature selection and weighting; (b) class association rules vs. support vector machines, for classification. The Arabic text is used in two forms: rootified and lightly stemmed. The results we obtain show that lightly stemmed text leads to better performance than rootified text; that class association rules are better suited for small feature sets obtained by dependency syntax constraints; and, finally, that support vector machines are better suited for large feature sets based on morphological feature selection criteria.
Text Classification Using Association Rules, Dependency Pruning and Hyperonymization
Jul 28, 2014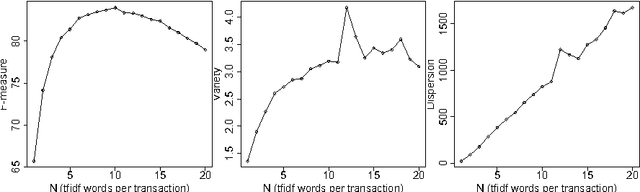
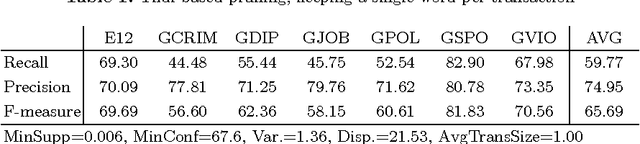
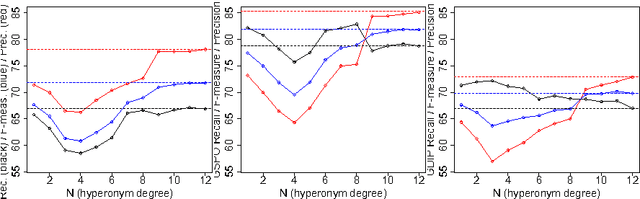
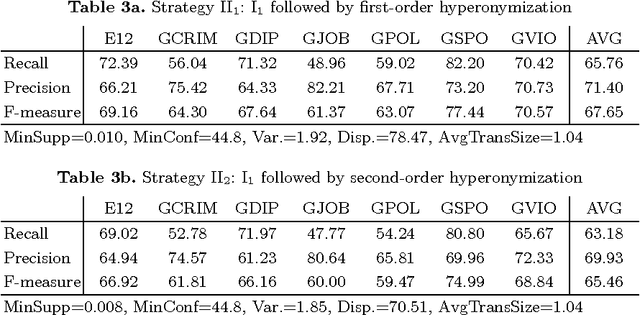
Abstract:We present new methods for pruning and enhancing item- sets for text classification via association rule mining. Pruning methods are based on dependency syntax and enhancing methods are based on replacing words by their hyperonyms of various orders. We discuss the impact of these methods, compared to pruning based on tfidf rank of words.
New Perspectives in Sinographic Language Processing Through the Use of Character Structure
May 21, 2014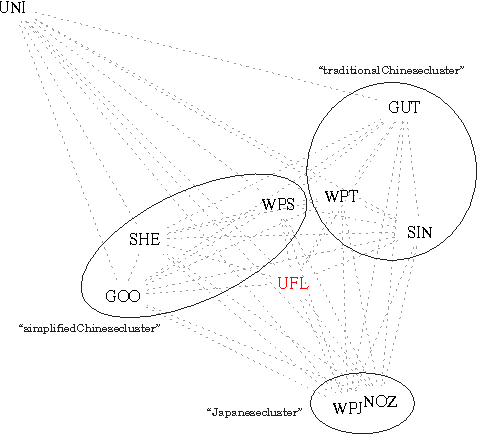
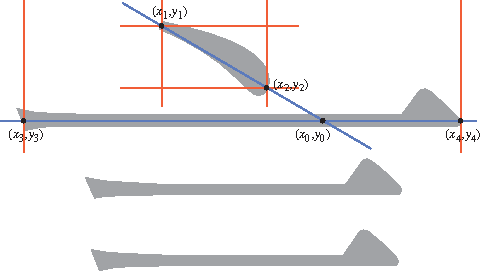
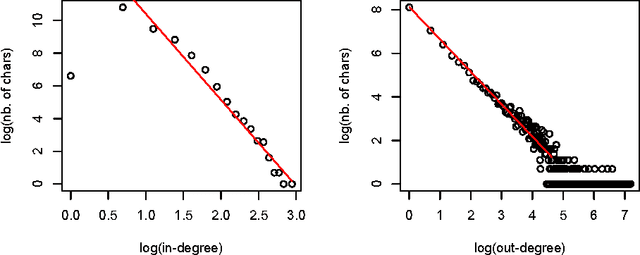
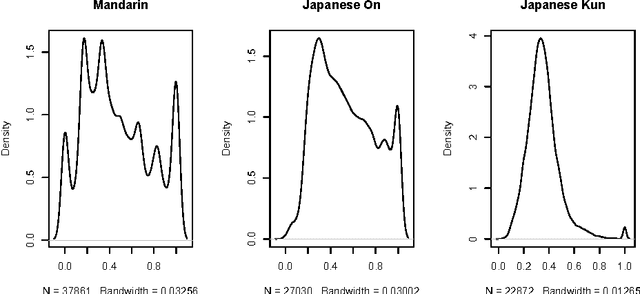
Abstract:Chinese characters have a complex and hierarchical graphical structure carrying both semantic and phonetic information. We use this structure to enhance the text model and obtain better results in standard NLP operations. First of all, to tackle the problem of graphical variation we define allographic classes of characters. Next, the relation of inclusion of a subcharacter in a characters, provides us with a directed graph of allographic classes. We provide this graph with two weights: semanticity (semantic relation between subcharacter and character) and phoneticity (phonetic relation) and calculate "most semantic subcharacter paths" for each character. Finally, adding the information contained in these paths to unigrams we claim to increase the efficiency of text mining methods. We evaluate our method on a text classification task on two corpora (Chinese and Japanese) of a total of 18 million characters and get an improvement of 3% on an already high baseline of 89.6% precision, obtained by a linear SVM classifier. Other possible applications and perspectives of the system are discussed.
* 17 pages, 5 figures, presented at CICLing 2013
Thematically Reinforced Explicit Semantic Analysis
May 17, 2014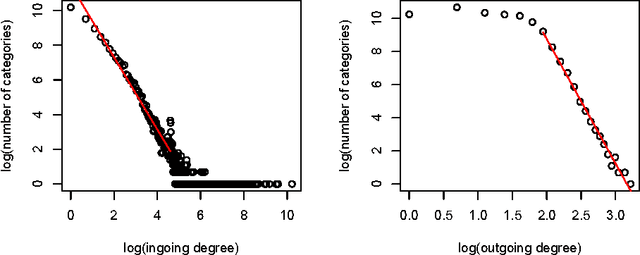
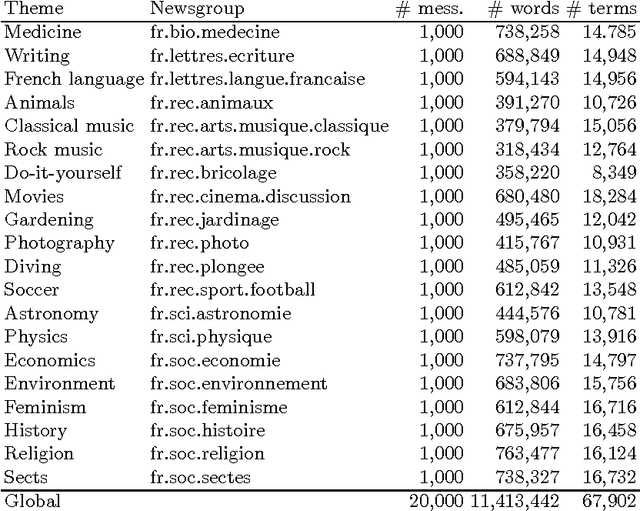
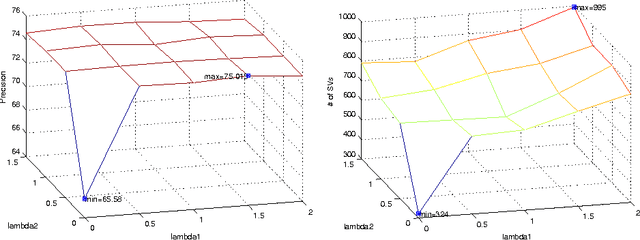
Abstract:We present an extended, thematically reinforced version of Gabrilovich and Markovitch's Explicit Semantic Analysis (ESA), where we obtain thematic information through the category structure of Wikipedia. For this we first define a notion of categorical tfidf which measures the relevance of terms in categories. Using this measure as a weight we calculate a maximal spanning tree of the Wikipedia corpus considered as a directed graph of pages and categories. This tree provides us with a unique path of "most related categories" between each page and the top of the hierarchy. We reinforce tfidf of words in a page by aggregating it with categorical tfidfs of the nodes of these paths, and define a thematically reinforced ESA semantic relatedness measure which is more robust than standard ESA and less sensitive to noise caused by out-of-context words. We apply our method to the French Wikipedia corpus, evaluate it through a text classification on a 37.5 MB corpus of 20 French newsgroups and obtain a precision increase of 9-10% compared with standard ESA.
* 13 pages, 2 figures, presented at CICLing 2013
Les mathématiques de la langue : l'approche formelle de Montague
May 16, 2014
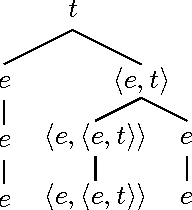

Abstract:We present a natural language modelization method which is strongely relying on mathematics. This method, called "Formal Semantics," has been initiated by the American linguist Richard M. Montague in the 1970's. It uses mathematical tools such as formal languages and grammars, first-order logic, type theory and $\lambda$-calculus. Our goal is to have the reader discover both Montagovian formal semantics and the mathematical tools that he used in his method. ----- Nous pr\'esentons une m\'ethode de mod\'elisation de la langue naturelle qui est fortement bas\'ee sur les math\'ematiques. Cette m\'ethode, appel\'ee {\guillemotleft}s\'emantique formelle{\guillemotright}, a \'et\'e initi\'ee par le linguiste am\'ericain Richard M. Montague dans les ann\'ees 1970. Elle utilise des outils math\'ematiques tels que les langages et grammaires formels, la logique du 1er ordre, la th\'eorie de types et le $\lambda$-calcul. Nous nous proposons de faire d\'ecouvrir au lecteur tant la s\'emantique formelle de Montague que les outils math\'ematiques dont il s'est servi.
INAUT, a Controlled Language for the French Coast Pilot Books Instructions nautiques
May 15, 2014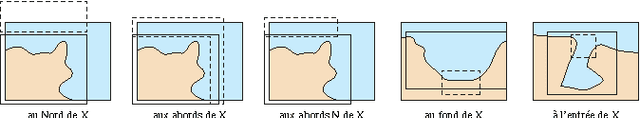
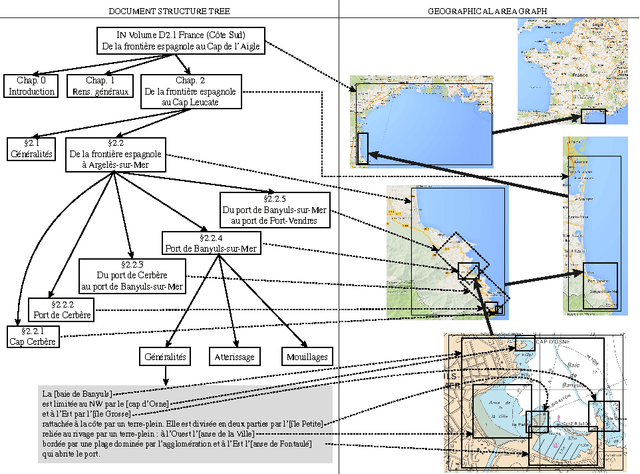
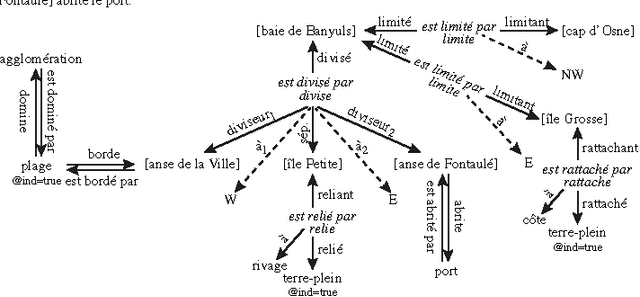
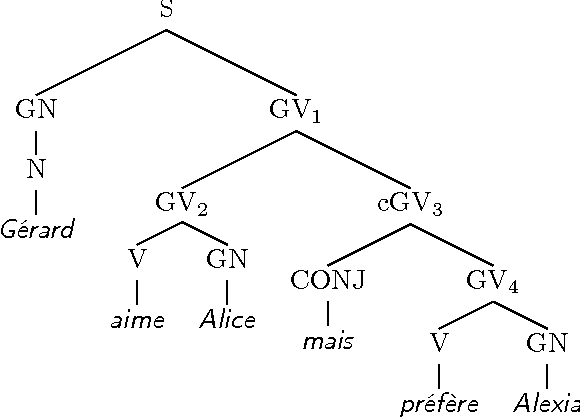
Abstract:We describe INAUT, a controlled natural language dedicated to collaborative update of a knowledge base on maritime navigation and to automatic generation of coast pilot books (Instructions nautiques) of the French National Hydrographic and Oceanographic Service SHOM. INAUT is based on French language and abundantly uses georeferenced entities. After describing the structure of the overall system, giving details on the language and on its generation, and discussing the three major applications of INAUT (document production, interaction with ENCs and collaborative updates of the knowledge base), we conclude with future extensions and open problems.
Querying Geometric Figures Using a Controlled Language, Ontological Graphs and Dependency Lattices
May 13, 2014


Abstract:Dynamic geometry systems (DGS) have become basic tools in many areas of geometry as, for example, in education. Geometry Automated Theorem Provers (GATP) are an active area of research and are considered as being basic tools in future enhanced educational software as well as in a next generation of mechanized mathematics assistants. Recently emerged Web repositories of geometric knowledge, like TGTP and Intergeo, are an attempt to make the already vast data set of geometric knowledge widely available. Considering the large amount of geometric information already available, we face the need of a query mechanism for descriptions of geometric constructions. In this paper we discuss two approaches for describing geometric figures (declarative and procedural), and present algorithms for querying geometric figures in declaratively and procedurally described corpora, by using a DGS or a dedicated controlled natural language for queries.
Wikipedia Arborification and Stratified Explicit Semantic Analysis
Feb 01, 2012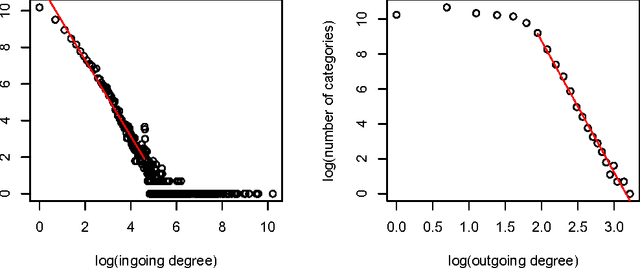
Abstract:[This is the translation of paper "Arborification de Wikip\'edia et analyse s\'emantique explicite stratifi\'ee" submitted to TALN 2012.] We present an extension of the Explicit Semantic Analysis method by Gabrilovich and Markovitch. Using their semantic relatedness measure, we weight the Wikipedia categories graph. Then, we extract a minimal spanning tree, using Chu-Liu & Edmonds' algorithm. We define a notion of stratified tfidf where the stratas, for a given Wikipedia page and a given term, are the classical tfidf and categorical tfidfs of the term in the ancestor categories of the page (ancestors in the sense of the minimal spanning tree). Our method is based on this stratified tfidf, which adds extra weight to terms that "survive" when climbing up the category tree. We evaluate our method by a text classification on the WikiNews corpus: it increases precision by 18%. Finally, we provide hints for future research
Query Expansion: Term Selection using the EWC Semantic Relatedness Measure
Aug 19, 2011
Abstract:This paper investigates the efficiency of the EWC semantic relatedness measure in an ad-hoc retrieval task. This measure combines the Wikipedia-based Explicit Semantic Analysis measure, the WordNet path measure and the mixed collocation index. In the experiments, the open source search engine Terrier was utilised as a tool to index and retrieve data. The proposed technique was tested on the NTCIR data collection. The experiments demonstrated promising results.
* 5 pages, 1 figure, accepted at ASIR'11 <http://fedcsis.org/?q=node/62>
A Semantic Relatedness Measure Based on Combined Encyclopedic, Ontological and Collocational Knowledge
Aug 19, 2011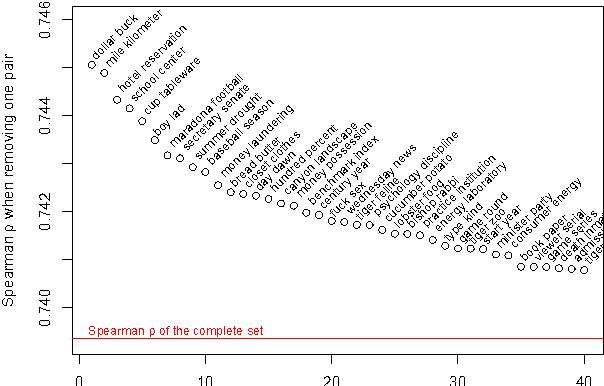
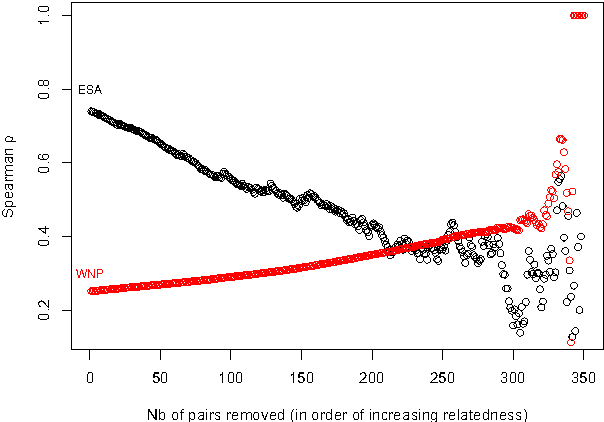
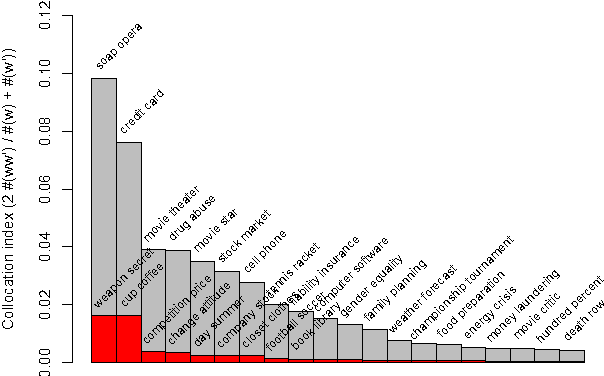
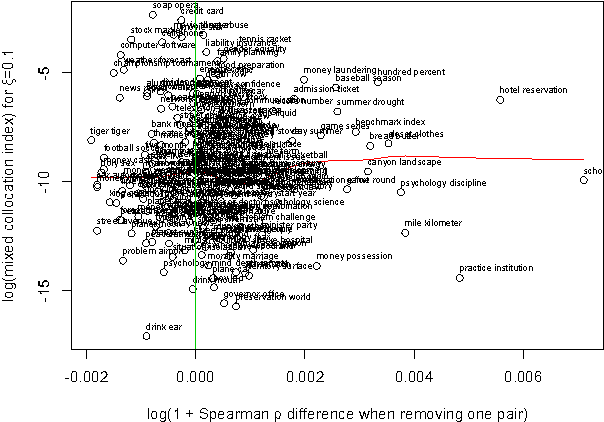
Abstract:We describe a new semantic relatedness measure combining the Wikipedia-based Explicit Semantic Analysis measure, the WordNet path measure and the mixed collocation index. Our measure achieves the currently highest results on the WS-353 test: a Spearman rho coefficient of 0.79 (vs. 0.75 in (Gabrilovich and Markovitch, 2007)) when applying the measure directly, and a value of 0.87 (vs. 0.78 in (Agirre et al., 2009)) when using the prediction of a polynomial SVM classifier trained on our measure. In the appendix we discuss the adaptation of ESA to 2011 Wikipedia data, as well as various unsuccessful attempts to enhance ESA by filtering at word, sentence, and section level.
* 6 pages, 6 figures, accepted for publication at IJCNLP2011 Conference
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge