Philippe Lenca
Community structure: A comparative evaluation of community detection methods
Jan 07, 2019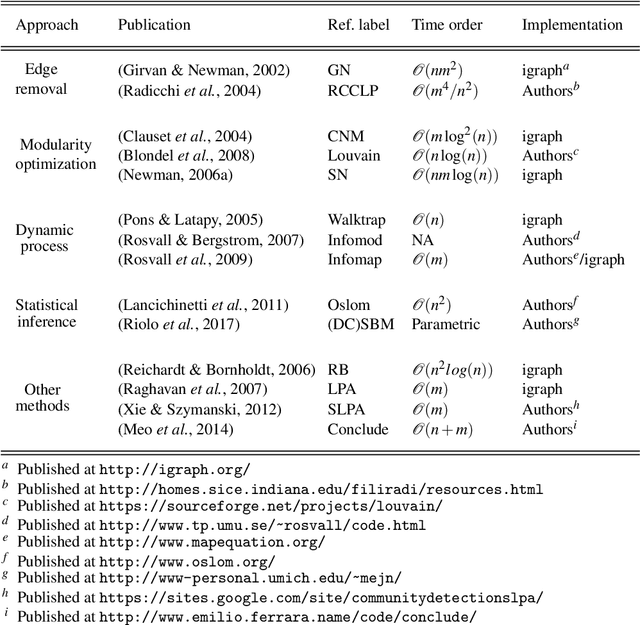
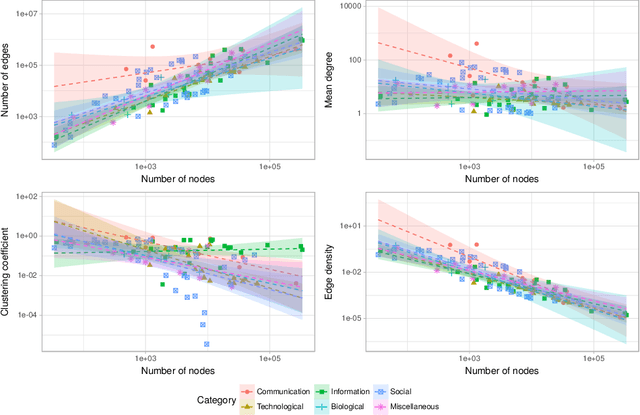
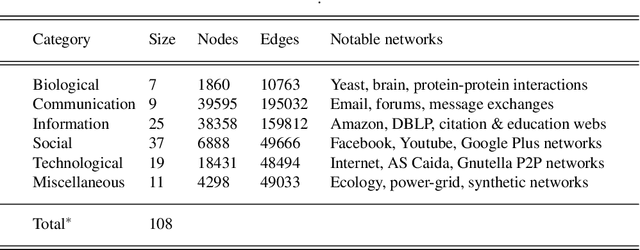
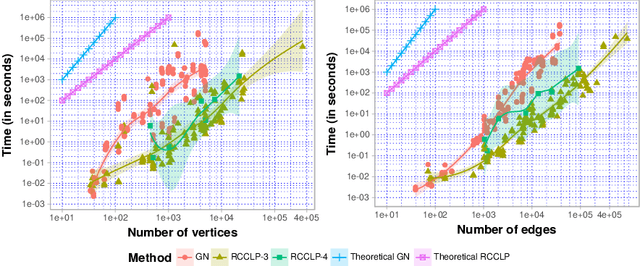
Abstract:Discovering community structure in complex networks is a mature field since a tremendous number of community detection methods have been introduced in the literature. Nevertheless, it is still very challenging for practioners to determine which method would be suitable to get insights into the structural information of the networks they study. Many recent efforts have been devoted to investigating various quality scores of the community structure, but the problem of distinguishing between different types of communities is still open. In this paper, we propose a comparative, extensive and empirical study to investigate what types of communities many state-of-the-art and well-known community detection methods are producing. Specifically, we provide comprehensive analyses on computation time, community size distribution, a comparative evaluation of methods according to their optimisation schemes as well as a comparison of their partioning strategy through validation metrics. We process our analyses on a very large corpus of hundreds of networks from five different network categories and propose ways to classify community detection methods, helping a potential user to navigate the complex landscape of community detection.
Arabic Language Text Classification Using Dependency Syntax-Based Feature Selection
Oct 17, 2014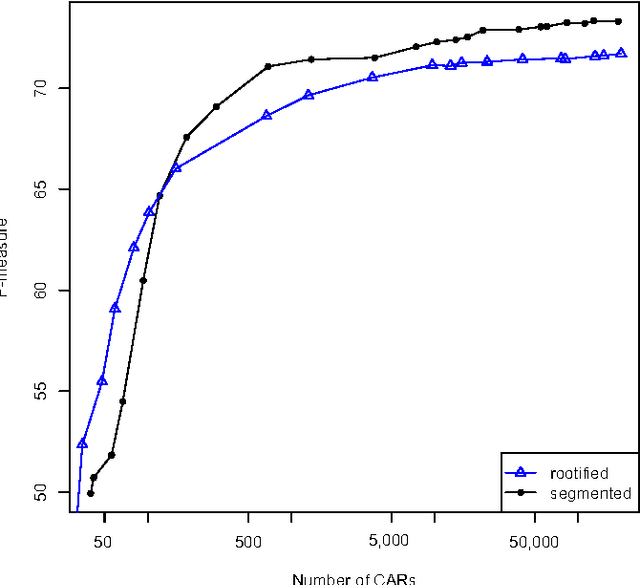
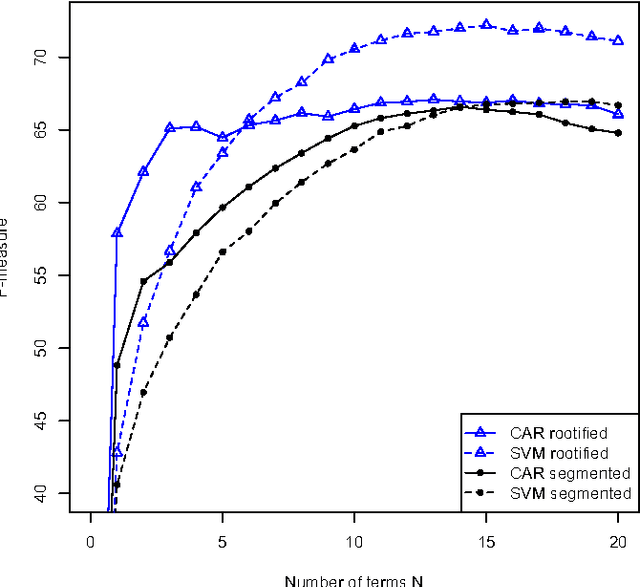
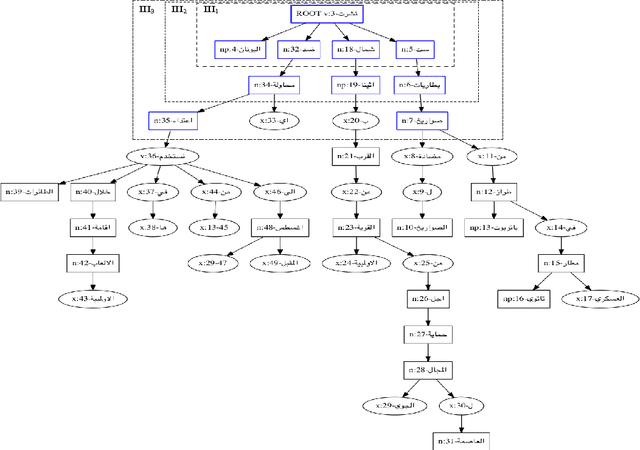
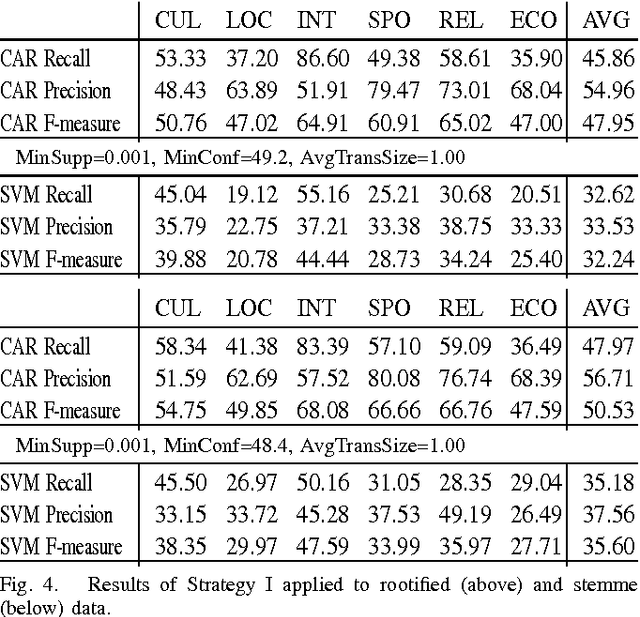
Abstract:We study the performance of Arabic text classification combining various techniques: (a) tfidf vs. dependency syntax, for feature selection and weighting; (b) class association rules vs. support vector machines, for classification. The Arabic text is used in two forms: rootified and lightly stemmed. The results we obtain show that lightly stemmed text leads to better performance than rootified text; that class association rules are better suited for small feature sets obtained by dependency syntax constraints; and, finally, that support vector machines are better suited for large feature sets based on morphological feature selection criteria.
Text Classification Using Association Rules, Dependency Pruning and Hyperonymization
Jul 28, 2014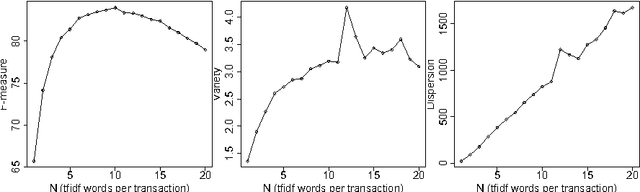
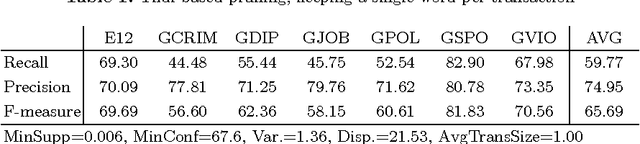
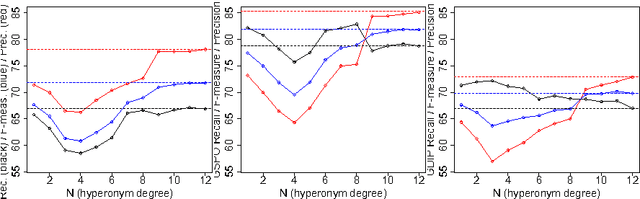
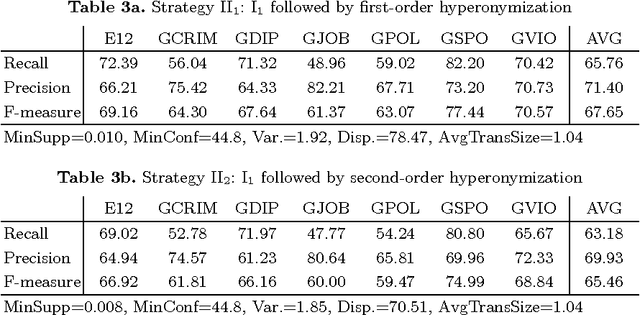
Abstract:We present new methods for pruning and enhancing item- sets for text classification via association rule mining. Pruning methods are based on dependency syntax and enhancing methods are based on replacing words by their hyperonyms of various orders. We discuss the impact of these methods, compared to pruning based on tfidf rank of words.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge