New Perspectives in Sinographic Language Processing Through the Use of Character Structure
Paper and Code
May 21, 2014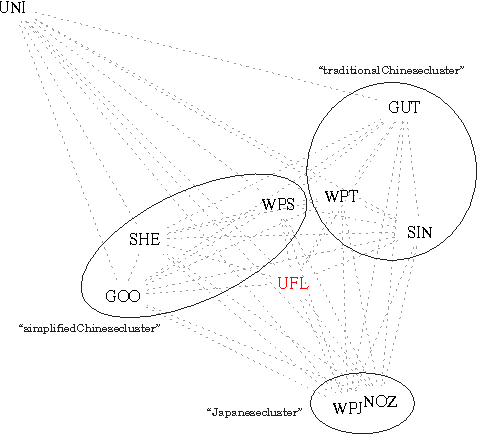
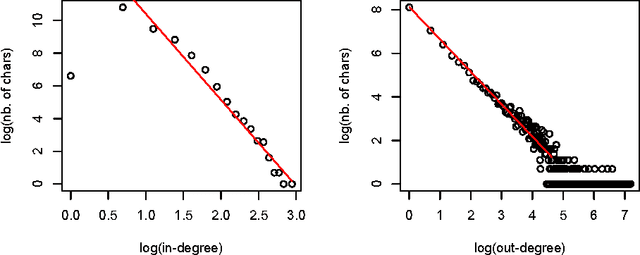
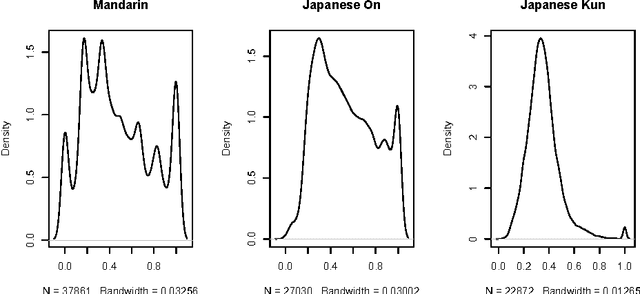
Chinese characters have a complex and hierarchical graphical structure carrying both semantic and phonetic information. We use this structure to enhance the text model and obtain better results in standard NLP operations. First of all, to tackle the problem of graphical variation we define allographic classes of characters. Next, the relation of inclusion of a subcharacter in a characters, provides us with a directed graph of allographic classes. We provide this graph with two weights: semanticity (semantic relation between subcharacter and character) and phoneticity (phonetic relation) and calculate "most semantic subcharacter paths" for each character. Finally, adding the information contained in these paths to unigrams we claim to increase the efficiency of text mining methods. We evaluate our method on a text classification task on two corpora (Chinese and Japanese) of a total of 18 million characters and get an improvement of 3% on an already high baseline of 89.6% precision, obtained by a linear SVM classifier. Other possible applications and perspectives of the system are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge