Yanghoon Kim
Index Tracking via Learning to Predict Market Sensitivities
Sep 02, 2022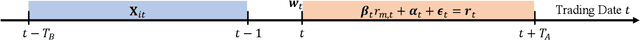
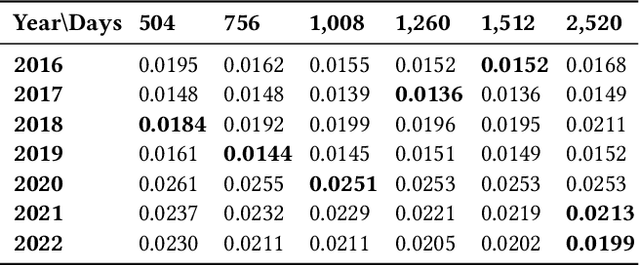
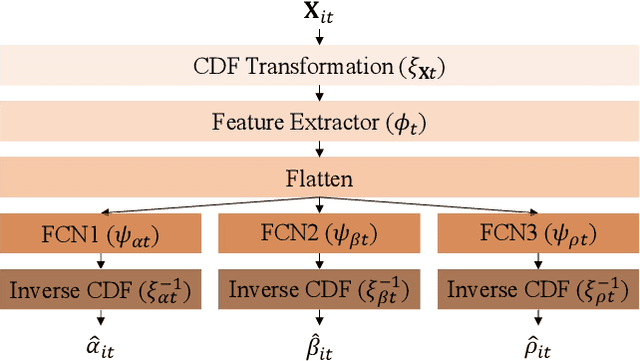

Abstract:A significant number of equity funds are preferred by index funds nowadays, and market sensitivities are instrumental in managing them. Index funds might replicate the index identically, which is, however, cost-ineffective and impractical. Moreover, to utilize market sensitivities to replicate the index partially, they must be predicted or estimated accurately. Accordingly, first, we examine deep learning models to predict market sensitivities. Also, we present pragmatic applications of data processing methods to aid training and generate target data for the prediction. Then, we propose a partial-index-tracking optimization model controlling the net predicted market sensitivities of the portfolios and index to be the same. These processes' efficacy is corroborated by the Korea Stock Price Index 200. Our experiments show a significant reduction of the prediction errors compared with historical estimations, and competitive tracking errors of replicating the index using fewer than half of the entire constituents. Therefore, we show that applying deep learning to predict market sensitivities is promising and that our portfolio construction methods are practically effective. Additionally, to our knowledge, this is the first study that addresses market sensitivities focused on deep learning.
Collaborative Training of GANs in Continuous and Discrete Spaces for Text Generation
Nov 04, 2020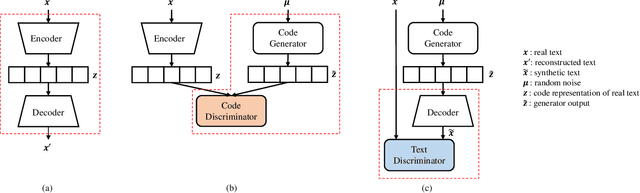
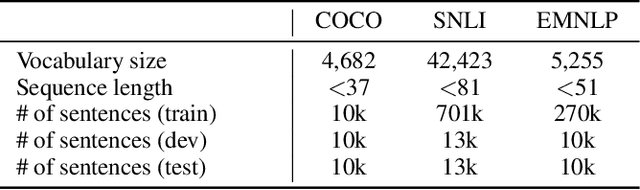
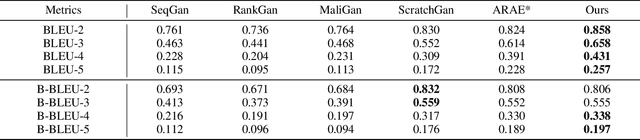
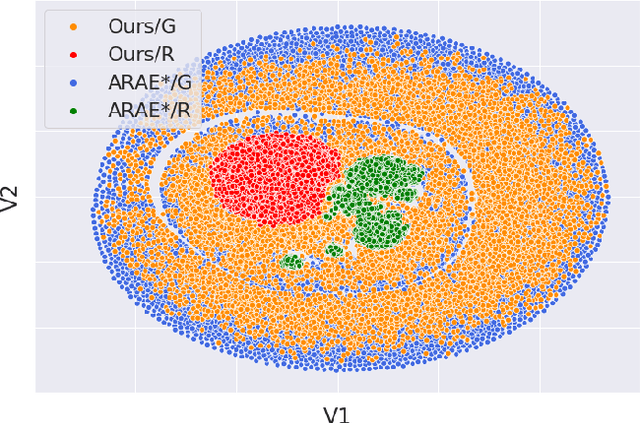
Abstract:Applying generative adversarial networks (GANs) to text-related tasks is challenging due to the discrete nature of language. One line of research resolves this issue by employing reinforcement learning (RL) and optimizing the next-word sampling policy directly in a discrete action space. Such methods compute the rewards from complete sentences and avoid error accumulation due to exposure bias. Other approaches employ approximation techniques that map the text to continuous representation in order to circumvent the non-differentiable discrete process. Particularly, autoencoder-based methods effectively produce robust representations that can model complex discrete structures. In this paper, we propose a novel text GAN architecture that promotes the collaborative training of the continuous-space and discrete-space methods. Our method employs an autoencoder to learn an implicit data manifold, providing a learning objective for adversarial training in a continuous space. Furthermore, the complete textual output is directly evaluated and updated via RL in a discrete space. The collaborative interplay between the two adversarial trainings effectively regularize the text representations in different spaces. The experimental results on three standard benchmark datasets show that our model substantially outperforms state-of-the-art text GANs with respect to quality, diversity, and global consistency.
Improving Neural Question Generation using Answer Separation
Sep 07, 2018



Abstract:Neural question generation (NQG) is the task of generating a question from a given passage with deep neural networks. Previous NQG models suffer from a problem that a significant proportion of the generated questions include words in the question target, resulting in the generation of unintended questions. In this paper, we propose answer-separated seq2seq, which better utilizes the information from both the passage and the target answer. By replacing the target answer in the original passage with a special token, our model learns to identify which interrogative word should be used. We also propose a new module termed keyword-net, which helps the model better capture the key information in the target answer and generate an appropriate question. Experimental results demonstrate that our answer separation method significantly reduces the number of improper questions which include answers. Consequently, our model significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art NQG models.
AttnConvnet at SemEval-2018 Task 1: Attention-based Convolutional Neural Networks for Multi-label Emotion Classification
Apr 17, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an attention-based classifier that predicts multiple emotions of a given sentence. Our model imitates human's two-step procedure of sentence understanding and it can effectively represent and classify sentences. With emoji-to-meaning preprocessing and extra lexicon utilization, we further improve the model performance. We train and evaluate our model with data provided by SemEval-2018 task 1-5, each sentence of which has several labels among 11 given sentiments. Our model achieves 5-th/1-th rank in English/Spanish respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge