Yamei Xia
Focus on Local Regions for Query-based Object Detection
Oct 10, 2023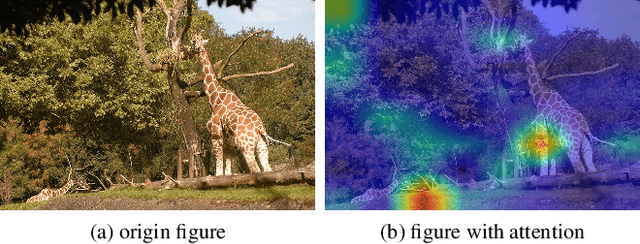
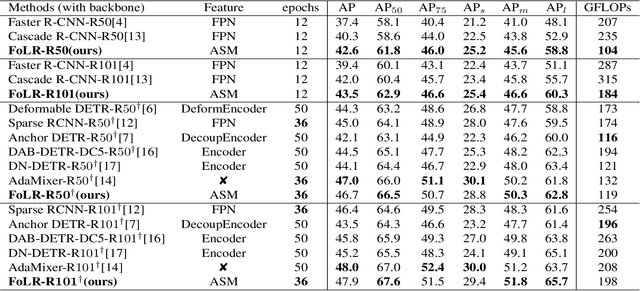
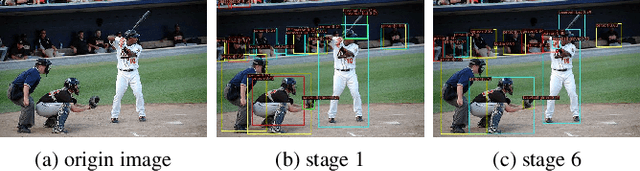
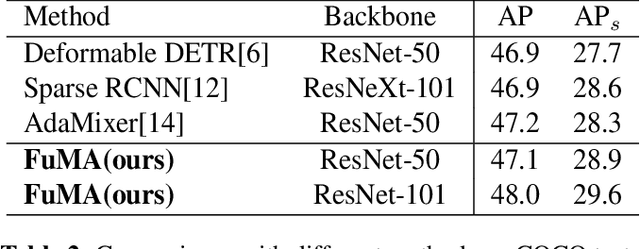
Abstract:Query-based methods have garnered significant attention in object detection since the advent of DETR, the pioneering end-to-end query-based detector. However, these methods face challenges like slow convergence and suboptimal performance. Notably, self-attention in object detection often hampers convergence due to its global focus. To address these issues, we propose FoLR, a transformer-like architecture with only decoders. We enhance the self-attention mechanism by isolating connections between irrelevant objects that makes it focus on local regions but not global regions. We also design the adaptive sampling method to extract effective features based on queries' local regions from feature maps. Additionally, we employ a look-back strategy for decoders to retain prior information, followed by the Feature Mixer module to fuse features and queries. Experimental results demonstrate FoLR's state-of-the-art performance in query-based detectors, excelling in convergence speed and computational efficiency.
CARE: Co-Attention Network for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:Joint entity and relation extraction is the fundamental task of information extraction, consisting of two subtasks: named entity recognition and relation extraction. Most existing joint extraction methods suffer from issues of feature confusion or inadequate interaction between two subtasks. In this work, we propose a Co-Attention network for joint entity and Relation Extraction (CARE). Our approach involves learning separate representations for each subtask, aiming to avoid feature overlap. At the core of our approach is the co-attention module that captures two-way interaction between two subtasks, allowing the model to leverage entity information for relation prediction and vice versa, thus promoting mutual enhancement. Extensive experiments on three joint entity-relation extraction benchmark datasets (NYT, WebNLG and SciERC) show that our proposed model achieves superior performance, surpassing existing baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge