Yafei Zhao
ARCQuant: Boosting NVFP4 Quantization with Augmented Residual Channels for LLMs
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The emergence of fine-grained numerical formats like NVFP4 presents new opportunities for efficient Large Language Model (LLM) inference. However, it is difficult to adapt existing Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) strategies to these formats: rotation-based methods compromise fine-grained block isolation; smoothing techniques struggle with significant 4-bit quantization errors; and mixed-precision approaches often conflict with hardware constraints on unified-precision computation. To address these challenges, we propose ARCQuant, a framework that boosts NVFP4 performance via Augmented Residual Channels. Distinct from methods that compromise block isolation or hardware uniformity, ARCQuant maintains a strictly unified NVFP4 format by augmenting the activation matrix with quantized residual channels. This design integrates the error compensation process directly into the matrix reduction dimension, enabling the use of standard, highly optimized GEMM kernels with minimal overhead. Theoretical analysis confirms that the worst-case error bound of our dual-stage NVFP4 quantization is comparable to that of standard 8-bit formats such as MXFP8. Extensive experiments on LLaMA and Qwen models demonstrate that ARCQuant achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, comparable to full-precision baselines in perplexity and downstream tasks. Furthermore, deployment on RTX 5090 and RTX PRO 6000 GPUs confirms practical benefits, achieving up to 3x speedup over FP16. Our code is available at https://github.com/actypedef/ARCQuant .
Joint Beam Scheduling and Beamforming Design for Cooperative Positioning in Multi-beam LEO Satellite Networks
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:Cooperative positioning with multiple low earth orbit (LEO) satellites is promising in providing location-based services and enhancing satellite-terrestrial communication. However, positioning accuracy is greatly affected by inter-beam interference and satellite-terrestrial topology geometry. To select the best combination of satellites from visible ones and suppress inter-beam interference, this paper explores the utilization of flexible beam scheduling and beamforming of multi-beam LEO satellites that can adjust beam directions toward the same earth-fixed cell to send positioning signals simultaneously. By leveraging Cram\'{e}r-Rao lower bound (CRLB) to characterize user Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) positioning accuracy, the concerned problem is formulated, aiming at optimizing user positioning accuracy under beam scheduling and beam transmission power constraints. To deal with the mixed-integer-nonconvex problem, we decompose it into an inner beamforming design problem and an outer beam scheduling problem. For the former, we first prove the monotonic relationship between user positioning accuracy and its perceived signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) to reformulate the problem, and then semidefinite relaxation (SDR) is adopted for beamforming design. For the outer problem, a heuristic low-complexity beam scheduling scheme is proposed, whose core idea is to schedule users with lower channel correlation to mitigate inter-beam interference while seeking a proper satellite-terrestrial topology geometry. Simulation results verify the superior positioning performance of our proposed positioning-oriented beamforming and beam scheduling scheme, and it is shown that average user positioning accuracy is improved by $17.1\%$ and $55.9\%$ when the beam transmission power is 20 dBw, compared to conventional beamforming and beam scheduling schemes, respectively.
Analyzing the Adoption Challenges of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart Cities in China
Apr 22, 2022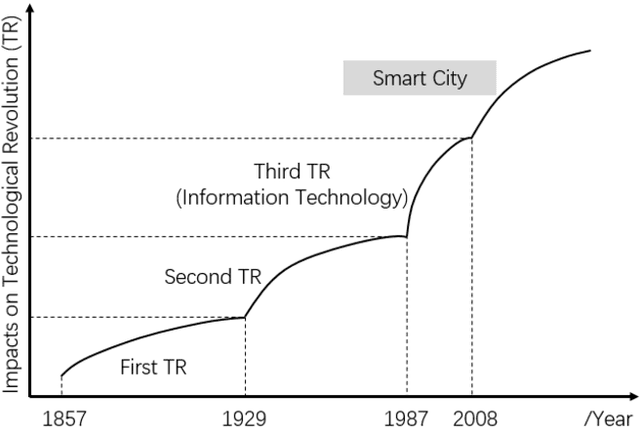
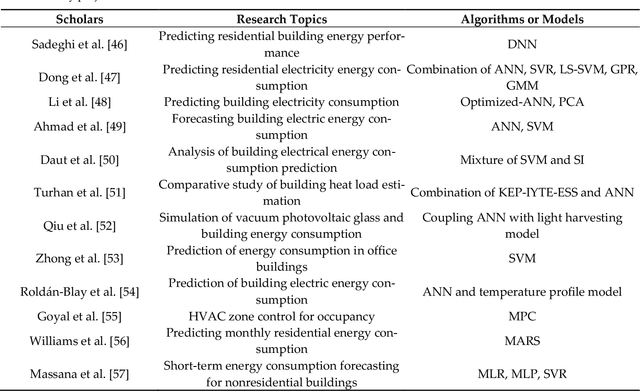
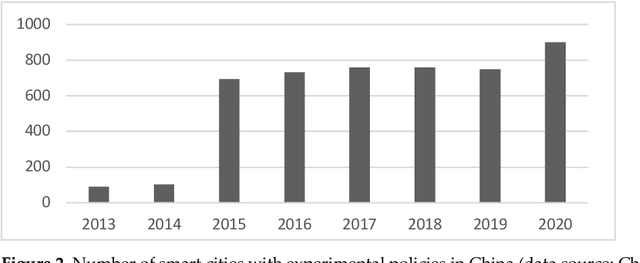
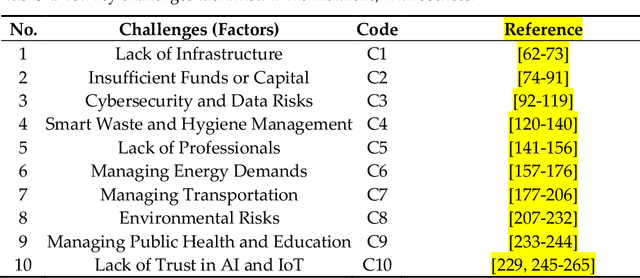
Abstract:Smart cities play a vital role in the growth of a nation. In recent years, several countries have made huge investments in developing smart cities to offer sustainable living. However, there are some challenges to overcome in smart city development, such as traffic and transportation man-agement, energy and water distribution and management, air quality and waste management monitoring, etc. The capabilities of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) can help to achieve some goals of smart cities, and there are proven examples from some cities like Singapore, Copenhagen, etc. However, the adoption of AI and the IoT in developing countries has some challenges. The analysis of challenges hindering the adoption of AI and the IoT are very limited. This study aims to fill this research gap by analyzing the causal relationships among the challenges in smart city development, and contains several parts that conclude the previous scholars work, as well as independent research and investigation, such as data collection and analysis based on DEMATEL. In this paper, we have reviewed the literature to extract key chal-lenges for the adoption of AI and the IoT. These helped us to proceed with the investigation and analyze the adoption status. Therefore, using the PRISMA method, 10 challenges were identified from the literature review. Subsequently, determination of the causal inter-relationships among the key challenges based on expert opinions using DEMATEL is performed. This study explored the driving and dependent power of the challenges, and causal relationships between the barriers were established.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge