Xudong Dai
Image-text Retrieval via Preserving Main Semantics of Vision
Apr 28, 2023



Abstract:Image-text retrieval is one of the major tasks of cross-modal retrieval. Several approaches for this task map images and texts into a common space to create correspondences between the two modalities. However, due to the content (semantics) richness of an image, redundant secondary information in an image may cause false matches. To address this issue, this paper presents a semantic optimization approach, implemented as a Visual Semantic Loss (VSL), to assist the model in focusing on an image's main content. This approach is inspired by how people typically annotate the content of an image by describing its main content. Thus, we leverage the annotated texts corresponding to an image to assist the model in capturing the main content of the image, reducing the negative impact of secondary content. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets (MSCOCO and Flickr30K) demonstrate the superior performance of our method. The code is available at: https://github.com/ZhangXu0963/VSL.
Information Sieve: Content Leakage Reduction in End-to-End Prosody For Expressive Speech Synthesis
Aug 04, 2021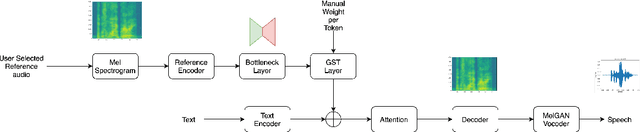
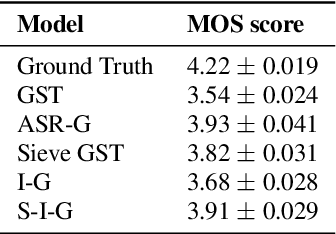
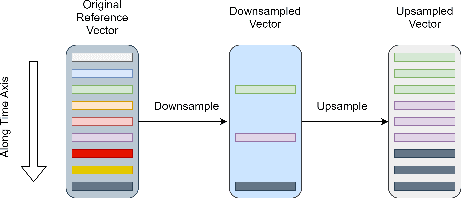

Abstract:Expressive neural text-to-speech (TTS) systems incorporate a style encoder to learn a latent embedding as the style information. However, this embedding process may encode redundant textual information. This phenomenon is called content leakage. Researchers have attempted to resolve this problem by adding an ASR or other auxiliary supervision loss functions. In this study, we propose an unsupervised method called the "information sieve" to reduce the effect of content leakage in prosody transfer. The rationale of this approach is that the style encoder can be forced to focus on style information rather than on textual information contained in the reference speech by a well-designed downsample-upsample filter, i.e., the extracted style embeddings can be downsampled at a certain interval and then upsampled by duplication. Furthermore, we used instance normalization in convolution layers to help the system learn a better latent style space. Objective metrics such as the significantly lower word error rate (WER) demonstrate the effectiveness of this model in mitigating content leakage. Listening tests indicate that the model retains its prosody transferability compared with the baseline models such as the original GST-Tacotron and ASR-guided Tacotron.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge