Xu-Ri Yao
Parallel compressive super-resolution imaging with wide field-of-view based on physics enhanced network
Oct 20, 2023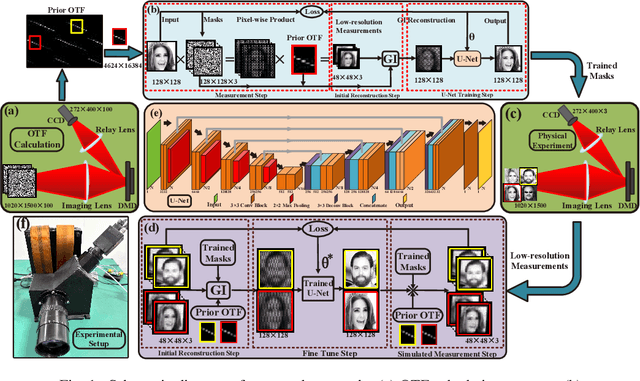
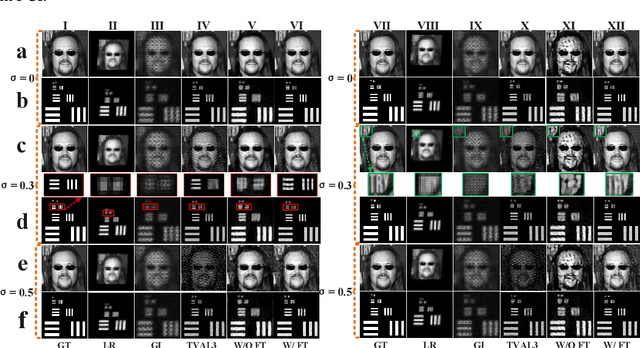

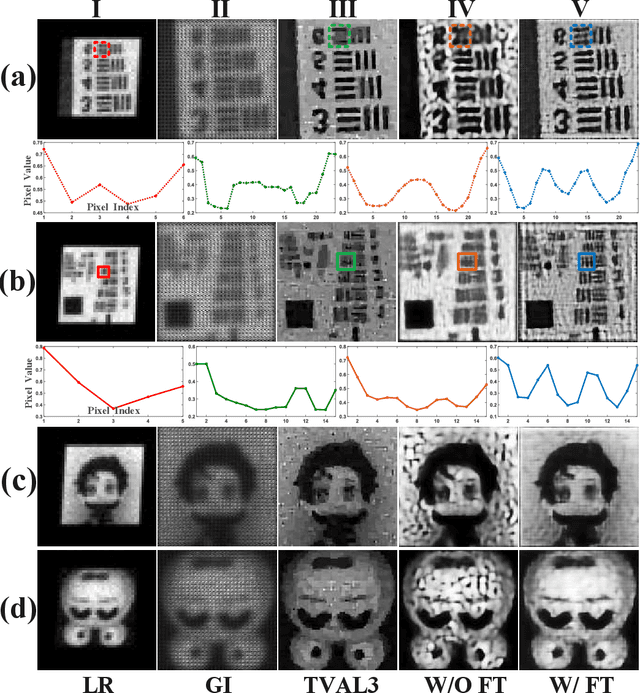
Abstract:Achieving both high-performance and wide field-of-view (FOV) super-resolution imaging has been attracting increasing attention in recent years. However, such goal suffers from long reconstruction time and huge storage space. Parallel compressive imaging (PCI) provides an efficient solution, but the super-resolution quality and imaging speed are strongly dependent on precise optical transfer function (OTF), modulation masks and reconstruction algorithm. In this work, we propose a wide FOV parallel compressive super-resolution imaging approach based on physics enhanced network. By training the network with the prior OTF of an arbitrary 128x128-pixel region and fine-tuning the network with other OTFs within rest regions of FOV, we realize both mask optimization and super-resolution imaging with up to 1020x1500 wide FOV. Numerical simulations and practical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed approach. We achieve high-quality reconstruction with 4x4 times super-resolution enhancement using only three designed masks to reach real-time imaging speed. The proposed approach promotes the technology of rapid imaging for super-resolution and wide FOV, ranging from infrared to Terahertz.
Efficient phase retrieval based on dark fringe recognition with an ability of bypassing invalid fringes
Dec 14, 2016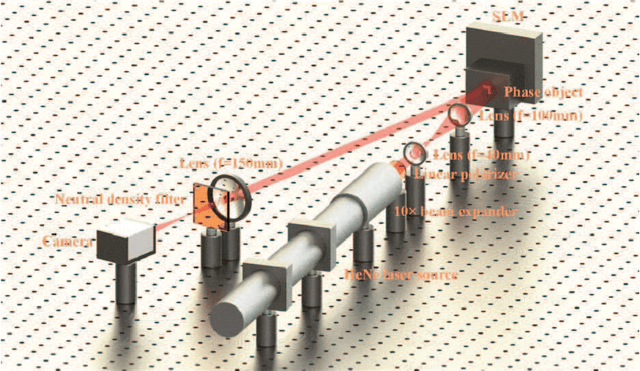
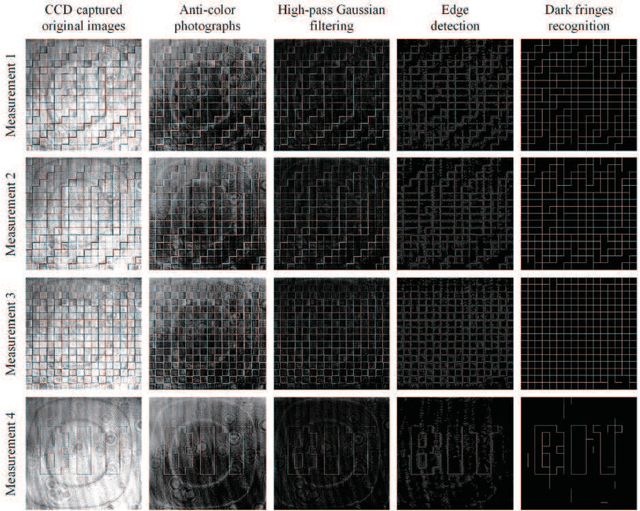
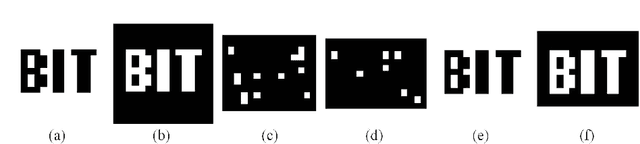
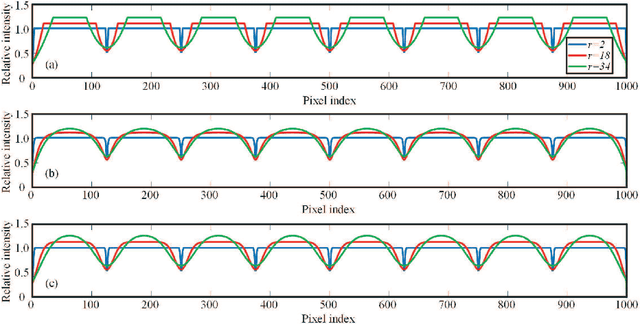
Abstract:This paper discusses the noisy phase retrieval problem: recovering a complex image signal with independent noise from quadratic measurements. Inspired by the dark fringes shown in the measured images of the array detector, a novel phase retrieval approach is proposed and demonstrated both theoretically and experimentally to recognize the dark fringes and bypass the invalid fringes. A more accurate relative phase ratio between arbitrary two pixels is achieved by calculating the multiplicative ratios (or the sum of phase difference) on the path between them. Then the object phase image can be reconstructed precisely. Our approach is a good choice for retrieving high-quality phase images from noisy signals and has many potential applications in the fields such as X-ray crystallography, diffractive imaging, and so on.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge