Xiuxiu Qiu
USD: Unsupervised Soft Contrastive Learning for Fault Detection in Multivariate Time Series
May 25, 2024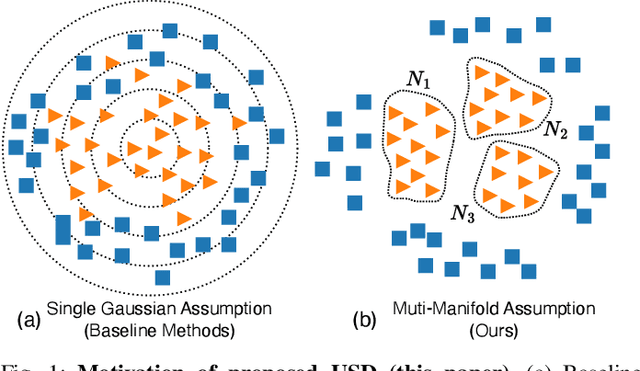
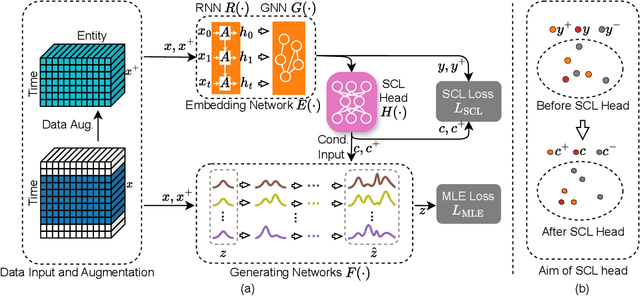
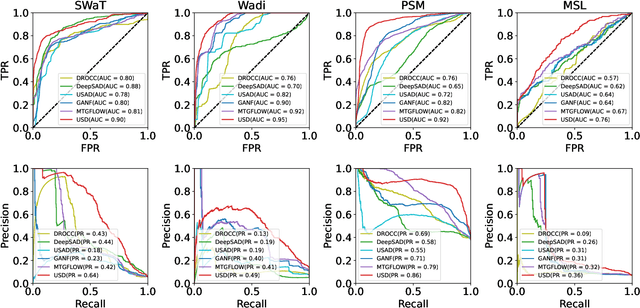
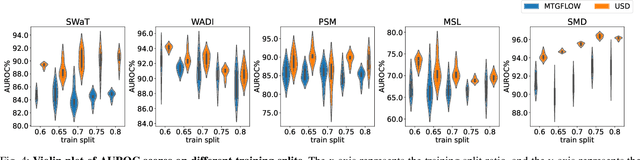
Abstract:Unsupervised fault detection in multivariate time series is critical for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of complex systems, with current methodologies largely focusing on statistical and machine learning techniques. However, these approaches often rest on the assumption that data distributions conform to Gaussian models, overlooking the diversity of patterns that can manifest in both normal and abnormal states, thereby diminishing discriminative performance. Our innovation addresses this limitation by introducing a combination of data augmentation and soft contrastive learning, specifically designed to capture the multifaceted nature of state behaviors more accurately. The data augmentation process enriches the dataset with varied representations of normal states, while soft contrastive learning fine-tunes the model's sensitivity to the subtle differences between normal and abnormal patterns, enabling it to recognize a broader spectrum of anomalies. This dual strategy significantly boosts the model's ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal states, leading to a marked improvement in fault detection performance across multiple datasets and settings, thereby setting a new benchmark for unsupervised fault detection in complex systems. The code of our method is available at \url{https://github.com/zangzelin/code_USD.git}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge