Xinxin Di
A Deep Bayesian Neural Network for Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification with Rejection from ECG Recordings
Feb 26, 2022

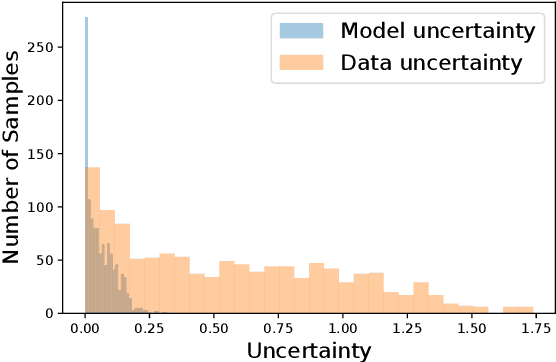
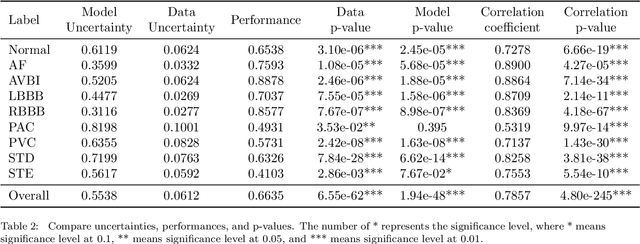
Abstract:With the development of deep learning-based methods, automated classification of electrocardiograms (ECGs) has recently gained much attention. Although the effectiveness of deep neural networks has been encouraging, the lack of information given by the outputs restricts clinicians' reexamination. If the uncertainty estimation comes along with the classification results, cardiologists can pay more attention to "uncertain" cases. Our study aims to classify ECGs with rejection based on data uncertainty and model uncertainty. We perform experiments on a real-world 12-lead ECG dataset. First, we estimate uncertainties using the Monte Carlo dropout for each classification prediction, based on our Bayesian neural network. Then, we accept predictions with uncertainty under a given threshold and provide "uncertain" cases for clinicians. Furthermore, we perform a simulation experiment using varying thresholds. Finally, with the help of a clinician, we conduct case studies to explain the results of large uncertainties and incorrect predictions with small uncertainties. The results show that correct predictions are more likely to have smaller uncertainties, and the performance on accepted predictions improves as the accepting ratio decreases (i.e. more rejections). Case studies also help explain why rejection can improve the performance. Our study helps neural networks produce more accurate results and provide information on uncertainties to better assist clinicians in the diagnosis process. It can also enable deep-learning-based ECG interpretation in clinical implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge