Xinlin Chen
Deep learning EPI-TIRF cross-modality enables background subtraction and axial super-resolution for widefield fluorescence microscopy
Nov 10, 2025


Abstract:The resolving ability of wide-field fluorescence microscopy is fundamentally limited by out-of-focus background owing to its low axial resolution, particularly for densely labeled biological samples. To address this, we developed ET2dNet, a deep learning-based EPI-TIRF cross-modality network that achieves TIRF-comparable background subtraction and axial super-resolution from a single wide-field image without requiring hardware modifications. The model employs a physics-informed hybrid architecture, synergizing supervised learning with registered EPI-TIRF image pairs and self-supervised physical modeling via convolution with the point spread function. This framework ensures exceptional generalization across microscope objectives, enabling few-shot adaptation to new imaging setups. Rigorous validation on cellular and tissue samples confirms ET2dNet's superiority in background suppression and axial resolution enhancement, while maintaining compatibility with deconvolution techniques for lateral resolution improvement. Furthermore, by extending this paradigm through knowledge distillation, we developed ET3dNet, a dedicated three-dimensional reconstruction network that produces artifact-reduced volumetric results. ET3dNet effectively removes out-of-focus background signals even when the input image stack lacks the source of background. This framework makes axial super-resolution imaging more accessible by providing an easy-to-deploy algorithm that avoids additional hardware costs and complexity, showing great potential for live cell studies and clinical histopathology.
G2PDiffusion: Genotype-to-Phenotype Prediction with Diffusion Models
Feb 07, 2025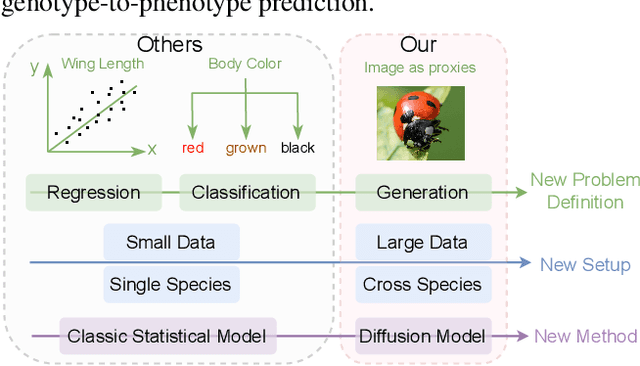
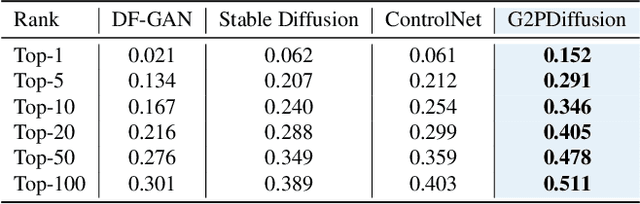
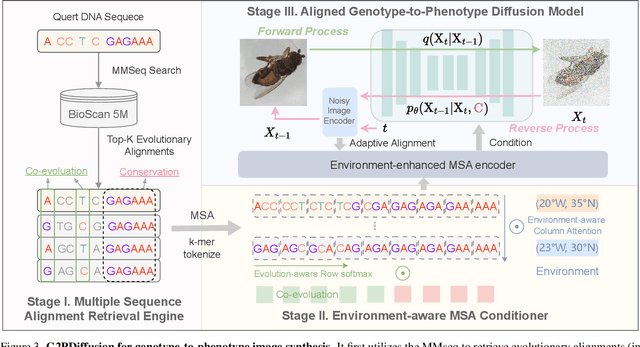
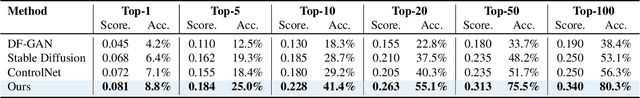
Abstract:Discovering the genotype-phenotype relationship is crucial for genetic engineering, which will facilitate advances in fields such as crop breeding, conservation biology, and personalized medicine. Current research usually focuses on single species and small datasets due to limitations in phenotypic data collection, especially for traits that require visual assessments or physical measurements. Deciphering complex and composite phenotypes, such as morphology, from genetic data at scale remains an open question. To break through traditional generic models that rely on simplified assumptions, this paper introduces G2PDiffusion, the first-of-its-kind diffusion model designed for genotype-to-phenotype generation across multiple species. Specifically, we use images to represent morphological phenotypes across species and redefine phenotype prediction as conditional image generation. To this end, this paper introduces an environment-enhanced DNA sequence conditioner and trains a stable diffusion model with a novel alignment method to improve genotype-to-phenotype consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach enhances phenotype prediction accuracy across species, capturing subtle genetic variations that contribute to observable traits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge