Xiaoqing Lyu
TGG: Transferable Graph Generation for Zero-shot and Few-shot Learning
Aug 30, 2019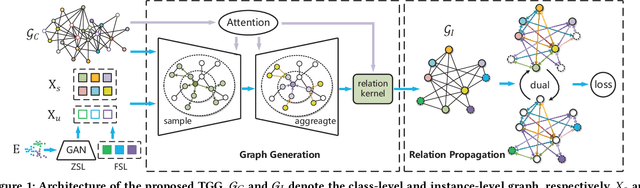
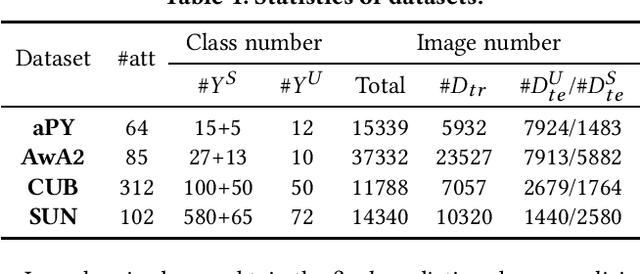
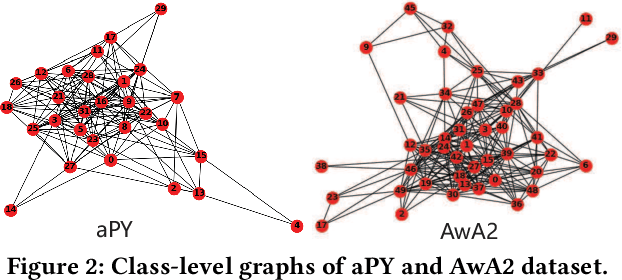
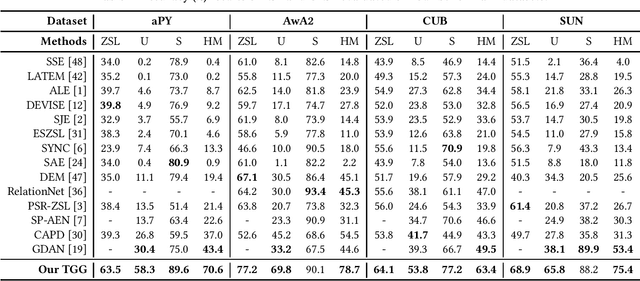
Abstract:Zero-shot and few-shot learning aim to improve generalization to unseen concepts, which are promising in many realistic scenarios. Due to the lack of data in unseen domain, relation modeling between seen and unseen domains is vital for knowledge transfer in these tasks. Most existing methods capture seen-unseen relation implicitly via semantic embedding or feature generation, resulting in inadequate use of relation and some issues remain (e.g. domain shift). To tackle these challenges, we propose a Transferable Graph Generation (TGG) approach, in which the relation is modeled and utilized explicitly via graph generation. Specifically, our proposed TGG contains two main components: (1) Graph generation for relation modeling. An attention-based aggregate network and a relation kernel are proposed, which generate instance-level graph based on a class-level prototype graph and visual features. Proximity information aggregating is guided by a multi-head graph attention mechanism, where seen and unseen features synthesized by GAN are revised as node embeddings. The relation kernel further generates edges with GCN and graph kernel method, to capture instance-level topological structure while tackling data imbalance and noise. (2) Relation propagation for relation utilization. A dual relation propagation approach is proposed, where relations captured by the generated graph are separately propagated from the seen and unseen subgraphs. The two propagations learn from each other in a dual learning fashion, which performs as an adaptation way for mitigating domain shift. All components are jointly optimized with a meta-learning strategy, and our TGG acts as an end-to-end framework unifying conventional zero-shot, generalized zero-shot and few-shot learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that it consistently surpasses existing methods of the above three fields by a significant margin.
Graph Attribute Aggregation Network with Progressive Margin Folding
May 14, 2019



Abstract:Graph convolutional neural networks (GCNNs) have been attracting increasing research attention due to its great potential in inference over graph structures. However, insufficient effort has been devoted to the aggregation methods between different convolution graph layers. In this paper, we introduce a graph attribute aggregation network (GAAN) architecture. Different from the conventional pooling operations, a graph-transformation-based aggregation strategy, progressive margin folding, PMF, is proposed for integrating graph features. By distinguishing internal and margin elements, we provide an approach for implementing the folding iteratively. And a mechanism is also devised for preserving the local structures during progressively folding. In addition, a hypergraph-based representation is introduced for transferring the aggregated information between different layers. Our experiments applied to the public molecule datasets demonstrate that the proposed GAAN outperforms the existing GCNN models with significant effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge