Xiaonan Qi
Attentional Graph Convolutional Network for Structure-aware Audio-Visual Scene Classification
Dec 31, 2022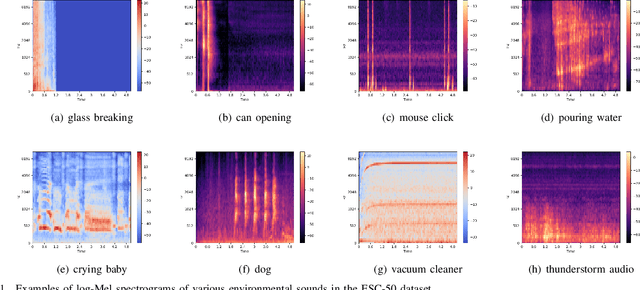
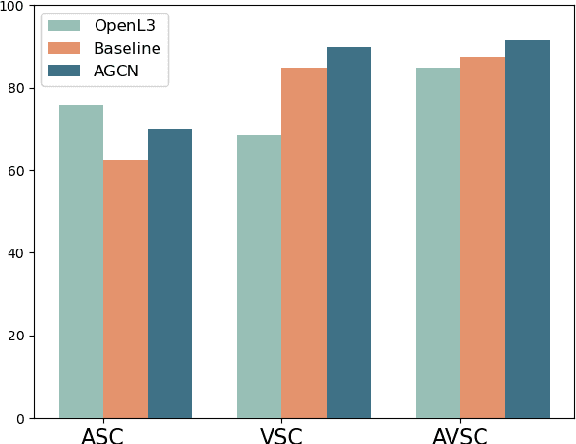
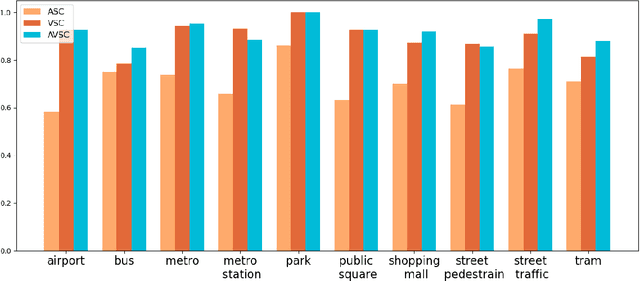
Abstract:Audio-Visual scene understanding is a challenging problem due to the unstructured spatial-temporal relations that exist in the audio signals and spatial layouts of different objects and various texture patterns in the visual images. Recently, many studies have focused on abstracting features from convolutional neural networks while the learning of explicit semantically relevant frames of sound signals and visual images has been overlooked. To this end, we present an end-to-end framework, namely attentional graph convolutional network (AGCN), for structure-aware audio-visual scene representation. First, the spectrogram of sound and input image is processed by a backbone network for feature extraction. Then, to build multi-scale hierarchical information of input features, we utilize an attention fusion mechanism to aggregate features from multiple layers of the backbone network. Notably, to well represent the salient regions and contextual information of audio-visual inputs, the salient acoustic graph (SAG) and contextual acoustic graph (CAG), salient visual graph (SVG), and contextual visual graph (CVG) are constructed for the audio-visual scene representation. Finally, the constructed graphs pass through a graph convolutional network for structure-aware audio-visual scene recognition. Extensive experimental results on the audio, visual and audio-visual scene recognition datasets show that promising results have been achieved by the AGCN methods. Visualizing graphs on the spectrograms and images have been presented to show the effectiveness of proposed CAG/SAG and CVG/SVG that could focus on the salient and semantic relevant regions.
Feature Pyramid Attention based Residual Neural Network for Environmental Sound Classification
May 28, 2022



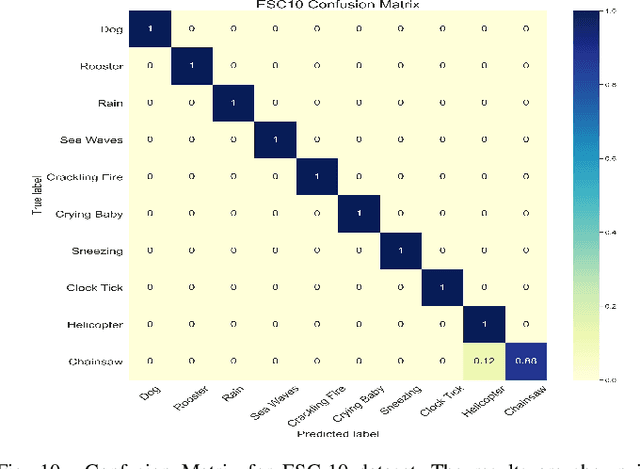
Abstract:Environmental sound classification (ESC) is a challenging problem due to the unstructured spatial-temporal relations that exist in the sound signals. Recently, many studies have focused on abstracting features from convolutional neural networks while the learning of semantically relevant frames of sound signals has been overlooked. To this end, we present an end-to-end framework, namely feature pyramid attention network (FPAM), focusing on abstracting the semantically relevant features for ESC. We first extract the feature maps of the preprocessed spectrogram of the sound waveform by a backbone network. Then, to build multi-scale hierarchical features of sound spectrograms, we construct a feature pyramid representation of the sound spectrograms by aggregating the feature maps from multi-scale layers, where the temporal frames and spatial locations of semantically relevant frames are localized by FPAM. Specifically, the multiple features are first processed by a dimension alignment module. Afterward, the pyramid spatial attention module (PSA) is attached to localize the important frequency regions spatially with a spatial attention module (SAM). Last, the processed feature maps are refined by a pyramid channel attention (PCA) to localize the important temporal frames. To justify the effectiveness of the proposed FPAM, visualization of attention maps on the spectrograms has been presented. The visualization results show that FPAM can focus more on the semantic relevant regions while neglecting the noises. The effectiveness of the proposed methods is validated on two widely used ESC datasets: the ESC-50 and ESC-10 datasets. The experimental results show that the FPAM yields comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods. A substantial performance increase has been achieved by FPAM compared with the baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge