Xiaocheng Zhou
Barycode-based GJK Algorithm
Nov 18, 2020
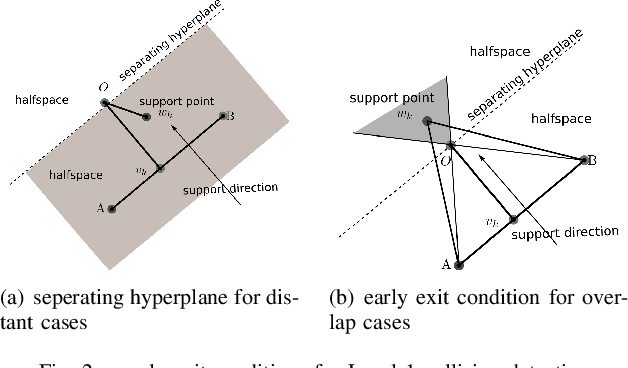

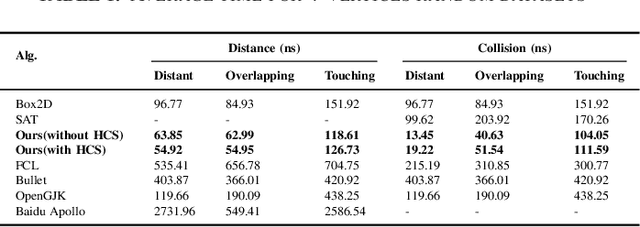
Abstract:In this paper, we present a more efficient GJK algorithm to solve the collision detection and distance query problems in 2D. We contribute in two aspects: First, we propose a new barycode-based sub-distance algorithm that does not only provide a simple and unified condition to determine the minimum simplex but also improve the efficiency in distant, touching, and overlap cases in distance query. Second, we provide a highly efficient implementation subroutine for collision detection by optimizing the exit conditions of our GJK distance algorithm, which shows dramatic improvements in run-time for applications that only need binary results. We benchmark our methods along with that of the well-known open-source collision detection libraries, such as Bullet, FCL, OpenGJK, Box2D, and Apollo over a range of random datasets. The results indicate that our methods and implementations outperform the state-of-the-art in both collision detection and distance query.
Learning Discriminative 3D Shape Representations by View Discerning Networks
Aug 20, 2018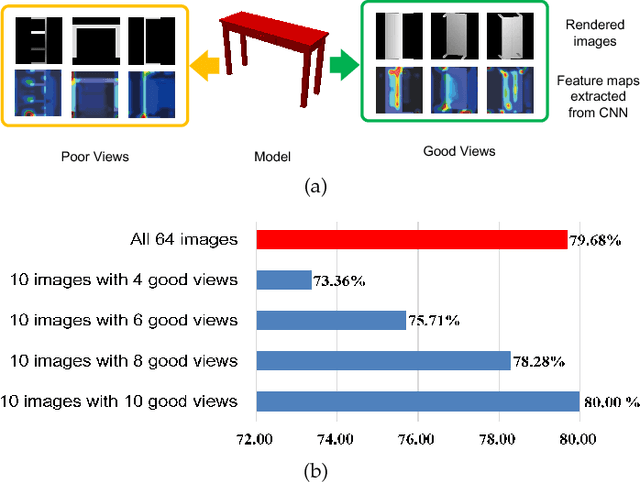

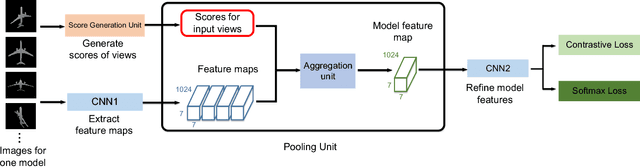

Abstract:In view-based 3D shape recognition, extracting discriminative visual representation of 3D shapes from projected images is considered the core problem. Projections with low discriminative ability can adversely influence the final 3D shape representation. Especially under the real situations with background clutter and object occlusion, the adverse effect is even more severe. To resolve this problem, we propose a novel deep neural network, View Discerning Network, which learns to judge the quality of views and adjust their contributions to the representation of shapes. In this network, a Score Generation Unit is devised to evaluate the quality of each projected image with score vectors. These score vectors are used to weight the image features and the weighted features perform much better than original features in 3D shape recognition task. In particular, we introduce two structures of Score Generation Unit, Channel-wise Score Unit and Part-wise Score Unit, to assess the quality of feature maps from different perspectives. Our network aggregates features and scores in an end-to-end framework, so that final shape descriptors are directly obtained from its output. Our experiments on ModelNet and ShapeNet Core55 show that View Discerning Network outperforms the state-of-the-arts in terms of the retrieval task, with excellent robustness against background clutter and object occlusion.
* Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics. Corresponding Author: Kai Xu (kevin.kai.xu@gmail.com)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge