Xianghua Chu
A Feature Transfer Enabled Multi-Task Deep Learning Model on Medical Imaging
Jun 05, 2019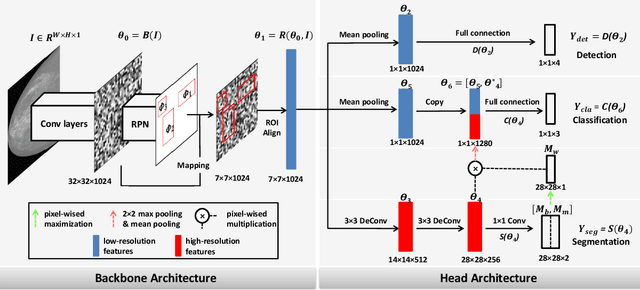
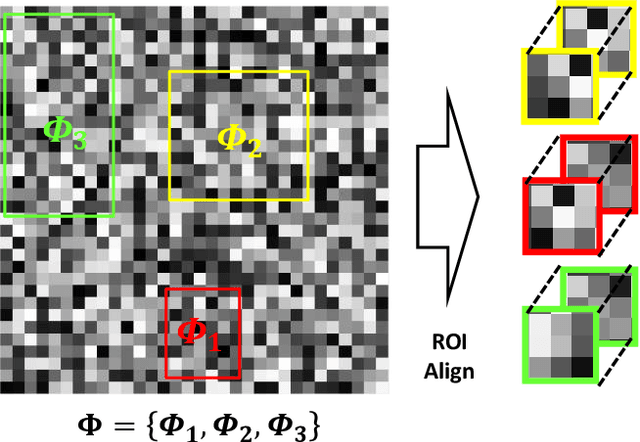
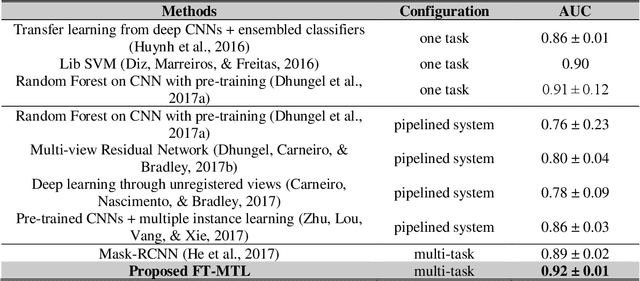
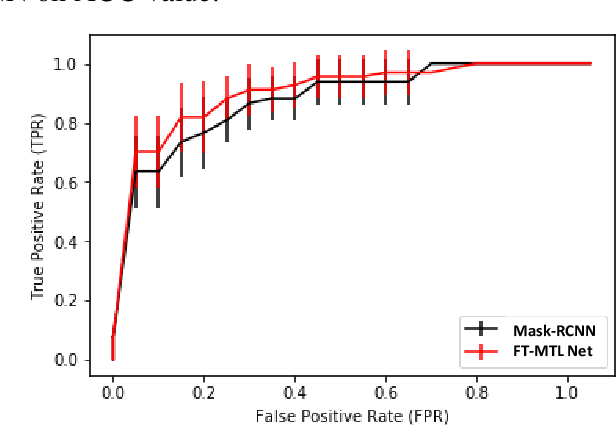
Abstract:Object detection, segmentation and classification are three common tasks in medical image analysis. Multi-task deep learning (MTL) tackles these three tasks jointly, which provides several advantages saving computing time and resources and improving robustness against overfitting. However, existing multitask deep models start with each task as an individual task and integrate parallelly conducted tasks at the end of the architecture with one cost function. Such architecture fails to take advantage of the combined power of the features from each individual task at an early stage of the training. In this research, we propose a new architecture, FTMTLNet, an MTL enabled by feature transferring. Traditional transfer learning deals with the same or similar task from different data sources (a.k.a. domain). The underlying assumption is that the knowledge gained from source domains may help the learning task on the target domain. Our proposed FTMTLNet utilizes the different tasks from the same domain. Considering features from the tasks are different views of the domain, the combined feature maps can be well exploited using knowledge from multiple views to enhance the generalizability. To evaluate the validity of the proposed approach, FTMTLNet is compared with models from literature including 8 classification models, 4 detection models and 3 segmentation models using a public full field digital mammogram dataset for breast cancer diagnosis. Experimental results show that the proposed FTMTLNet outperforms the competing models in classification and detection and has comparable results in segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge