Xavier Sevillano
A 3D Facial Reconstruction Evaluation Methodology: Comparing Smartphone Scans with Deep Learning Based Methods Using Geometry and Morphometry Criteria
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Three-dimensional (3D) facial shape analysis has gained interest due to its potential clinical applications. However, the high cost of advanced 3D facial acquisition systems limits their widespread use, driving the development of low-cost acquisition and reconstruction methods. This study introduces a novel evaluation methodology that goes beyond traditional geometry-based benchmarks by integrating morphometric shape analysis techniques, providing a statistical framework for assessing facial morphology preservation. As a case study, we compare smartphone-based 3D scans with state-of-the-art deep learning reconstruction methods from 2D images, using high-end stereophotogrammetry models as ground truth. This methodology enables a quantitative assessment of global and local shape differences, offering a biologically meaningful validation approach for low-cost 3D facial acquisition and reconstruction techniques.
BioFace3D: A fully automatic pipeline for facial biomarkers extraction of 3D face reconstructions segmented from MRI
Oct 01, 2024Abstract:Facial dysmorphologies have emerged as potential critical indicators in the diagnosis and prognosis of genetic, psychotic and rare disorders. While in certain conditions these dysmorphologies are severe, in other cases may be subtle and not perceivable to the human eye, requiring precise quantitative tools for their identification. Manual coding of facial dysmorphologies is a burdensome task and is subject to inter- and intra-observer variability. To overcome this gap, we present BioFace3D as a fully automatic tool for the calculation of facial biomarkers using facial models reconstructed from magnetic resonance images. The tool is divided into three automatic modules for the extraction of 3D facial models from magnetic resonance images, the registration of homologous 3D landmarks encoding facial morphology, and the calculation of facial biomarkers from anatomical landmarks coordinates using geometric morphometrics techniques.
Western Mediterranean wetlands bird species classification: evaluating small-footprint deep learning approaches on a new annotated dataset
Jul 12, 2022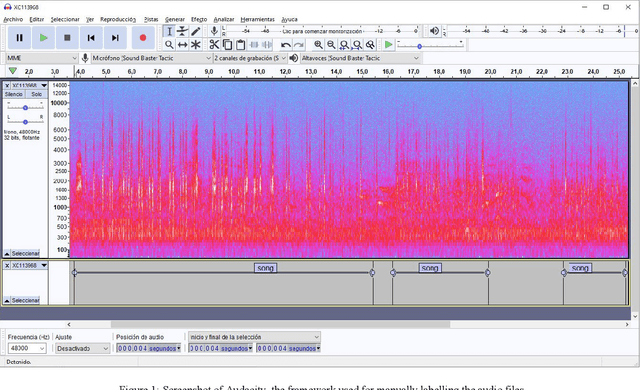
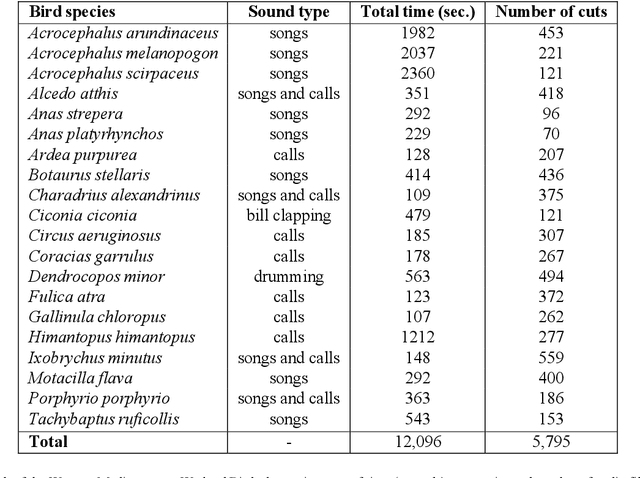
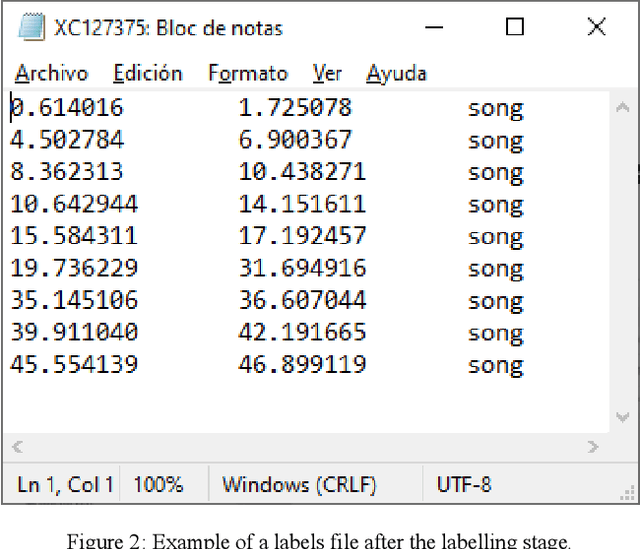
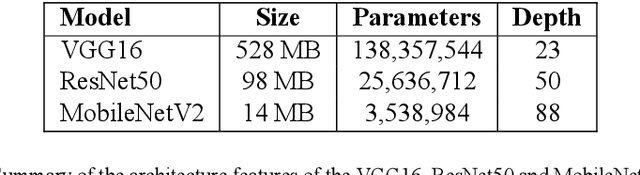
Abstract:The deployment of an expert system running over a wireless acoustic sensors network made up of bioacoustic monitoring devices that recognise bird species from their sounds would enable the automation of many tasks of ecological value, including the analysis of bird population composition or the detection of endangered species in areas of environmental interest. Endowing these devices with accurate audio classification capabilities is possible thanks to the latest advances in artificial intelligence, among which deep learning techniques excel. However, a key issue to make bioacoustic devices affordable is the use of small footprint deep neural networks that can be embedded in resource and battery constrained hardware platforms. For this reason, this work presents a critical comparative analysis between two heavy and large footprint deep neural networks (VGG16 and ResNet50) and a lightweight alternative, MobileNetV2. Our experimental results reveal that MobileNetV2 achieves an average F1-score less than a 5\% lower than ResNet50 (0.789 vs. 0.834), performing better than VGG16 with a footprint size nearly 40 times smaller. Moreover, to compare the models, we have created and made public the Western Mediterranean Wetland Birds dataset, consisting of 201.6 minutes and 5,795 audio excerpts of 20 endemic bird species of the Aiguamolls de l'Empord\`a Natural Park.
Guiding GANs: How to control non-conditional pre-trained GANs for conditional image generation
Jan 04, 2021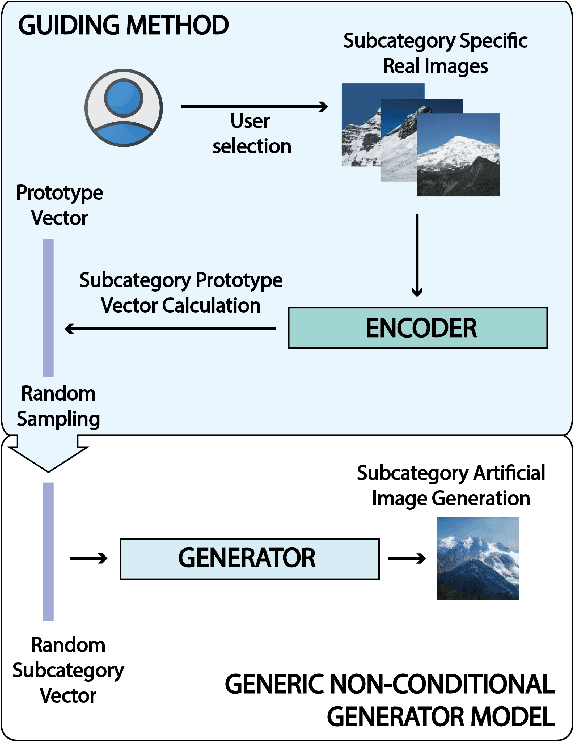
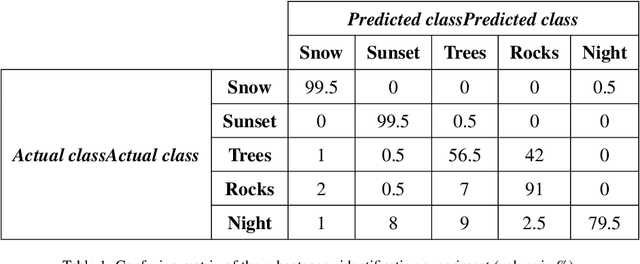
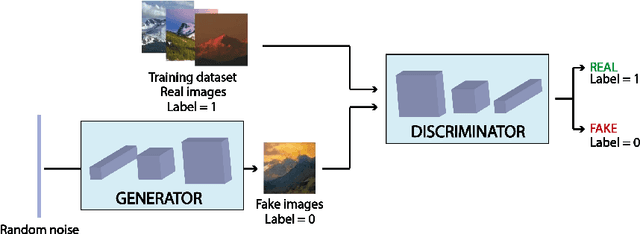
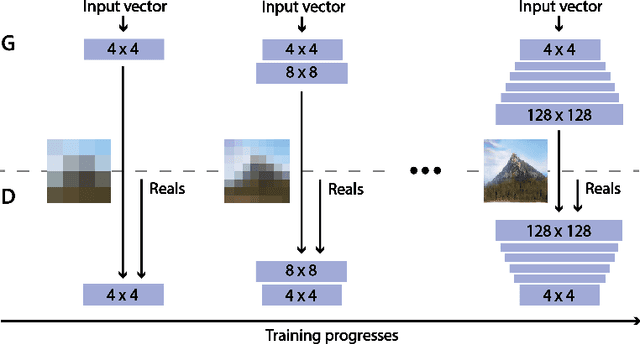
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are an arrange of two neural networks -- the generator and the discriminator -- that are jointly trained to generate artificial data, such as images, from random inputs. The quality of these generated images has recently reached such levels that can often lead both machines and humans into mistaking fake for real examples. However, the process performed by the generator of the GAN has some limitations when we want to condition the network to generate images from subcategories of a specific class. Some recent approaches tackle this \textit{conditional generation} by introducing extra information prior to the training process, such as image semantic segmentation or textual descriptions. While successful, these techniques still require defining beforehand the desired subcategories and collecting large labeled image datasets representing them to train the GAN from scratch. In this paper we present a novel and alternative method for guiding generic non-conditional GANs to behave as conditional GANs. Instead of re-training the GAN, our approach adds into the mix an encoder network to generate the high-dimensional random input vectors that are fed to the generator network of a non-conditional GAN to make it generate images from a specific subcategory. In our experiments, when compared to training a conditional GAN from scratch, our guided GAN is able to generate artificial images of perceived quality comparable to that of non-conditional GANs after training the encoder on just a few hundreds of images, which substantially accelerates the process and enables adding new subcategories seamlessly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge