Wonkyo Choe
RWKV-edge: Deeply Compressed RWKV for Resource-Constrained Devices
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:To deploy LLMs on resource-contained platforms such as mobile robotics and wearables, non-transformers LLMs have achieved major breakthroughs. Recently, a novel RNN-based LLM family, Repentance Weighted Key Value (RWKV) models have shown promising results in text generation on resource-constrained devices thanks to their computational efficiency. However, these models remain too large to be deployed on embedded devices due to their high parameter count. In this paper, we propose an efficient suite of compression techniques, tailored to the RWKV architecture. These techniques include low-rank approximation, sparsity predictors, and clustering head, designed to align with the model size. Our methods compress the RWKV models by 4.95--3.8x with only 2.95pp loss in accuracy.
Efficient NLP Inference at the Edge via Elastic Pipelining
Jul 12, 2022

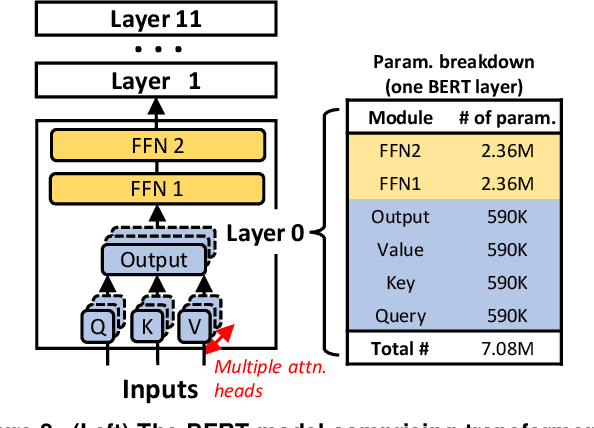

Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) inference is seeing increasing adoption by mobile applications, where on-device inference is desirable for crucially preserving user data privacy and avoiding network roundtrips. Yet, the unprecedented size of an NLP model stresses both latency and memory, the two key resources of a mobile device. To meet a target latency, holding the whole model in memory launches execution as soon as possible but increases one app's memory footprints by several times, limiting its benefits to only a few inferences before being recycled by mobile memory management. On the other hand, loading the model from storage on demand incurs a few seconds long IO, far exceeding the delay range satisfying to a user; pipelining layerwise model loading and execution does not hide IO either, due to the large skewness between IO and computation delays. To this end, we propose WRX. Built on the key idea of maximizing IO/compute resource utilization on the most important parts of a model, WRX reconciles the latency/memory tension via two novel techniques. First, model sharding. WRX manages model parameters as independently tunable shards and profiles their importance to accuracy. Second, elastic pipeline planning with a preload buffer. WRX instantiates an IO/computation pipeline and uses a small buffer for preload shards to bootstrap execution without stalling in early stages; it judiciously selects, tunes, and assembles shards per their importance for resource-elastic execution, which maximizes inference accuracy. Atop two commodity SoCs, we build WRX and evaluate it against a wide range of NLP tasks, under a practical range of target latencies, and on both CPU and GPU. We demonstrate that, WRX delivers high accuracies with 1--2 orders of magnitude lower memory, outperforming competitive baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge