Wonjun Kim
Konkuk University
DropGaussian: Structural Regularization for Sparse-view Gaussian Splatting
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:Recently, 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has gained considerable attentions in the field of novel view synthesis due to its fast performance while yielding the excellent image quality. However, 3DGS in sparse-view settings (e.g., three-view inputs) often faces with the problem of overfitting to training views, which significantly drops the visual quality of novel view images. Many existing approaches have tackled this issue by using strong priors, such as 2D generative contextual information and external depth signals. In contrast, this paper introduces a prior-free method, so-called DropGaussian, with simple changes in 3D Gaussian splatting. Specifically, we randomly remove Gaussians during the training process in a similar way of dropout, which allows non-excluded Gaussians to have larger gradients while improving their visibility. This makes the remaining Gaussians to contribute more to the optimization process for rendering with sparse input views. Such simple operation effectively alleviates the overfitting problem and enhances the quality of novel view synthesis. By simply applying DropGaussian to the original 3DGS framework, we can achieve the competitive performance with existing prior-based 3DGS methods in sparse-view settings of benchmark datasets without any additional complexity. The code and model are publicly available at: https://github.com/DCVL-3D/DropGaussian release.
Sampling is Matter: Point-guided 3D Human Mesh Reconstruction
Apr 19, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a simple yet powerful method for 3D human mesh reconstruction from a single RGB image. Most recently, the non-local interactions of the whole mesh vertices have been effectively estimated in the transformer while the relationship between body parts also has begun to be handled via the graph model. Even though those approaches have shown the remarkable progress in 3D human mesh reconstruction, it is still difficult to directly infer the relationship between features, which are encoded from the 2D input image, and 3D coordinates of each vertex. To resolve this problem, we propose to design a simple feature sampling scheme. The key idea is to sample features in the embedded space by following the guide of points, which are estimated as projection results of 3D mesh vertices (i.e., ground truth). This helps the model to concentrate more on vertex-relevant features in the 2D space, thus leading to the reconstruction of the natural human pose. Furthermore, we apply progressive attention masking to precisely estimate local interactions between vertices even under severe occlusions. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show that the proposed method efficiently improves the performance of 3D human mesh reconstruction. The code and model are publicly available at: https://github.com/DCVL-3D/PointHMR_release.
Towards Deep Learning-aided Wireless Channel Estimation and Channel State Information Feedback for 6G
Sep 05, 2022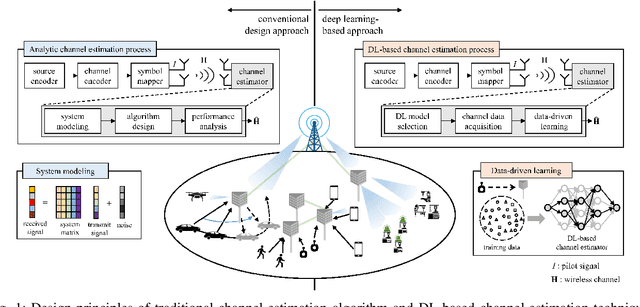
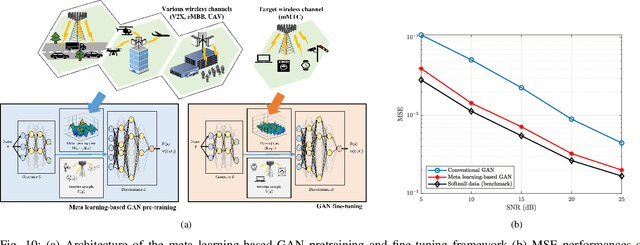
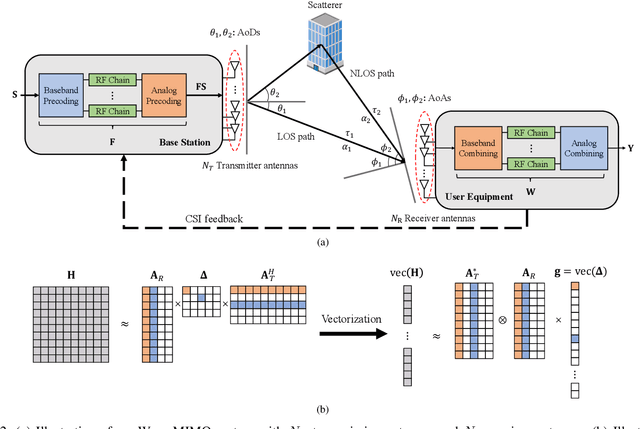
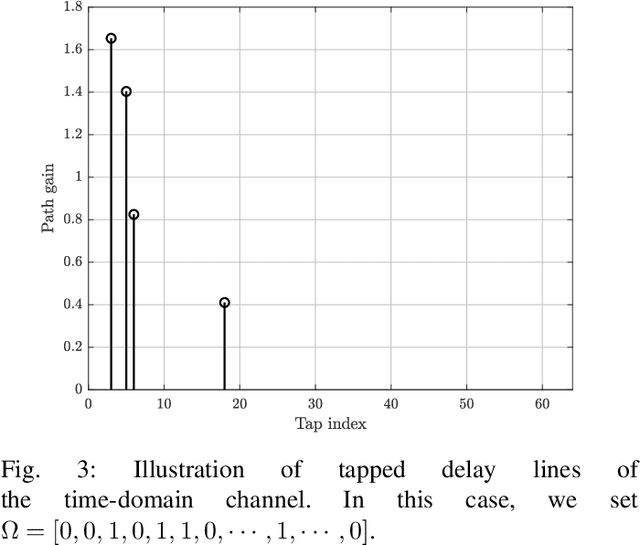
Abstract:Deep learning (DL), a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, has shown great promise in various disciplines such as image classification and segmentation, speech recognition, language translation, among others. This remarkable success of DL has stimulated increasing interest in applying this paradigm to wireless channel estimation in recent years. Since DL principles are inductive in nature and distinct from the conventional rule-based algorithms, when one tries to use DL technique to the channel estimation, one might easily get stuck and confused by so many knobs to control and small details to be aware of. The primary purpose of this paper is to discuss key issues and possible solutions in DL-based wireless channel estimation and channel state information (CSI) feedback including the DL model selection, training data acquisition, and neural network design for 6G. Specifically, we present several case studies together with the numerical experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of the DL-based wireless channel estimation framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge