Wiebke Laffers
Spectral-Spatial Recurrent-Convolutional Networks for In-Vivo Hyperspectral Tumor Type Classification
Jul 02, 2020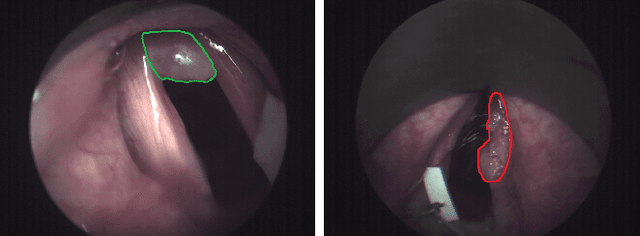
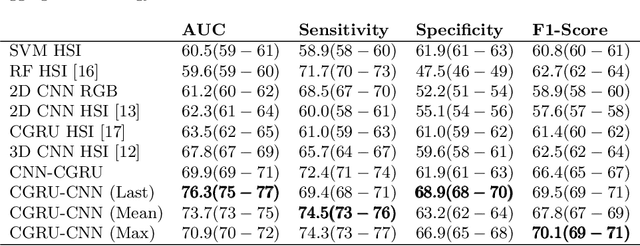
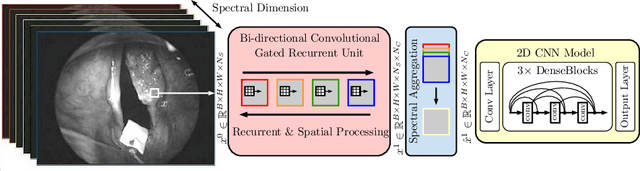
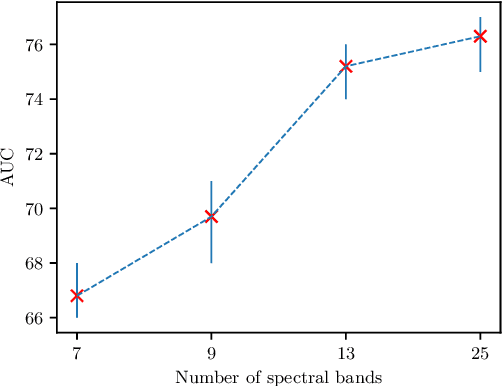
Abstract:Early detection of cancerous tissue is crucial for long-term patient survival. In the head and neck region, a typical diagnostic procedure is an endoscopic intervention where a medical expert manually assesses tissue using RGB camera images. While healthy and tumor regions are generally easier to distinguish, differentiating benign and malignant tumors is very challenging. This requires an invasive biopsy, followed by histological evaluation for diagnosis. Also, during tumor resection, tumor margins need to be verified by histological analysis. To avoid unnecessary tissue resection, a non-invasive, image-based diagnostic tool would be very valuable. Recently, hyperspectral imaging paired with deep learning has been proposed for this task, demonstrating promising results on ex-vivo specimens. In this work, we demonstrate the feasibility of in-vivo tumor type classification using hyperspectral imaging and deep learning. We analyze the value of using multiple hyperspectral bands compared to conventional RGB images and we study several machine learning models' ability to make use of the additional spectral information. Based on our insights, we address spectral and spatial processing using recurrent-convolutional models for effective spectral aggregating and spatial feature learning. Our best model achieves an AUC of 76.3%, significantly outperforming previous conventional and deep learning methods.
Spatio-spectral deep learning methods for in-vivo hyperspectral laryngeal cancer detection
Apr 21, 2020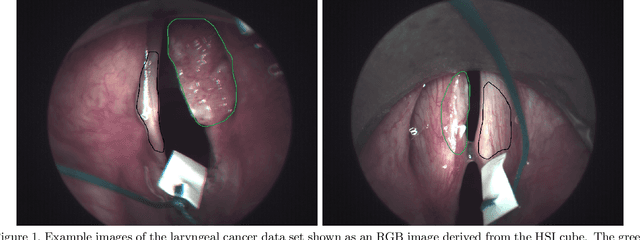
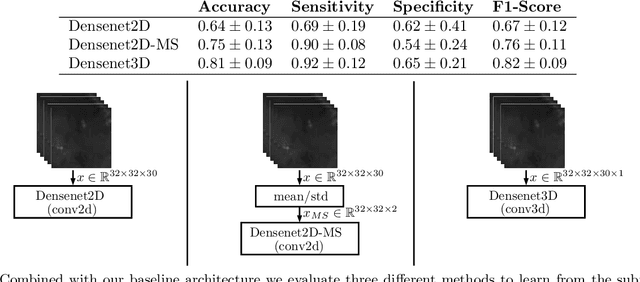
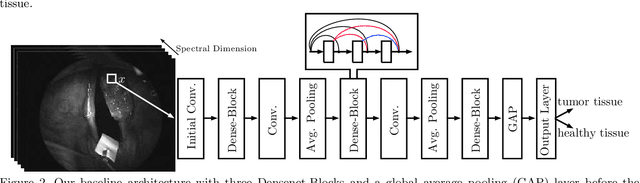
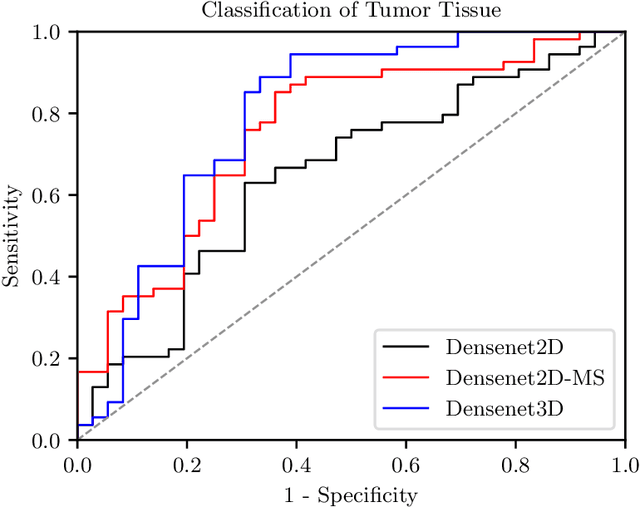
Abstract:Early detection of head and neck tumors is crucial for patient survival. Often, diagnoses are made based on endoscopic examination of the larynx followed by biopsy and histological analysis, leading to a high inter-observer variability due to subjective assessment. In this regard, early non-invasive diagnostics independent of the clinician would be a valuable tool. A recent study has shown that hyperspectral imaging (HSI) can be used for non-invasive detection of head and neck tumors, as precancerous or cancerous lesions show specific spectral signatures that distinguish them from healthy tissue. However, HSI data processing is challenging due to high spectral variations, various image interferences, and the high dimensionality of the data. Therefore, performance of automatic HSI analysis has been limited and so far, mostly ex-vivo studies have been presented with deep learning. In this work, we analyze deep learning techniques for in-vivo hyperspectral laryngeal cancer detection. For this purpose we design and evaluate convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with 2D spatial or 3D spatio-spectral convolutions combined with a state-of-the-art Densenet architecture. For evaluation, we use an in-vivo data set with HSI of the oral cavity or oropharynx. Overall, we present multiple deep learning techniques for in-vivo laryngeal cancer detection based on HSI and we show that jointly learning from the spatial and spectral domain improves classification accuracy notably. Our 3D spatio-spectral Densenet achieves an average accuracy of 81%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge