Wesley Khademi
Point-based Instance Completion with Scene Constraints
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Recent point-based object completion methods have demonstrated the ability to accurately recover the missing geometry of partially observed objects. However, these approaches are not well-suited for completing objects within a scene, as they do not consider known scene constraints (e.g., other observed surfaces) in their completions and further expect the partial input to be in a canonical coordinate system, which does not hold for objects within scenes. While instance scene completion methods have been proposed for completing objects within a scene, they lag behind point-based object completion methods in terms of object completion quality and still do not consider known scene constraints during completion. To overcome these limitations, we propose a point cloud-based instance completion model that can robustly complete objects at arbitrary scales and pose in the scene. To enable reasoning at the scene level, we introduce a sparse set of scene constraints represented as point clouds and integrate them into our completion model via a cross-attention mechanism. To evaluate the instance scene completion task on indoor scenes, we further build a new dataset called ScanWCF, which contains labeled partial scans as well as aligned ground truth scene completions that are watertight and collision-free. Through several experiments, we demonstrate that our method achieves improved fidelity to partial scans, higher completion quality, and greater plausibility over existing state-of-the-art methods.
Diverse Shape Completion via Style Modulated Generative Adversarial Networks
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:Shape completion aims to recover the full 3D geometry of an object from a partial observation. This problem is inherently multi-modal since there can be many ways to plausibly complete the missing regions of a shape. Such diversity would be indicative of the underlying uncertainty of the shape and could be preferable for downstream tasks such as planning. In this paper, we propose a novel conditional generative adversarial network that can produce many diverse plausible completions of a partially observed point cloud. To enable our network to produce multiple completions for the same partial input, we introduce stochasticity into our network via style modulation. By extracting style codes from complete shapes during training, and learning a distribution over them, our style codes can explicitly carry shape category information leading to better completions. We further introduce diversity penalties and discriminators at multiple scales to prevent conditional mode collapse and to train without the need for multiple ground truth completions for each partial input. Evaluations across several synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements in respecting the partial observations while obtaining greater diversity in completions.
Self-Supervised Poisson-Gaussian Denoising
Feb 21, 2020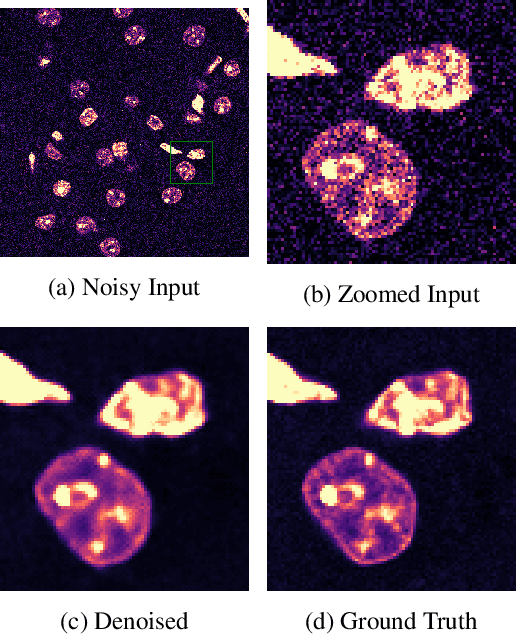
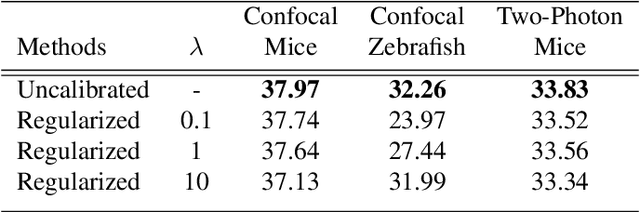
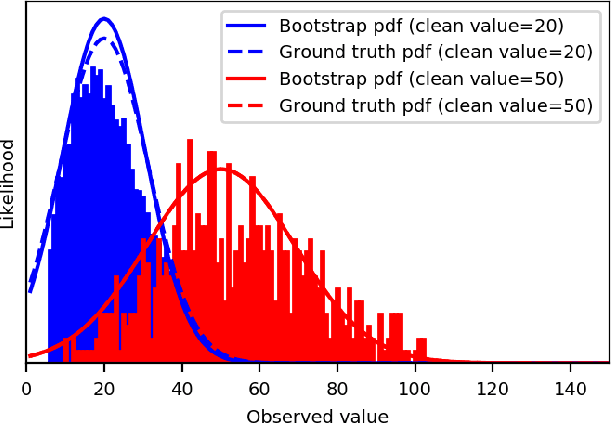
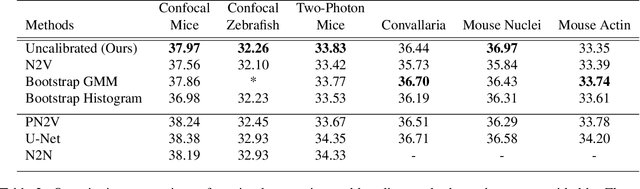
Abstract:We extend the blindspot model for self-supervised denoising to handle Poisson-Gaussian noise and introduce an improved training scheme that avoids hyperparameters and adapts the denoiser to the test data. Self-supervised models for denoising learn to denoise from only noisy data and do not require corresponding clean images, which are difficult or impossible to acquire in some application areas of interest such as low-light microscopy. We introduce a new training strategy to handle Poisson-Gaussian noise which is the standard noise model for microscope images. Our new strategy eliminates hyperparameters from the loss function, which is important in a self-supervised regime where no ground truth data is available to guide hyperparameter tuning. We show how our denoiser can be adapted to the test data to improve performance. Our evaluation on a microscope image denoising benchmark validates our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge