Weiqi Zhai
Unmasking Reasoning Processes: A Process-aware Benchmark for Evaluating Structural Mathematical Reasoning in LLMs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) achieve near-saturation accuracy on many established mathematical reasoning benchmarks, raising concerns about their ability to diagnose genuine reasoning competence. This saturation largely stems from the dominance of template-based computation and shallow arithmetic decomposition in existing datasets, which underrepresent reasoning skills such as multi-constraint coordination, constructive logical synthesis, and spatial inference. To address this gap, we introduce ReasoningMath-Plus, a benchmark of 150 carefully curated problems explicitly designed to evaluate structural reasoning. Each problem emphasizes reasoning under interacting constraints, constructive solution formation, or non-trivial structural insight, and is annotated with a minimal reasoning skeleton to support fine-grained process-level evaluation. Alongside the dataset, we introduce HCRS (Hazard-aware Chain-based Rule Score), a deterministic step-level scoring function, and train a Process Reward Model (PRM) on the annotated reasoning traces. Empirically, while leading models attain relatively high final-answer accuracy (up to 5.8/10), HCRS-based holistic evaluation yields substantially lower scores (average 4.36/10, best 5.14/10), showing that answer-only metrics can overestimate reasoning robustness.
VANER: Leveraging Large Language Model for Versatile and Adaptive Biomedical Named Entity Recognition
Apr 27, 2024Abstract:Prevalent solution for BioNER involves using representation learning techniques coupled with sequence labeling. However, such methods are inherently task-specific, demonstrate poor generalizability, and often require dedicated model for each dataset. To leverage the versatile capabilities of recently remarkable large language models (LLMs), several endeavors have explored generative approaches to entity extraction. Yet, these approaches often fall short of the effectiveness of previouly sequence labeling approaches. In this paper, we utilize the open-sourced LLM LLaMA2 as the backbone model, and design specific instructions to distinguish between different types of entities and datasets. By combining the LLM's understanding of instructions with sequence labeling techniques, we use mix of datasets to train a model capable of extracting various types of entities. Given that the backbone LLMs lacks specialized medical knowledge, we also integrate external entity knowledge bases and employ instruction tuning to compel the model to densely recognize carefully curated entities. Our model VANER, trained with a small partition of parameters, significantly outperforms previous LLMs-based models and, for the first time, as a model based on LLM, surpasses the majority of conventional state-of-the-art BioNER systems, achieving the highest F1 scores across three datasets.
DMNER: Biomedical Entity Recognition by Detection and Matching
Jul 05, 2023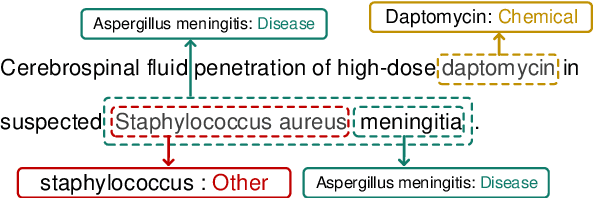
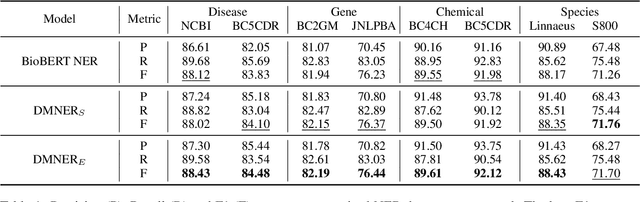
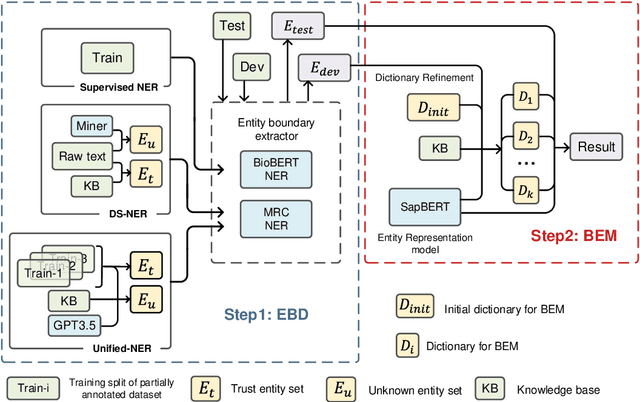
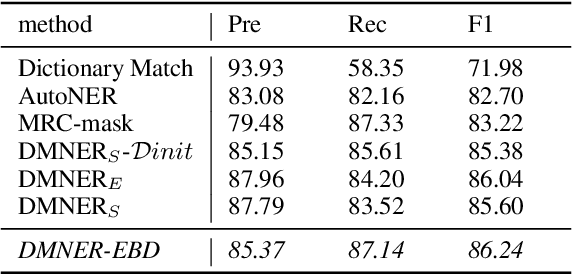
Abstract:Biomedical named entity recognition (BNER) serves as the foundation for numerous biomedical text mining tasks. Unlike general NER, BNER require a comprehensive grasp of the domain, and incorporating external knowledge beyond training data poses a significant challenge. In this study, we propose a novel BNER framework called DMNER. By leveraging existing entity representation models SAPBERT, we tackle BNER as a two-step process: entity boundary detection and biomedical entity matching. DMNER exhibits applicability across multiple NER scenarios: 1) In supervised NER, we observe that DMNER effectively rectifies the output of baseline NER models, thereby further enhancing performance. 2) In distantly supervised NER, combining MRC and AutoNER as span boundary detectors enables DMNER to achieve satisfactory results. 3) For training NER by merging multiple datasets, we adopt a framework similar to DS-NER but additionally leverage ChatGPT to obtain high-quality phrases in the training. Through extensive experiments conducted on 10 benchmark datasets, we demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of DMNER.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge