Wade Kent
High-Throughput Image-Based Plant Stand Count Estimation Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 23, 2020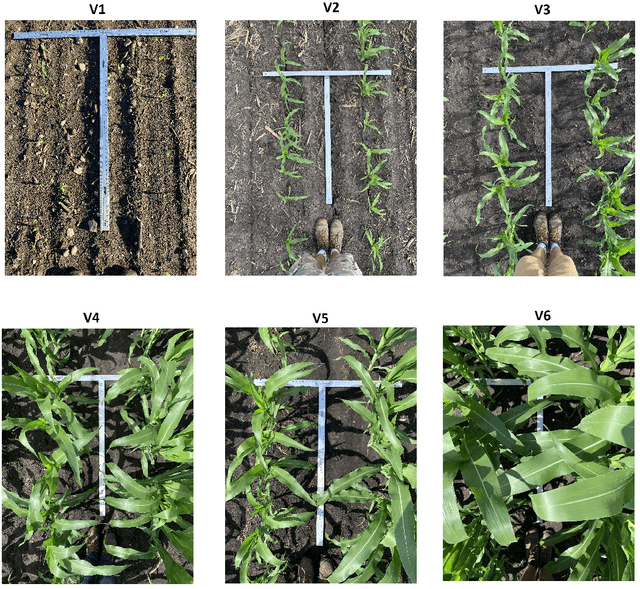
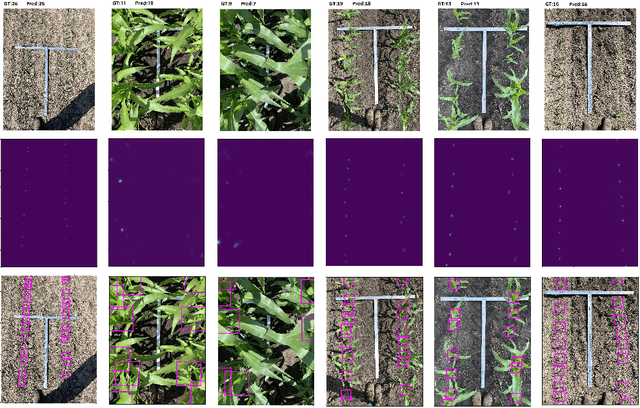
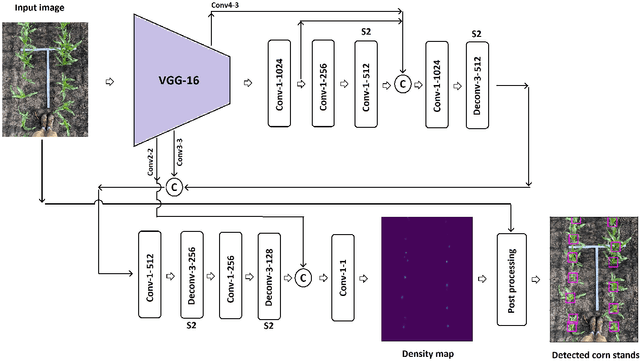
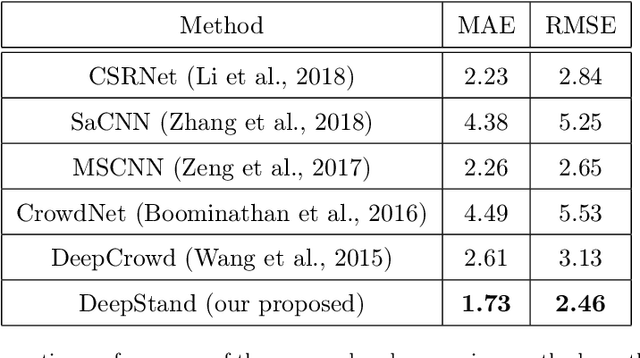

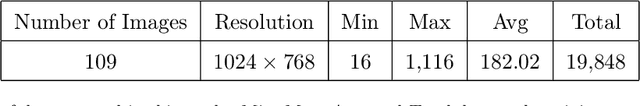
Abstract:The future landscape of modern farming and plant breeding is rapidly changing due to the complex needs of our society. The explosion of collectable data has started a revolution in agriculture to the point where innovation must occur. To a commercial organization, the accurate and efficient collection of information is necessary to ensure that optimal decisions are made at key points of the breeding cycle. However, due to the shear size of a breeding program and current resource limitations, the ability to collect precise data on individual plants is not possible. In particular, efficient phenotyping of crops to record its color, shape, chemical properties, disease susceptibility, etc. is severely limited due to labor requirements and, oftentimes, expert domain knowledge. In this paper, we propose a deep learning based approach, named DeepStand, for image-based corn stand counting at early phenological stages. The proposed method adopts a truncated VGG-16 network as a backbone feature extractor and merges multiple feature maps with different scales to make the network robust against scale variation. Our extensive computational experiments suggest that our proposed method can successfully count corn stands and out-perform other state-of-the-art methods. It is the goal of our work to be used by the larger agricultural community as a way to enable high-throughput phenotyping without the use of extensive time and labor requirements.
DeepCorn: A Semi-Supervised Deep Learning Method for High-Throughput Image-Based Corn Kernel Counting and Yield Estimation
Jul 20, 2020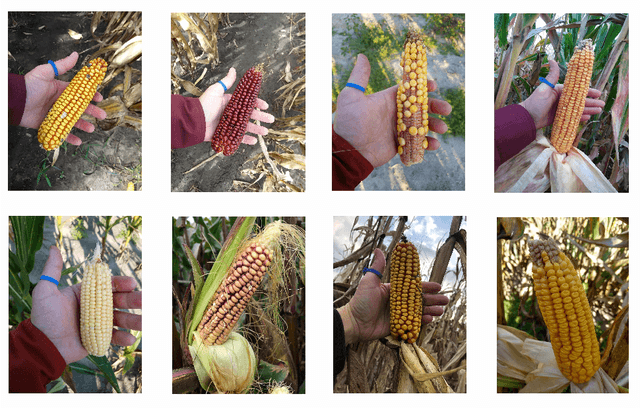
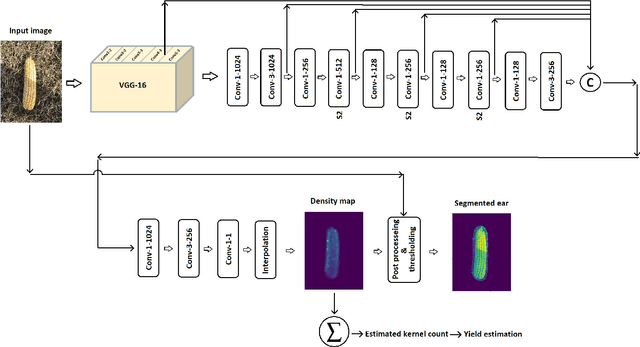
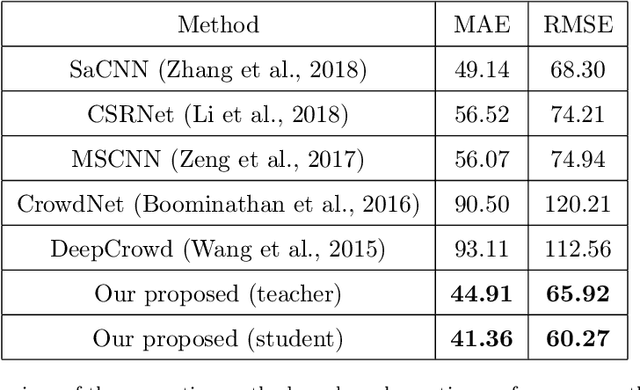
Abstract:The success of modern farming and plant breeding relies on accurate and efficient collection of data. For a commercial organization that manages large amounts of crops, collecting accurate and consistent data is a bottleneck. Due to limited time and labor, accurately phenotyping crops to record color, head count, height, weight, etc. is severely limited. However, this information, combined with other genetic and environmental factors, is vital for developing new superior crop species that help feed the world's growing population. Recent advances in machine learning, in particular deep learning, have shown promise in mitigating this bottleneck. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning method for counting on-ear corn kernels in-field to aid in the gathering of real-time data and, ultimately, to improve decision making to maximize yield. We name this approach DeepCorn, and show that this framework is robust under various conditions and can accurately and efficiently count corn kernels. We also adopt a semi-supervised learning approach to further improve the performance of our proposed method. Our experimental results demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our proposed method compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Convolutional Neural Networks for Image-based Corn Kernel Detection and Counting
Apr 20, 2020
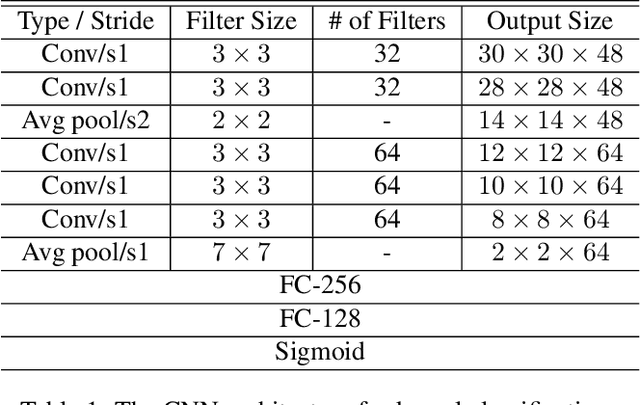
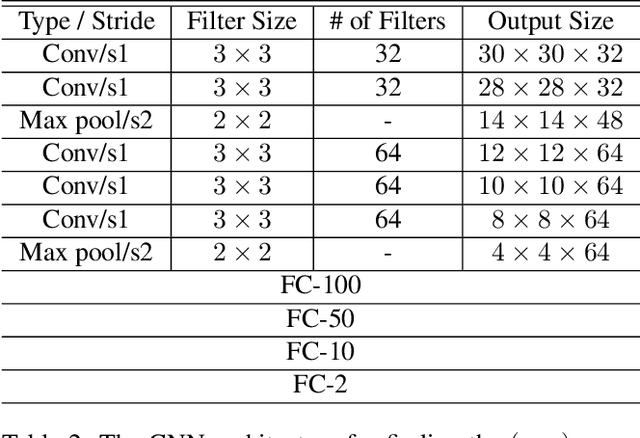

Abstract:Precise in-season corn grain yield estimates enable farmers to make real-time accurate harvest and grain marketing decisions minimizing possible losses of profitability. A well developed corn ear can have up to 800 kernels, but manually counting the kernels on an ear of corn is labor-intensive, time consuming and prone to human error. From an algorithmic perspective, the detection of the kernels from a single corn ear image is challenging due to the large number of kernels at different angles and very small distance among the kernels. In this paper, we propose a kernel detection and counting method based on a sliding window approach. The proposed method detect and counts all corn kernels in a single corn ear image taken in uncontrolled lighting conditions. The sliding window approach uses a convolutional neural network (CNN) for kernel detection. Then, a non-maximum suppression (NMS) is applied to remove overlapping detections. Finally, windows that are classified as kernel are passed to another CNN regression model for finding the (x,y) coordinates of the center of kernel image patches. Our experiments indicate that the proposed method can successfully detect the corn kernels with a low detection error and is also able to detect kernels on a batch of corn ears positioned at different angles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge