Volkan Dedeoglu
BadDet+: Robust Backdoor Attacks for Object Detection
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Backdoor attacks pose a severe threat to deep learning, yet their impact on object detection remains poorly understood compared to image classification. While attacks have been proposed, we identify critical weaknesses in existing detection-based methods, specifically their reliance on unrealistic assumptions and a lack of physical validation. To bridge this gap, we introduce BadDet+, a penalty-based framework that unifies Region Misclassification Attacks (RMA) and Object Disappearance Attacks (ODA). The core mechanism utilizes a log-barrier penalty to suppress true-class predictions for triggered inputs, resulting in (i) position and scale invariance, and (ii) enhanced physical robustness. On real-world benchmarks, BadDet+ achieves superior synthetic-to-physical transfer compared to existing RMA and ODA baselines while preserving clean performance. Theoretical analysis confirms the proposed penalty acts within a trigger-specific feature subspace, reliably inducing attacks without degrading standard inference. These results highlight significant vulnerabilities in object detection and the necessity for specialized defenses.
Backdoor Mitigation via Invertible Pruning Masks
Sep 19, 2025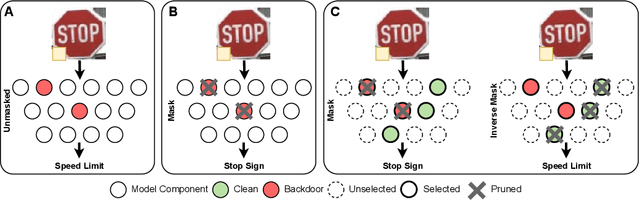
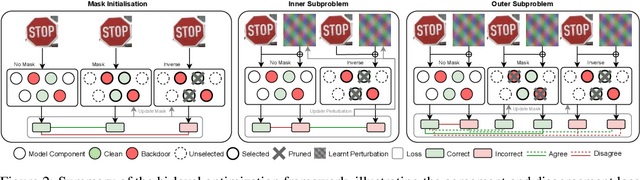
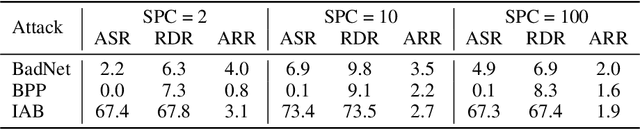
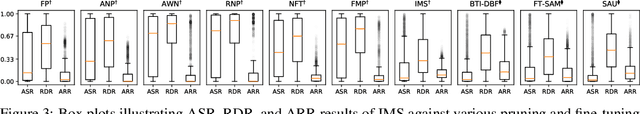
Abstract:Model pruning has gained traction as a promising defense strategy against backdoor attacks in deep learning. However, existing pruning-based approaches often fall short in accurately identifying and removing the specific parameters responsible for inducing backdoor behaviors. Despite the dominance of fine-tuning-based defenses in recent literature, largely due to their superior performance, pruning remains a compelling alternative, offering greater interpretability and improved robustness in low-data regimes. In this paper, we propose a novel pruning approach featuring a learned \emph{selection} mechanism to identify parameters critical to both main and backdoor tasks, along with an \emph{invertible} pruning mask designed to simultaneously achieve two complementary goals: eliminating the backdoor task while preserving it through the inverse mask. We formulate this as a bi-level optimization problem that jointly learns selection variables, a sparse invertible mask, and sample-specific backdoor perturbations derived from clean data. The inner problem synthesizes candidate triggers using the inverse mask, while the outer problem refines the mask to suppress backdoor behavior without impairing clean-task accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing pruning-based backdoor mitigation approaches, maintains strong performance under limited data conditions, and achieves competitive results compared to state-of-the-art fine-tuning approaches. Notably, the proposed approach is particularly effective in restoring correct predictions for compromised samples after successful backdoor mitigation.
Countering Backdoor Attacks in Image Recognition: A Survey and Evaluation of Mitigation Strategies
Nov 17, 2024
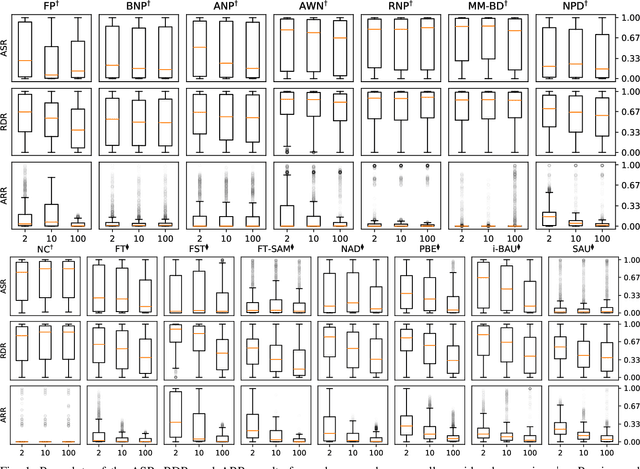
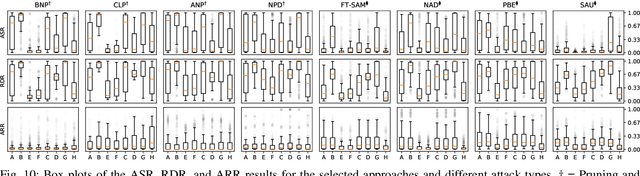
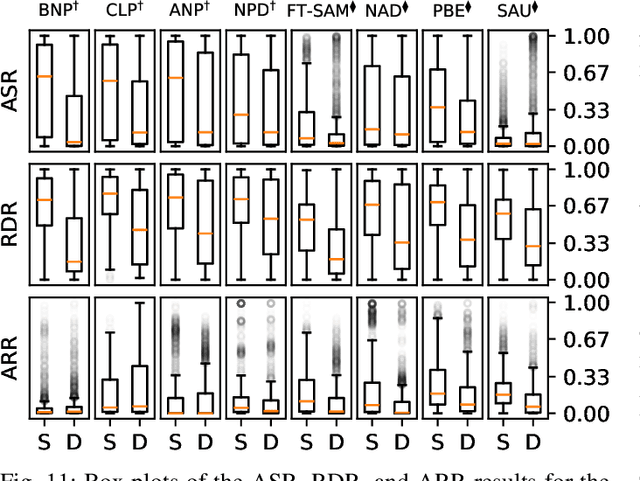
Abstract:The widespread adoption of deep learning across various industries has introduced substantial challenges, particularly in terms of model explainability and security. The inherent complexity of deep learning models, while contributing to their effectiveness, also renders them susceptible to adversarial attacks. Among these, backdoor attacks are especially concerning, as they involve surreptitiously embedding specific triggers within training data, causing the model to exhibit aberrant behavior when presented with input containing the triggers. Such attacks often exploit vulnerabilities in outsourced processes, compromising model integrity without affecting performance on clean (trigger-free) input data. In this paper, we present a comprehensive review of existing mitigation strategies designed to counter backdoor attacks in image recognition. We provide an in-depth analysis of the theoretical foundations, practical efficacy, and limitations of these approaches. In addition, we conduct an extensive benchmarking of sixteen state-of-the-art approaches against eight distinct backdoor attacks, utilizing three datasets, four model architectures, and three poisoning ratios. Our results, derived from 122,236 individual experiments, indicate that while many approaches provide some level of protection, their performance can vary considerably. Furthermore, when compared to two seminal approaches, most newer approaches do not demonstrate substantial improvements in overall performance or consistency across diverse settings. Drawing from these findings, we propose potential directions for developing more effective and generalizable defensive mechanisms in the future.
Unlearning Backdoor Attacks through Gradient-Based Model Pruning
May 07, 2024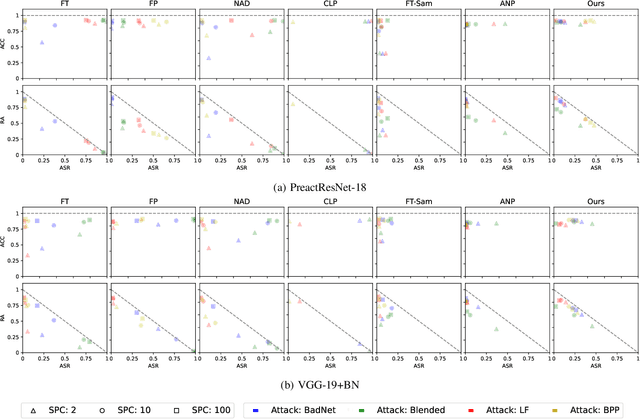
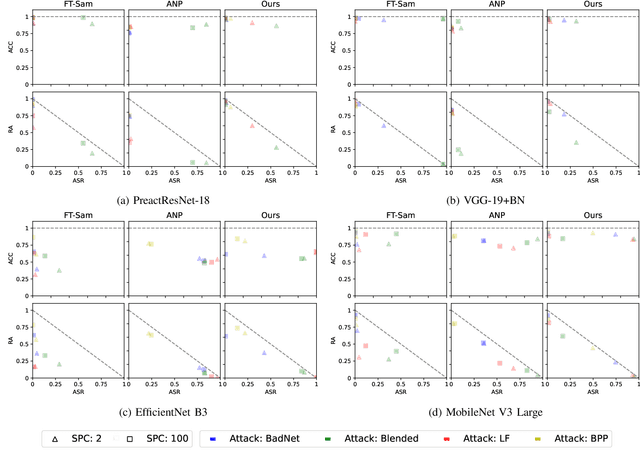
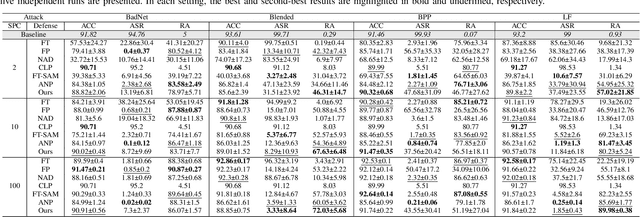
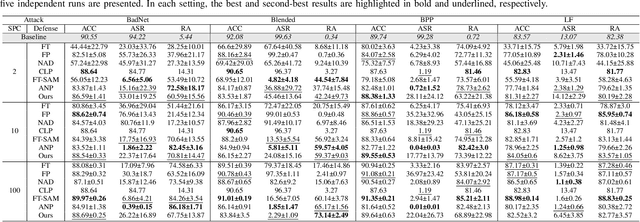
Abstract:In the era of increasing concerns over cybersecurity threats, defending against backdoor attacks is paramount in ensuring the integrity and reliability of machine learning models. However, many existing approaches require substantial amounts of data for effective mitigation, posing significant challenges in practical deployment. To address this, we propose a novel approach to counter backdoor attacks by treating their mitigation as an unlearning task. We tackle this challenge through a targeted model pruning strategy, leveraging unlearning loss gradients to identify and eliminate backdoor elements within the model. Built on solid theoretical insights, our approach offers simplicity and effectiveness, rendering it well-suited for scenarios with limited data availability. Our methodology includes formulating a suitable unlearning loss and devising a model-pruning technique tailored for convolutional neural networks. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed approach compared to state-of-the-art approaches, particularly in realistic data settings.
IoT Data Trust Evaluation via Machine Learning
Aug 15, 2023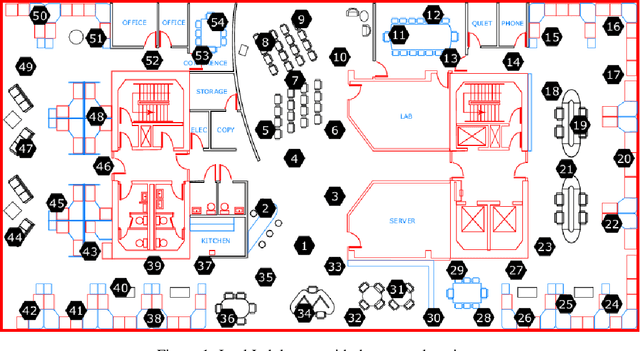
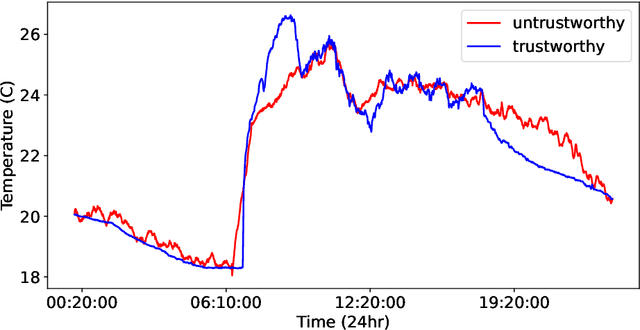
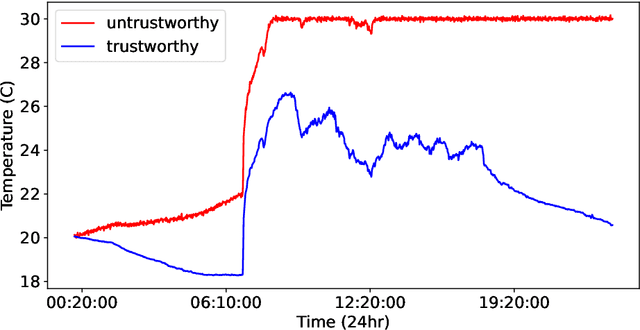
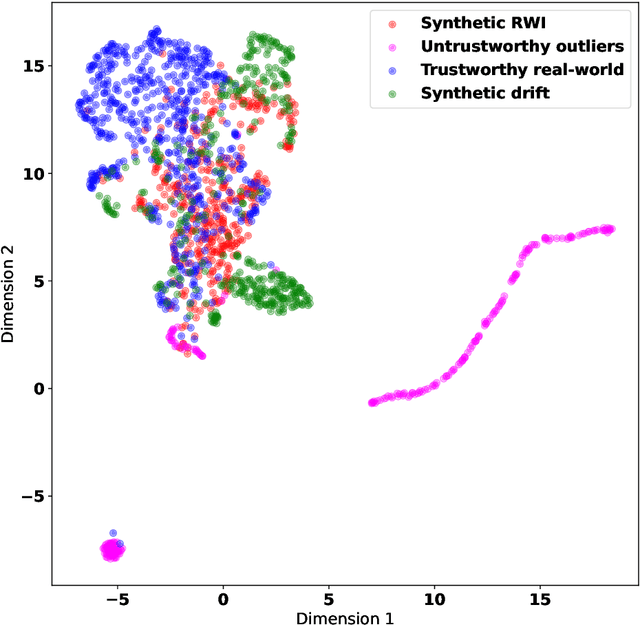
Abstract:Various approaches based on supervised or unsupervised machine learning (ML) have been proposed for evaluating IoT data trust. However, assessing their real-world efficacy is hard mainly due to the lack of related publicly-available datasets that can be used for benchmarking. Since obtaining such datasets is challenging, we propose a data synthesis method, called random walk infilling (RWI), to augment IoT time-series datasets by synthesizing untrustworthy data from existing trustworthy data. Thus, RWI enables us to create labeled datasets that can be used to develop and validate ML models for IoT data trust evaluation. We also extract new features from IoT time-series sensor data that effectively capture its auto-correlation as well as its cross-correlation with the data of the neighboring (peer) sensors. These features can be used to learn ML models for recognizing the trustworthiness of IoT sensor data. Equipped with our synthesized ground-truth-labeled datasets and informative correlation-based feature, we conduct extensive experiments to critically examine various approaches to evaluating IoT data trust via ML. The results reveal that commonly used ML-based approaches to IoT data trust evaluation, which rely on unsupervised cluster analysis to assign trust labels to unlabeled data, perform poorly. This poor performance can be attributed to the underlying unsubstantiated assumption that clustering provides reliable labels for data trust, a premise that is found to be untenable. The results also show that the ML models learned from datasets augmented via RWI while using the proposed features generalize well to unseen data and outperform existing related approaches. Moreover, we observe that a semi-supervised ML approach that requires only about 10% of the data labeled offers competitive performance while being practically more appealing compared to the fully-supervised approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge