Vladislav Tishin
Sberbank, National University of Science and Technology MISIS
Revising deep learning methods in parking lot occupancy detection
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Parking guidance systems have recently become a popular trend as a part of the smart cities' paradigm of development. The crucial part of such systems is the algorithm allowing drivers to search for available parking lots across regions of interest. The classic approach to this task is based on the application of neural network classifiers to camera records. However, existing systems demonstrate a lack of generalization ability and appropriate testing regarding specific visual conditions. In this study, we extensively evaluate state-of-the-art parking lot occupancy detection algorithms, compare their prediction quality with the recently emerged vision transformers, and propose a new pipeline based on EfficientNet architecture. Performed computational experiments have demonstrated the performance increase in the case of our model, which was evaluated on 5 different datasets.
Logistics, Graphs, and Transformers: Towards improving Travel Time Estimation
Jul 12, 2022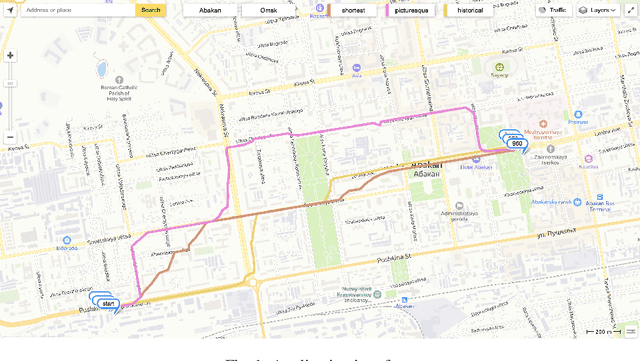
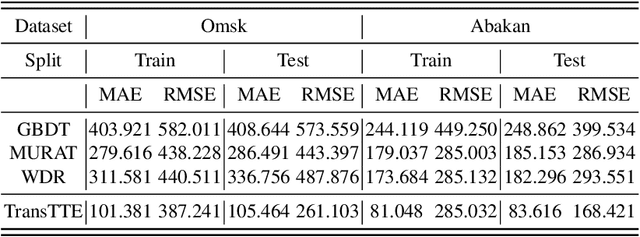
Abstract:The problem of travel time estimation is widely considered as the fundamental challenge of modern logistics. The complex nature of interconnections between spatial aspects of roads and temporal dynamics of ground transport still preserves an area to experiment with. However, the total volume of currently accumulated data encourages the construction of the learning models which have the perspective to significantly outperform earlier solutions. In order to address the problems of travel time estimation, we propose a new method based on transformer architecture - TransTTE.
Citation network applications in a scientific co-authorship recommender system
Nov 22, 2021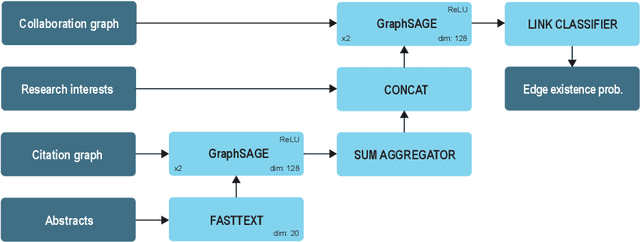
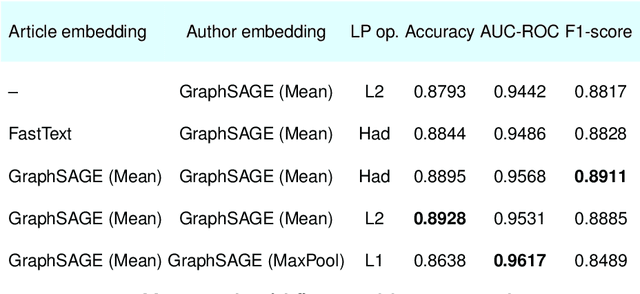
Abstract:The problem of co-authors selection in the area of scientific collaborations might be a daunting one. In this paper, we propose a new pipeline that effectively utilizes citation data in the link prediction task on the co-authorship network. In particular, we explore the capabilities of a recommender system based on data aggregation strategies on different graphs. Since graph neural networks proved their efficiency on a wide range of tasks related to recommendation systems, we leverage them as a relevant method for the forecasting of potential collaborations in the scientific community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge