Vint Lee
Chip Placement with Diffusion
Jul 17, 2024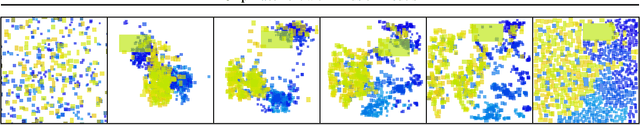



Abstract:Macro placement is a vital step in digital circuit design that defines the physical location of large collections of components, known as macros, on a 2-dimensional chip. The physical layout obtained during placement determines key performance metrics of the chip, such as power consumption, area, and performance. Existing learning-based methods typically fall short because of their reliance on reinforcement learning, which is slow and limits the flexibility of the agent by casting placement as a sequential process. Instead, we use a powerful diffusion model to place all components simultaneously. To enable such models to train at scale, we propose a novel architecture for the denoising model, as well as an algorithm to generate large synthetic datasets for pre-training. We empirically show that our model can tackle the placement task, and achieve competitive performance on placement benchmarks compared to state-of-the-art methods.
DreamSmooth: Improving Model-based Reinforcement Learning via Reward Smoothing
Nov 02, 2023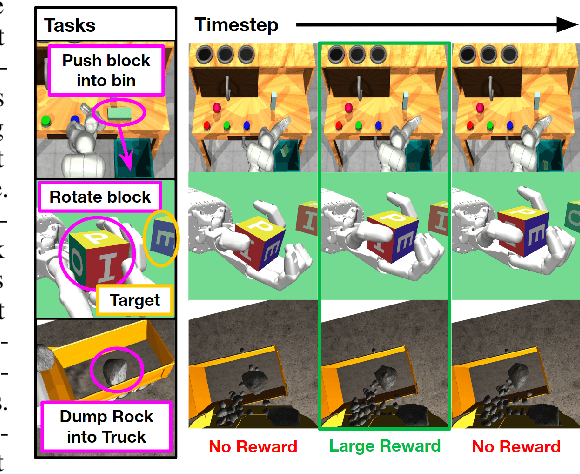
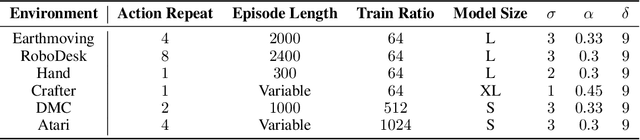
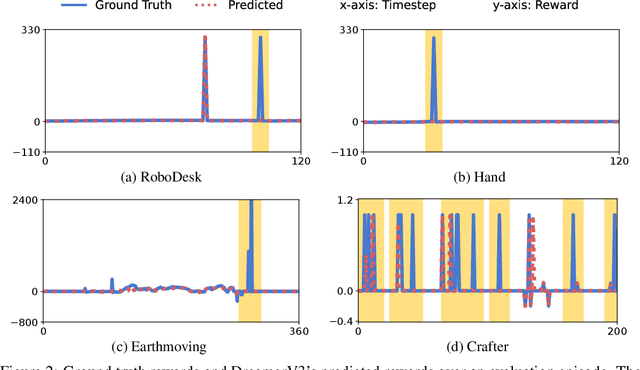

Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) has gained much attention for its ability to learn complex behaviors in a sample-efficient way: planning actions by generating imaginary trajectories with predicted rewards. Despite its success, we found that surprisingly, reward prediction is often a bottleneck of MBRL, especially for sparse rewards that are challenging (or even ambiguous) to predict. Motivated by the intuition that humans can learn from rough reward estimates, we propose a simple yet effective reward smoothing approach, DreamSmooth, which learns to predict a temporally-smoothed reward, instead of the exact reward at the given timestep. We empirically show that DreamSmooth achieves state-of-the-art performance on long-horizon sparse-reward tasks both in sample efficiency and final performance without losing performance on common benchmarks, such as Deepmind Control Suite and Atari benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge