Vineet Madan
Stress Testing of Meta-learning Approaches for Few-shot Learning
Jan 21, 2021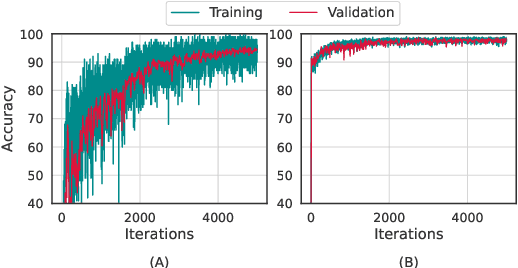
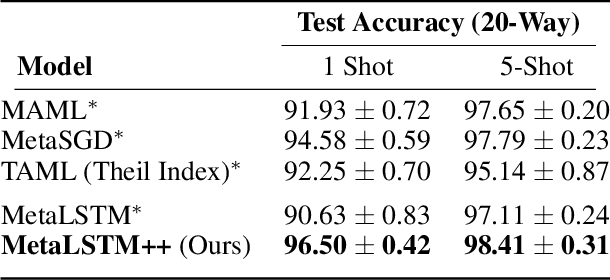
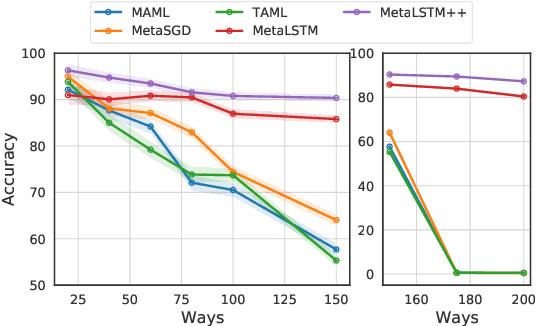
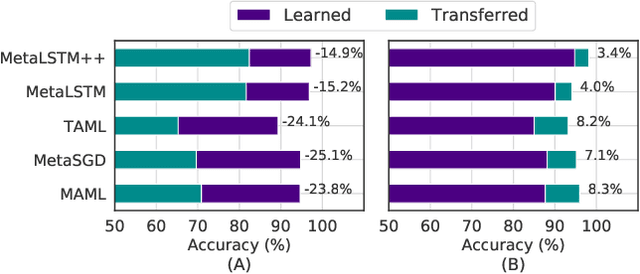
Abstract:Meta-learning (ML) has emerged as a promising learning method under resource constraints such as few-shot learning. ML approaches typically propose a methodology to learn generalizable models. In this work-in-progress paper, we put the recent ML approaches to a stress test to discover their limitations. Precisely, we measure the performance of ML approaches for few-shot learning against increasing task complexity. Our results show a quick degradation in the performance of initialization strategies for ML (MAML, TAML, and MetaSGD), while surprisingly, approaches that use an optimization strategy (MetaLSTM) perform significantly better. We further demonstrate the effectiveness of an optimization strategy for ML (MetaLSTM++) trained in a MAML manner over a pure optimization strategy. Our experiments also show that the optimization strategies for ML achieve higher transferability from simple to complex tasks.
On Duality Gap as a Measure for Monitoring GAN Training
Dec 12, 2020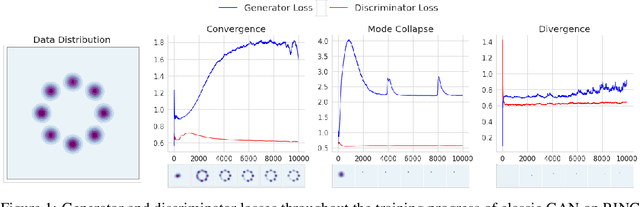
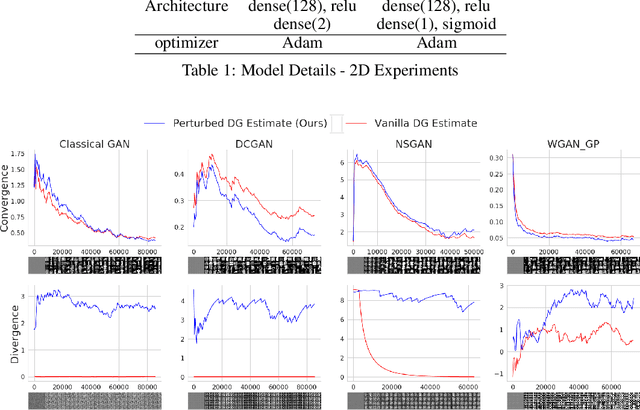
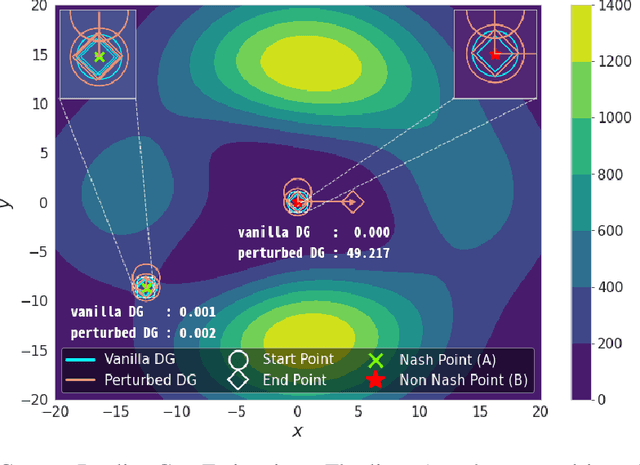
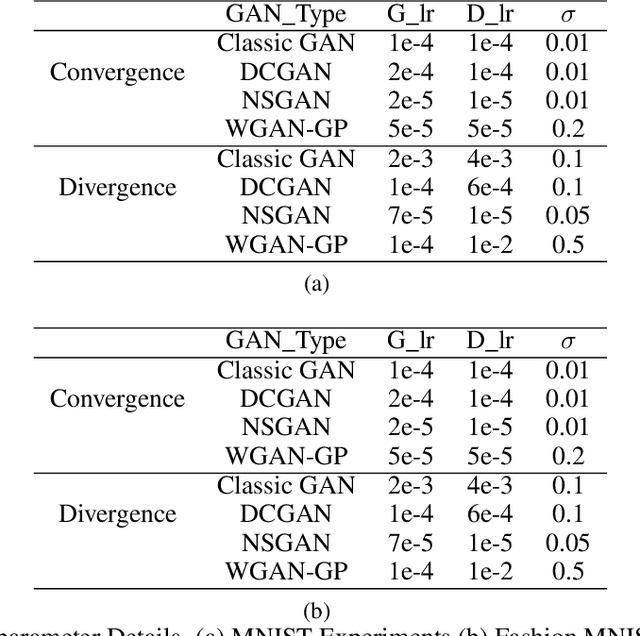
Abstract:Generative adversarial network (GAN) is among the most popular deep learning models for learning complex data distributions. However, training a GAN is known to be a challenging task. This is often attributed to the lack of correlation between the training progress and the trajectory of the generator and discriminator losses and the need for the GAN's subjective evaluation. A recently proposed measure inspired by game theory - the duality gap, aims to bridge this gap. However, as we demonstrate, the duality gap's capability remains constrained due to limitations posed by its estimation process. This paper presents a theoretical understanding of this limitation and proposes a more dependable estimation process for the duality gap. At the crux of our approach is the idea that local perturbations can help agents in a zero-sum game escape non-Nash saddle points efficiently. Through exhaustive experimentation across GAN models and datasets, we establish the efficacy of our approach in capturing the GAN training progress with minimal increase to the computational complexity. Further, we show that our estimate, with its ability to identify model convergence/divergence, is a potential performance measure that can be used to tune the hyperparameters of a GAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge