Vikas Singh Kim
Graph Neural Networks to Predict Customer Satisfaction Following Interactions with a Corporate Call Center
Jan 31, 2021
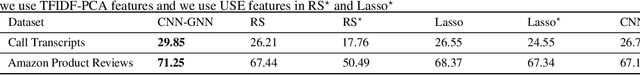

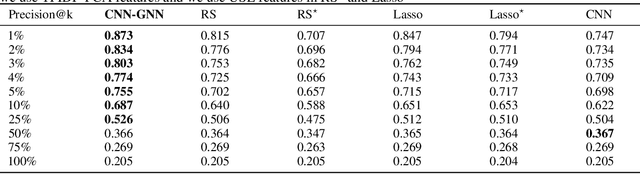
Abstract:Customer satisfaction is an important factor in creating and maintaining long-term relationships with customers. Near real-time identification of potentially dissatisfied customers following phone calls can provide organizations the opportunity to take meaningful interventions and to foster ongoing customer satisfaction and loyalty. This work describes a fully operational system we have developed at a large US company for predicting customer satisfaction following incoming phone calls. The system takes as an input speech-to-text transcriptions of calls and predicts call satisfaction reported by customers on post-call surveys (scale from 1 to 10). Because of its ordinal, subjective, and often highly-skewed nature, predicting survey scores is not a trivial task and presents several modeling challenges. We introduce a graph neural network (GNN) approach that takes into account the comparative nature of the problem by considering the relative scores among batches, instead of only pairs of calls when training. This approach produces more accurate predictions than previous approaches including standard regression and classification models that directly fit the survey scores with call data. Our proposed approach can be easily generalized to other customer satisfaction prediction problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge